respiratory system anatomy.pdf
- 1. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 1 The Respiratory System
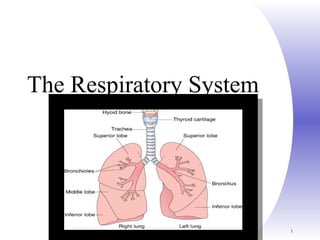
- 2. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 2 Respiratory System Figure 22.1
- 3. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 3
- 4. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Respiratory System Anatomy Structurally Upper respiratory system Nose, pharynx and associated structures Lower respiratory system Larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs
- 5. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 5 Respiratory System Functionally Consists of the respiratory and conducting zones Respiratory zone Site of gas exchange Consists of bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli
- 6. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 6 Respiratory System Conducting zone Provides rigid structures for air to reach the sites of gas exchange Includes all other respiratory structures (e.g., nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea)
- 7. Respiratory muscles – diaphragm and other muscles that promote ventilation Chapter 22, Respiratory System 7
- 8. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 8 Structure of the Nose Figure 22.2a
- 9. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 9 Structure of the Nose The nose is divided into two regions The external nose The internal nasal cavity
- 10. The external nose, including the root, bridge, dorsum nasi, and apex Philtrum – a shallow vertical groove inferior to the apex The external nares (nostrils) are bounded laterally by the alae Chapter 22, Respiratory System 10
- 11. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 11 Structure of the Nose Figure 22.2b
- 12. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 12 Nasal Cavity Lies in and posterior to the external nose Is divided by a midline nasal septum Opens posteriorly into the nasal pharynx via internal nares The ethmoid and sphenoid bones form the roof The floor is formed by the hard and soft palates
- 13. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 13 Nasal Cavity Vestibule – nasal cavity superior to the nares Vibrissae – hairs that filter coarse particles from inspired air Olfactory mucosa Lines the superior nasal cavity Contains smell receptors
- 14. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 14 Nasal Cavity Respiratory mucosa Lines the balance of the nasal cavity Glands secrete mucus containing lysozyme and defensins to help destroy bacteria
- 15. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 15 Nasal Cavity Figure 22.3b
- 16. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 16 Nasal Cavity Inspired air is: Humidified by the high water content in the nasal cavity Warmed by rich plexuses of capillaries Ciliated mucosal cells remove contaminated mucus
- 17. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 17 Nasal Cavity Superior, medial, and inferior conchae: Protrude medially from the lateral walls Increase mucosal area Enhance air turbulence and help filter air Sensitive mucosa triggers sneezing when stimulated by irritating particles
- 18. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 18 Function of the Nose The only externally visible part of the respiratory system that functions by: Providing an airway for respiration Moistening (humidifying) and warming the entering air Filtering inspired air and cleaning it of foreign matter Serving as a resonating chamber for speech Housing the olfactory receptors
- 19. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 19 Functions of the Nasal Mucosa and Conchae During inhalation the conchae and nasal mucosa: Filter, heat, and moisten air During exhalation these structures: Reclaim heat and moisture Minimize heat and moisture loss
- 20. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 20 Paranasal Sinuses Sinuses in bones that surround the nasal cavity Sinuses lighten the skull and help to warm and moisten the air
- 21. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 21 Pharynx Funnel-shaped tube of skeletal muscle that connects to the: Nasal cavity and mouth superiorly Larynx and esophagus inferiorly Extends from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebra
- 22. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 22 Pharynx It is divided into three regions Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx
- 23. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 23 Nasopharynx Lies posterior to the nasal cavity, inferior to the sphenoid, and superior to the level of the soft palate Strictly an air passageway Lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium Closes during swallowing to prevent food from entering the nasal cavity The pharyngeal tonsil lies high on the posterior wall Pharyngotympanic (auditory) tubes open into the lateral walls
- 24. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 24 Oropharynx Extends inferiorly from the level of the soft palate to the epiglottis Serves as a common passageway for food and air The epithelial lining is protective stratified squamous epithelium Palatine tonsils lie in the lateral walls Lingual tonsil covers the base of the tongue
- 25. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 25 Laryngopharynx Serves as a common passageway for food and air Lies posterior to the upright epiglottis Extends to the larynx, where the respiratory and digestive pathways diverge
- 26. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Larynx
- 27. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Larynx Short passageway connecting laryngopharynx with trachea Composed of 9 pieces of cartilage Thyroid cartilage or Adam’s apple Cricoid cartilage hallmark for tracheotomy
- 28. Epiglottis closes off glottis during swallowing Glottis – pair of folds of mucous membranes, vocal folds (true vocal cords, and rima glottidis (space) Cilia in upper respiratory tract move mucous and trapped particles down toward pharynx Cilia in lower respiratory tract move them up toward pharynx Chapter 22, Respiratory System 28
- 29. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 29 Larynx (Voice Box) Attaches to the hyoid bone and opens into the laryngopharynx superiorly Continuous with the trachea posteriorly
- 30. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 30 Framework of the Larynx Figure 22.4a, b
- 31. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Structures of Voice Production Mucous membrane of larynx forms Ventricular folds (false vocal cords) – superior pair Function in holding breath against pressure in thoracic cavity Vocal folds (true vocal cords) – inferior pair Muscle contraction pulls elastic ligaments which stretch vocal folds out into airway Vibrate and produce sound with air Folds can move apart or together, elongate or shorten, tighter or looser
- 32. Androgens make folds thicker and longer – slower vibration and lower pitch Chapter 22, Respiratory System 32
- 33. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 33 Movements of Vocal Cords Figure 22.5
- 34. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 34 Framework of the Larynx Cartilages (hyaline) of the larynx Shield-shaped anterosuperior thyroid cartilage with a midline laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple) Signet ring–shaped anteroinferior cricoid cartilage Three pairs of small arytenoid, cuneiform, and corniculate cartilages Epiglottis – elastic cartilage that covers the laryngeal inlet during swallowing
- 35. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 35 Vocal Ligaments Attach the arytenoid cartilages to the thyroid cartilage Composed of elastic fibers that form mucosal folds called true vocal cords The medial opening between them is the glottis They vibrate to produce sound as air rushes up from the lungs
- 36. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 36 Vocal Ligaments False vocal cords Mucosal folds superior to the true vocal cords Have no part in sound production
- 37. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 37 Vocal Production Speech – intermittent release of expired air while opening and closing the glottis Pitch – determined by the length and tension of the vocal cords Loudness – depends upon the force at which the air rushes across the vocal cords The pharynx resonates, amplifies, and enhances sound quality Sound is “shaped” into language by action of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate, and lips
- 38. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 38 Movements of Vocal Cords Figure 22.5
- 39. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- 40. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 40 Sphincter Functions of the Larynx The larynx is closed during coughing, sneezing, and Valsalva’s maneuver Valsalva’s maneuver Air is temporarily held in the lower respiratory tract by closing the glottis Causes intra-abdominal pressure to rise when abdominal muscles contract Helps to empty the rectum
- 41. Functions The three functions of the larynx are: To provide a patent airway To act as a switching mechanism to route air and food into the proper channels To function in voice production Chapter 22, Respiratory System 41
- 42. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 42 Trachea Flexible and mobile tube extending from the larynx into the mediastinum Extends from larynx to superior border of T5 Divides into right and left primary bronchi
- 43. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Trachea 4 layers Mucosa Submucosa Hyaline cartilage Adventitia
- 44. Layers Mucosa – made up of goblet cells and ciliated epithelium Submucosa – connective tissue deep to the mucosa Hyaline cartilage -16-20 C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage Open part faces esophagus Adventitia – outermost layer Chapter 22, Respiratory System 44
- 45. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 45 Trachea Figure 22.6a
- 46. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Location of Trachea
- 47. The Trachea or Windpipe (cont’d.) Supporting cartilage: stack of Cs Cough reflex stimulated by foreign object Tracheostomy done if object cannot be expelled Usually done between second and third tracheal cartilages Can be closed when object removed
- 48. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- 49. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Bronchi Right and left primary bronchus goes to right and left lungs Carina – internal ridge Most sensitive area for triggering cough reflex Divide to form bronchial tree Secondary lobar bronchi (one for each lobe), tertiary (segmental) bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles
- 50. Structural changes with branching Mucous membrane changes Incomplete rings become plates and then disappear As cartilage decreases, smooth muscle increases Sympathetic ANS – relaxation/ dilation Parasympathetic ANS – contraction/ constriction Chapter 22, Respiratory System 50
- 51. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 51 Bronchi The carina of the last tracheal cartilage marks the end of the trachea and the beginning of the right and left bronchi Bronchi subdivide into secondary bronchi, each supplying a lobe of the lungs Air passages undergo 23 orders of branching in the lungs
- 52. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 52 Bronchial Tree Tissue walls of bronchi mimic that of the trachea As conducting tubes become smaller, structural changes occur Cartilage support structures change Epithelium types change Amount of smooth muscle increases
- 53. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 53 Bronchioles Consist of cuboidal epithelium Have a complete layer of circular smooth muscle Lack cartilage support and mucus-producing cells
- 54. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 54 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs Lungs occupy all of the thoracic cavity except the mediastinum Root – site of vascular and bronchial attachments Costal surface – anterior, lateral, and posterior surfaces in contact with the ribs Apex – narrow superior tip Base – inferior surface that rests on the diaphragm Hilus – indentation that contains pulmonary and systemic blood vessels
- 55. Pleura Each lung enclosed by double-layered pleural membrane Parietal pleura – lines wall of thoracic cavity Visceral pleura – covers lungs themselves Pleural cavity is space between layers Pleural fluid reduces friction, produces surface tension (stick together) Chapter 22, Respiratory System 55
- 56. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 56 Pleurae Thin, double-layered serosa Parietal pleura Covers the thoracic wall and superior face of the diaphragm Continues around heart and between lungs
- 57. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 57 Pleurae Visceral, or pulmonary, pleura Covers the external lung surface Divides the thoracic cavity into three chambers The central mediastinum Two lateral compartments, each containing a lung
- 58. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Relationship of the Pleural Membranes to Lungs
- 59. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Lungs Separated from each other by the heart and other structures in the mediastinum Cardiac notch – heart makes left lung 10% smaller than right
- 60. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 60 Lungs Cardiac notch (impression) – cavity that accommodates the heart Left lung – separated into upper and lower lobes by the oblique fissure Right lung – separated into three lobes by the oblique and horizontal fissures There are 10 bronchopulmonary segments in each lung
- 61. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 61 Gross Anatomy of Lungs Base, apex (cupula), costal surface, cardiac notch Oblique & horizontal fissure in right lung results in 3 lobes Oblique fissure only in left lung produces 2 lobes
- 62. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 62 Mediastinal Surface of Lungs Blood vessels & airways enter lungs at hilus Forms root of lungs Covered with pleura (parietal becomes visceral)
- 63. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Anatomy of Lungs Lobes – each lung divides by 1 or 2 fissures Each lobe receives it own secondary (lobar) bronchus that branch into tertiary (segmental) bronchi Lobules wrapped in elastic connective tissue and contains a lymphatic vessel, arteriole, venule and branch from terminal bronchiole Terminal bronchioles branch into respiratory bronchioles which divide into alveolar ducts About 25 orders of branching
- 64. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Microscopic Anatomy of Lobule of Lungs
- 65. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 65 Respiratory Zone Begins as terminal bronchioles feed into respiratory bronchioles and then to alveoli Respiratory bronchioles lead to alveolar ducts, then to terminal clusters of alveolar sacs composed of alveoli Approximately 300 million alveoli: Account for most of the lungs’ volume Provide tremendous surface area for gas exchange
- 66. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Alveoli Cup-shaped outpouching Alveolar sac – 2 or more alveoli sharing a common opening
- 67. Alveolar cells 2 types of alveolar epithelial cells Type I alveolar cells – Form nearly continuous lining, More numerous than type II, Main site of gas exchange Type II alveolar cells (septal cells) – Free surfaces contain microvilli, Secrete alveolar fluid Surfactant reduces tendency to collapse Chapter 22, Respiratory System 67
- 68. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 68 Respiratory Zone Figure 22.8a
- 69. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 69 Respiratory Zone Figure 22.8b
- 70. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Alveolus Respiratory membrane Alveolar wall – type I and type II alveolar cells Epithelial basement membrane Capillary basement membrane Capillary endothelium Very thin – only 0.5 µm thick to allow rapid diffusion of gases
- 71. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Components of Alveolus
- 72. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 72 Respiratory Membrane Figure 22.9.c, d
- 73. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 73 Respiratory Membrane This air-blood barrier is composed of: Alveolar and capillary walls Their fused basal laminas Alveolar walls: Are a single layer of type I epithelial cells Permit gas exchange by simple diffusion Secrete angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)
- 74. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 74 Respiratory Membrane Figure 22.9b
- 75. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 75 Blood Supply to Lungs Lungs are perfused by two circulations: pulmonary and bronchial Pulmonary arteries – supply systemic venous blood to be oxygenated Branch profusely, along with bronchi Ultimately feed into the pulmonary capillary network surrounding the alveoli Pulmonary veins – carry oxygenated blood from respiratory zones to the heart
- 76. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 76 Blood Supply to Lungs Bronchial arteries – provide systemic blood to the lung tissue Arise from aorta and enter the lungs at the hilus Supply all lung tissue except the alveoli Bronchial veins anastomose with pulmonary veins Pulmonary veins carry most venous blood back to the heart
- 77. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 77 Figure 22.24 Control of Respiration: Medullary Respiratory Centers
- 78. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 78 Pons centers: Influence and modify activity of the medullary centers Smooth out inspiration and expiration transitions and vice versa Control of Respiration: Pons Respiratory Centers
- 79. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 79 Pulmonary Function Tests Spirometer – an instrument used to evaluate respiratory function
- 80. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 80 Pulmonary Function Tests Total ventilation – total amount of gas flow into or out of the respiratory tract in one minute Forced vital capacity (FVC) – gas forcibly expelled after taking a deep breath Forced expiratory volume (FEV) – the amount of gas expelled during specific time intervals of the FVC
- 81. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 81 Pulmonary Function Tests Increases in TLC, FRC, and RV may occur as a result of obstructive disease Reduction in VC, TLC, FRC, and RV result from restrictive disease
- 82. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 82 Hyperventilation – increased depth and rate of breathing that: Quickly flushes carbon dioxide from the blood Occurs in response to hypercapnia Depth and Rate of Breathing: PCO2
- 83. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 83 Hypoventilation – slow and shallow breathing due to abnormally low PCO2 levels Apnea (breathing cessation) may occur until PCO2 levels rise Depth and Rate of Breathing: PCO2
- 84. Applied anatomy Chapter 22, Respiratory System 84
- 85. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 85 Pneumothorax Pleural cavities are sealed cavities not open to the outside Injuries to the chest wall that let air enter the intrapleural space causes a pneumothorax collapsed lung on same side as injury
- 86. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 86
- 87. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 87
- 88. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 88 Exemplified by chronic bronchitis Patients have a history of: Smoking Dyspnea Coughing and frequent pulmonary infections Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- 89. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 89 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 90. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 90 Characterized by dyspnea, wheezing, and chest tightness Active inflammation of the airways precedes bronchospasms Airways thickened with inflammatory exudates magnify the effect of bronchospasms Asthma
- 91. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 91 Infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis Symptoms include fever, night sweats, weight loss, a racking cough, and splitting headache Treatment entails a 12-month course of antibiotics Tuberculosis
- 92. Chapter 22, Respiratory System 92 90% of all patients with lung cancer were smokers Lung Cancer