Hearing
- 2. Sound Sound is a form of energy It is transmitted through a medium as a longitudinal pressure wave. The wave consists of a series of compressions and rarefactions of the molecules in the medium. The ear is capable of capturing this energy and perceiving it as sound information
- 4. Properties of sound The wave motion of sound can be described in terms of Amplitude, Frequency, Velocity and Wavelength
- 5. Properties of sound Wavelength Refers to the physical distance between successive compressions and is thus dependant on the speed of sound in the medium divided by its frequency Amplitude (Intensity or loudness) Refers to the difference between maximum and minimum pressure Frequency (pitch) Refers to the number of peak-to-peak fluctuations in pressure that pass a particular point in space in one second Velocity Refers to the speed of travel of the sound wave. This varies between mediums and is also dependant on temperature (in air at 20°C it is 343 m/s)
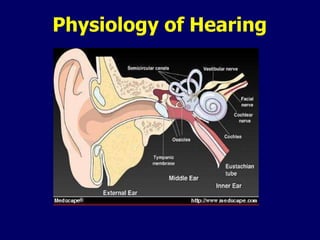
- 6. Transmission of sounds through the ear External ear – Mostly through air (External acoustic meatus) Middle ear – Through solid medium - bone (ossicles) Inner ear – Through fluid medium – endolymph (cochlea)
- 7. Parts of the ear
- 8. Air and bone conduction There are two methods by which hair cells can be stimulated. – Air conduction Sound stimulus travelling through the external and middle ear and activating the hair cells – Bone conduction Sound stimulus travelling though the bones of the skull activating the hair cells Whatever method it takes, the sound stimulus finally activate hair cells in the cochlea
- 9. External ear Consists of – Pinna – External auditory meatus
- 10. Middle ear composed of – the tympanic membrane – the tympanic cavity – the ossicles Malleus Incus Stapes (connected to the oval window of the cochlea) – two muscles the tensor tympani attached to the malleus the stapedius muscle attached to the stapes – the Eustachian tube
- 11. Inner ear Consists of two main parts – the cochlea (end organ for hearing) – the vestibule and semicircular canals (end organ for balance) The inner ear can be thought of as a series of tunnels or canals within the temporal bone Within these canals are a series of membranous sacs (termed labyrinths) which house the sensory epithelium The membranous labyrinth is filled with a fluid termed endolymph It is surrounded within the bony labyrinth by a second fluid termed perilymph The cochlea can be thought of as a canal that spirals around itself similar to a snail. It makes roughly 2 1/2 to 2 3/4 turns
- 13. Cross section through cochlea
- 14. Cochlea • The bony canal of the cochlea is divided into an upper chamber, the scala vestibuli and a lower chamber, the scala tympani by the membranous labyrinth also known as the cochlear duct. • The floor of the scala media is formed by the basilar membrane, the roof by Reissner's membrane. • The scala vestibuli and scala tympani contain perilymph. • The scala media contains endolymph.
- 15. Endolymph and perilymph Endolymph is similar in ionic content to intracellular fluid (high K, low Na) Perilymph resembles extracellular fluid (low K, high Na) The cochlear duct contains several types of specialized cells responsible for auditory perception
- 16. The sensory cells responsible for hearing are located on the basilar membrane within a structure known as the organ of Corti. This is partitioned by two rows of peculiar shaped cells known as pillar cells. The pillar cells enclose the tunnel of Corti, Situated on the basilar membrane is a single row of inner hair cells medially and three rows of outer hair cells laterally. The hair cells and other supporting cells are connected to one another at their apices by tight junctions forming a surface known as reticular lamina. The cells have specialized stereocilia on their apical surfaces
- 17. Organ of Corti
- 18. Attached to the medial aspect of the scala media is a fibrous structure called the tectorial membrane It lies above the inner and outer hair cells coming in contact with their stereocilia
- 19. The fluid in the space between the tectorial membrane and reticular lamina is endolymph Thus the endolymp bathes the stercocillia But the body of the hair cells which lies below the reticular lamina is bathed by perilymph
- 21. Hair cells
- 22. Synapsing with the base of the hair cells are dendrites from the auditory nerve The auditory nerve leaves the cochlear and temporal bone via the internal auditory canal and travels to the brainstem
- 23. Transmission of sound waves The outer ear and external auditory canal act passively to capture the acoustic energy and direct it to the tympanic membrane There, the sound waves strike the tympanic membrane causing it to vibrate These mechanical vibrations are then transmitted via the ossicles to the perilymph of the inner ear The perilymph is stimulated by the mechanical (vibrations) energy vibrations to form a fluid wave within the cochlea
- 24. Middle ear The middle ear acts as an impendance-matching device Sound waves travel much easier through air (low impedance) than water (high impedance) If sound waves were directed at the oval window (water) almost all of the acoustic energy would be reflected back to the middle ear (air) and only 1% would enter the cochlea. This would be a very inefficient method. To increase the efficiency of the system, the middle ear acts to transform the acoustic energy to mechanical energy which then stimulates the cochlear fluid
- 25. Middle ear • The middle ear also acts to increase the acoustic energy reaching the cochlea by essentially two mechanical phenomenon. • The area of the tympanic membrane is much greater than that of the stapes footplate (oval window) causing the force applied at the footplate per square area to be greater than the tympanic membrane • The ossicles act as a lever increasing once again the force applied at the stapes footplate. • Overall, the increase in sound energy reaching the cochlea is approximately 22 times
- 26. Cochlea The cochlea consists of a fluid filled bony canal within which lies the cochlear duct containing the sensory epithelium Energy enters the cochlea via the stapes bone at the oval window and is dissipated through a second opening (which is covered by a membrane) the round window Vibrations of the stapes footplate cause the perilymph to form a wave This wave travels the length of the cochlea It takes approximately 5 msec to travel the length of the cochlea
- 27. Cochlea As it passes the basilar membrane of the cochlear duct, the fluid wave causes the basilar membrane to move in a wave-like fashion (i.e. up and down) The wave form travels the length of the cochlea and is dissipated at the round window Due to changes in the mechanical properties of the basilar membrane, the amplitude of vibration changes as one travels along the basilar membrane
- 28. The place principle Low frequency stimuli cause the greatest vibration of basilar membrane at its apex, high frequency stimuli at its base
- 29. As the basilar membrane is displaced superiorly by the perilymph wave, the stereocilia at the apex of each inner and outer hair cell, which are imbedded in the tectorial membrane undergo a shearing force (i.e. they are bent) This shearing force causes a change in the resting membrane potential of the hair cell which is transmitted to its basal end There a synapse is formed with a dendrite from the auditory nerve The hair cell membrane potential change is transmitted across this synapse (? via acetylcholine) causing depolarization of the nerve fiber This neural impulse is then propagated to the auditory centres of the brain
- 30. THANK YOU
