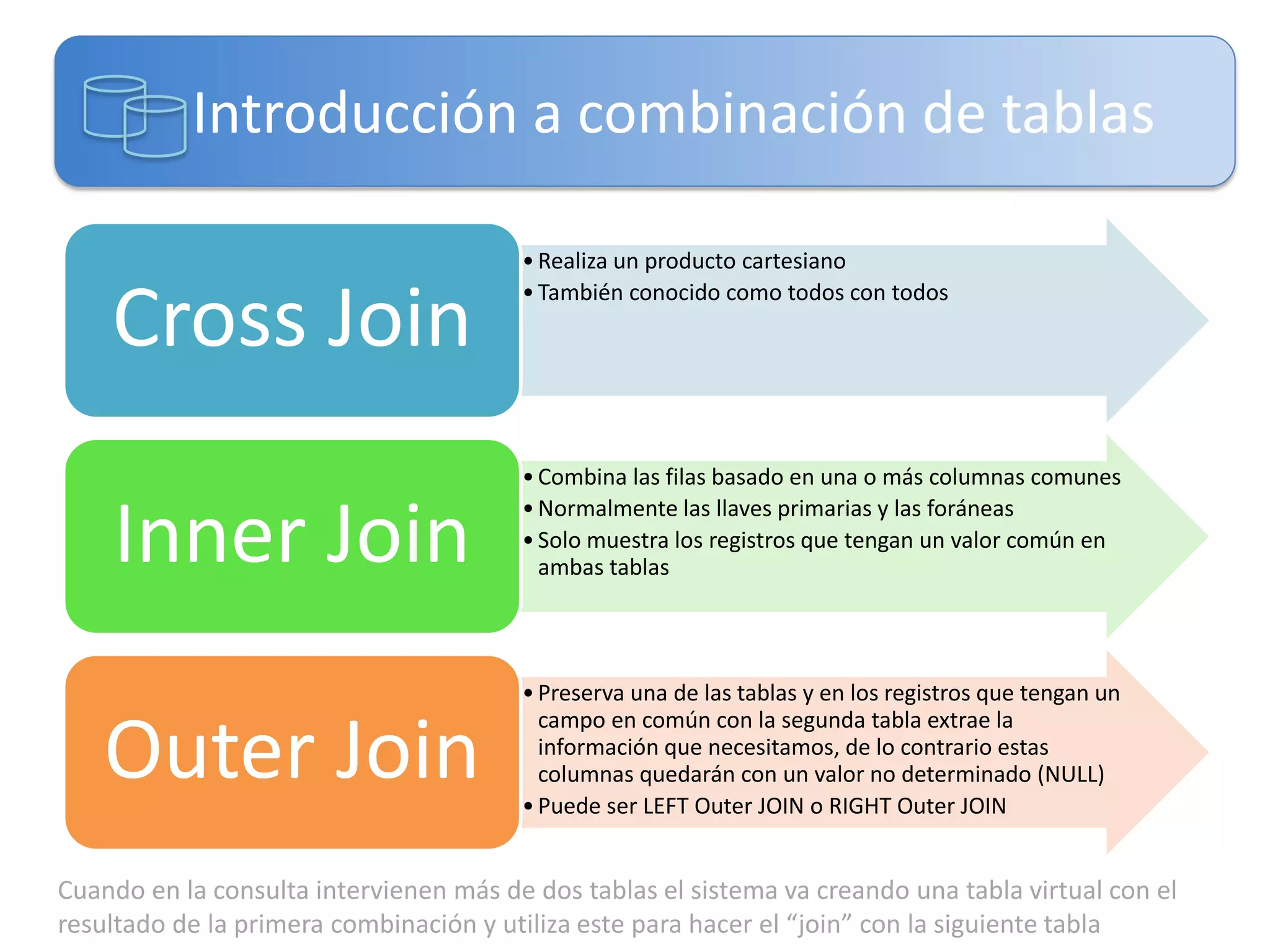
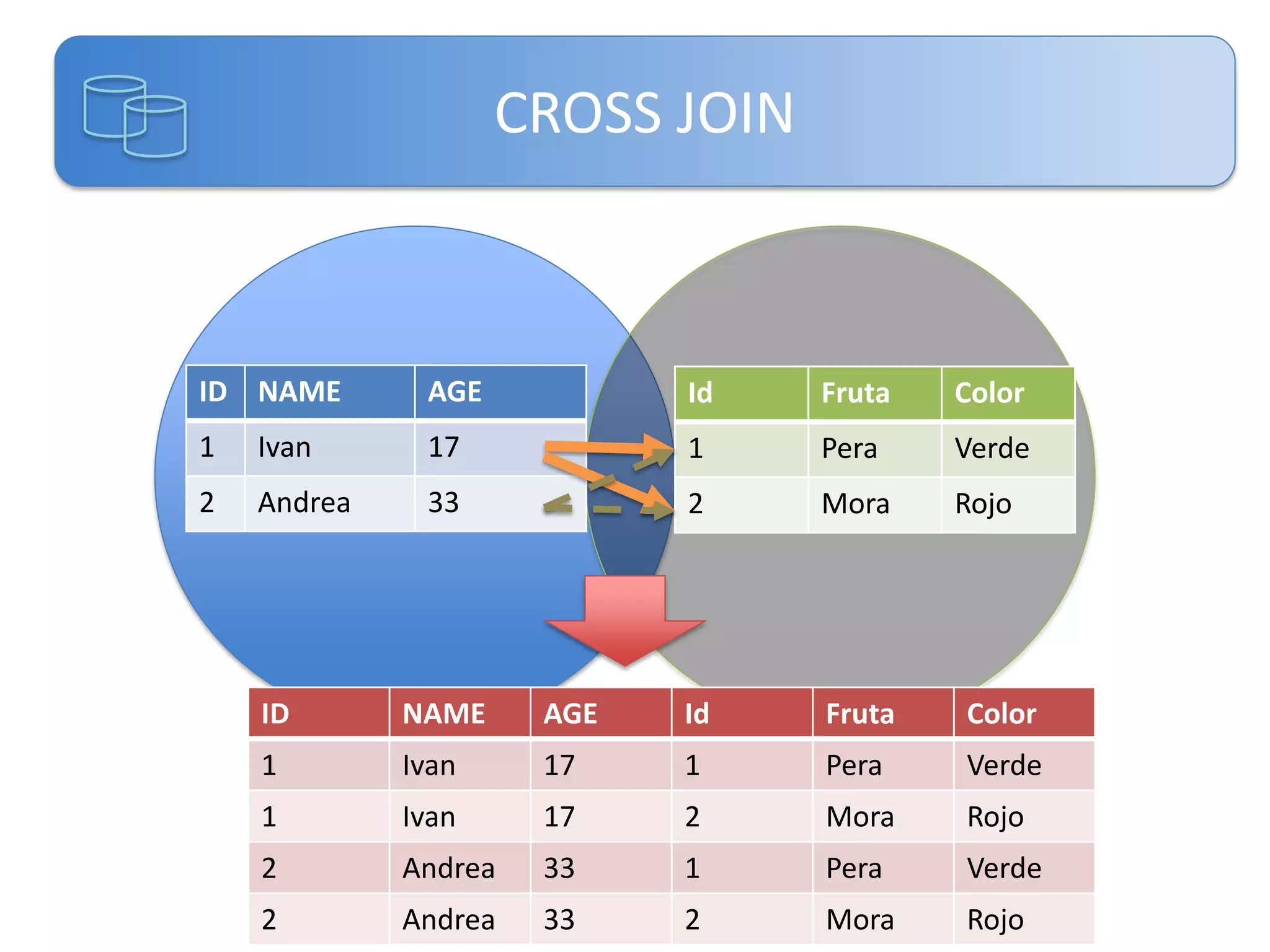
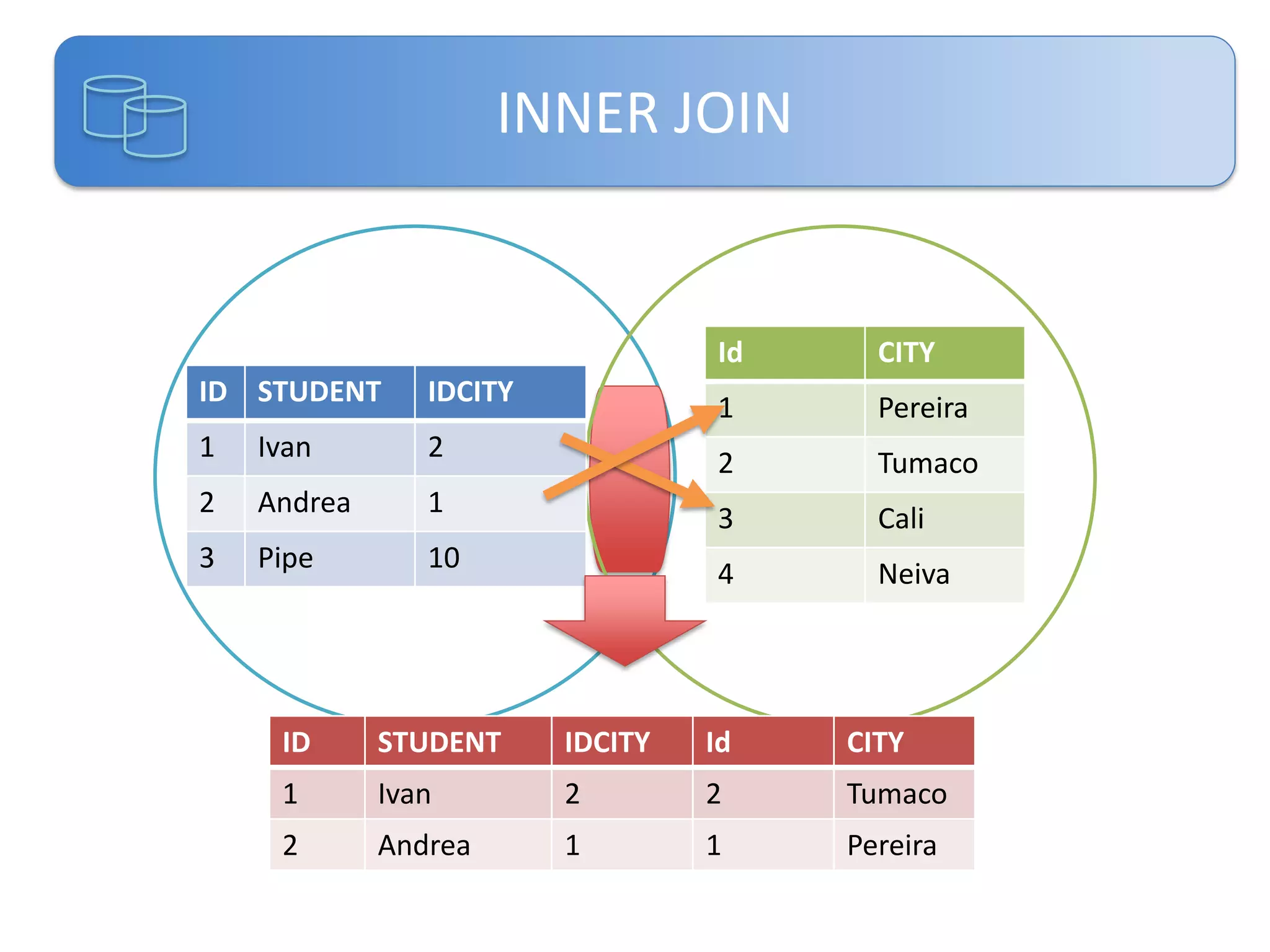
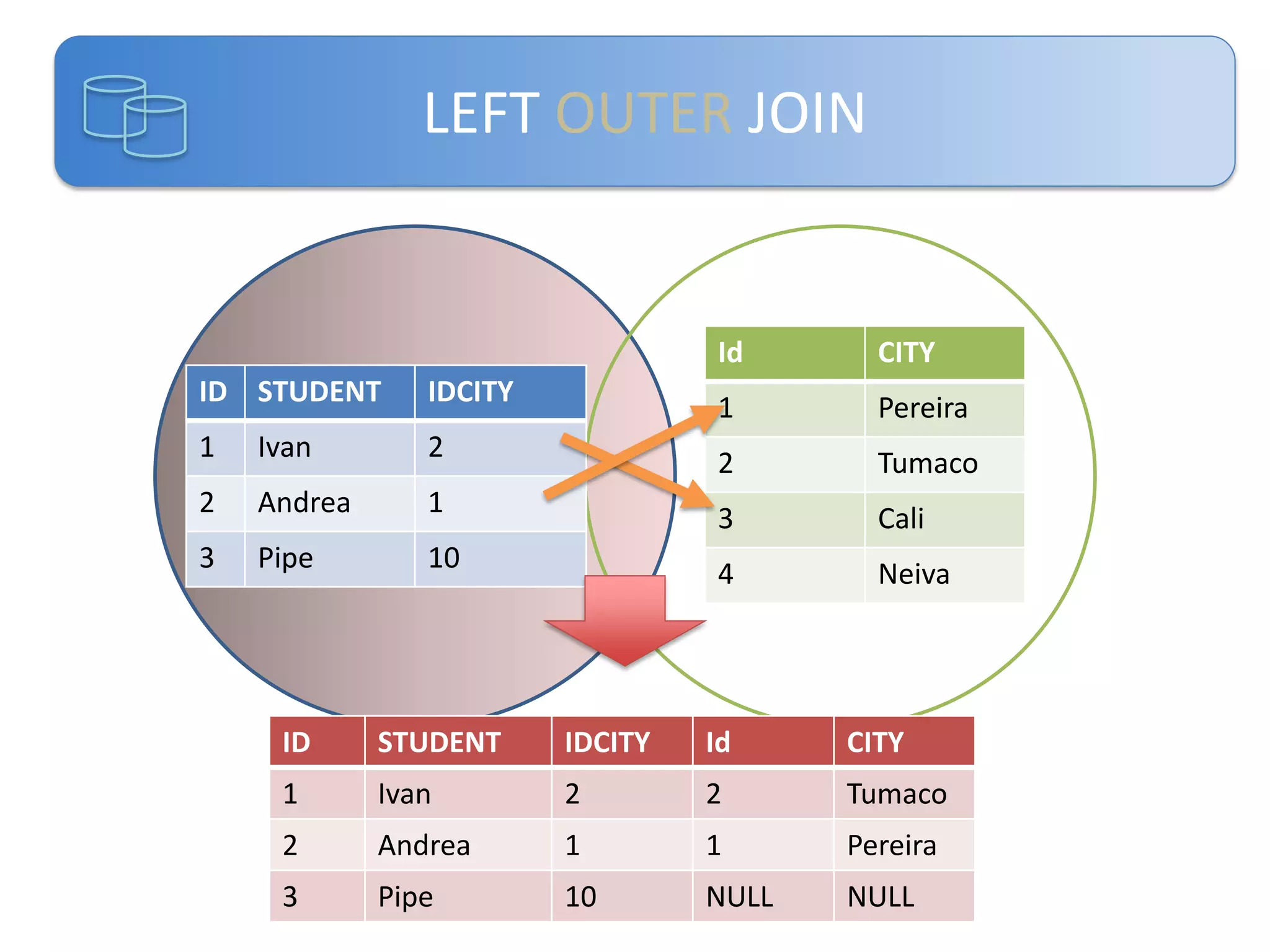
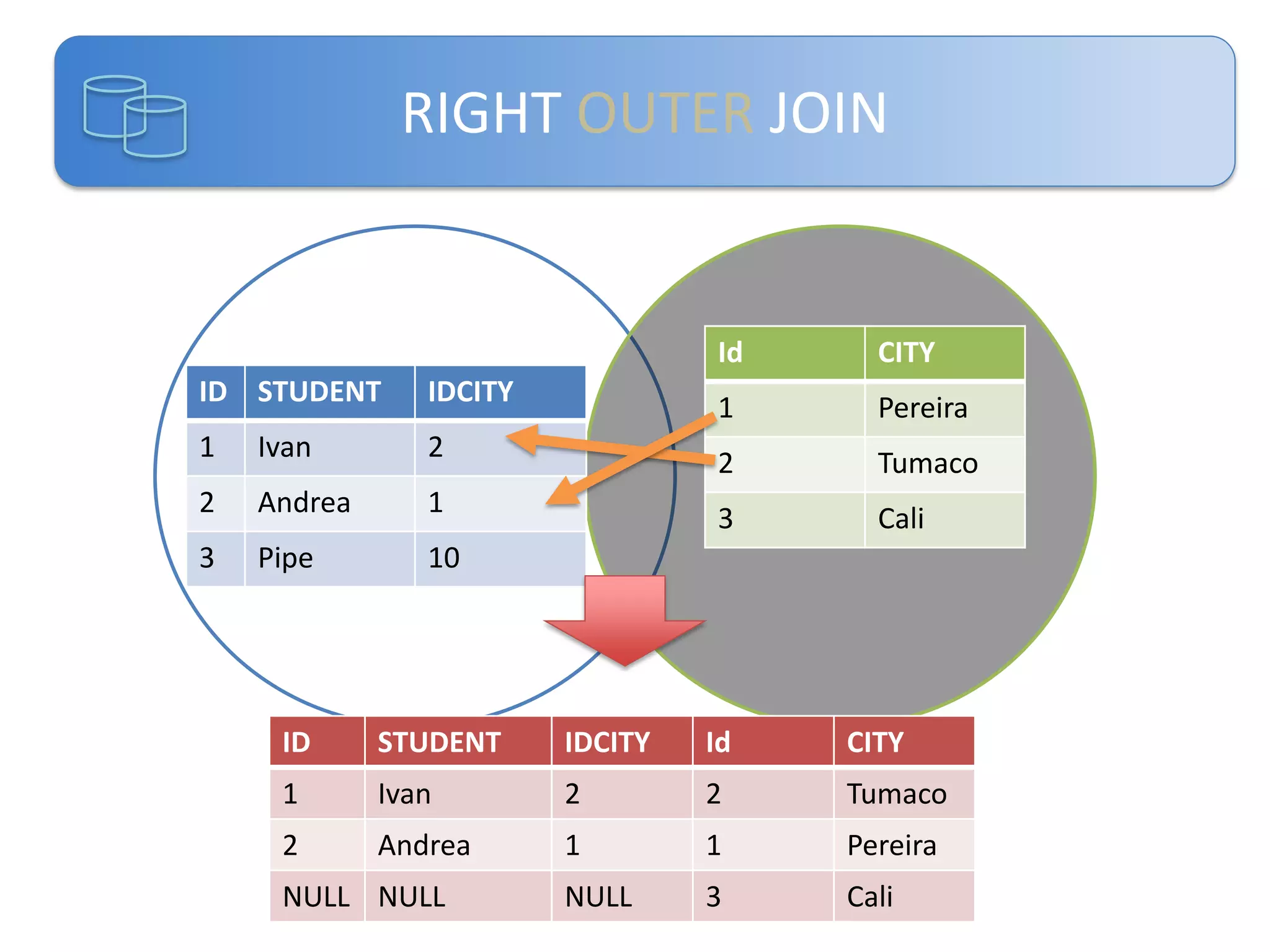
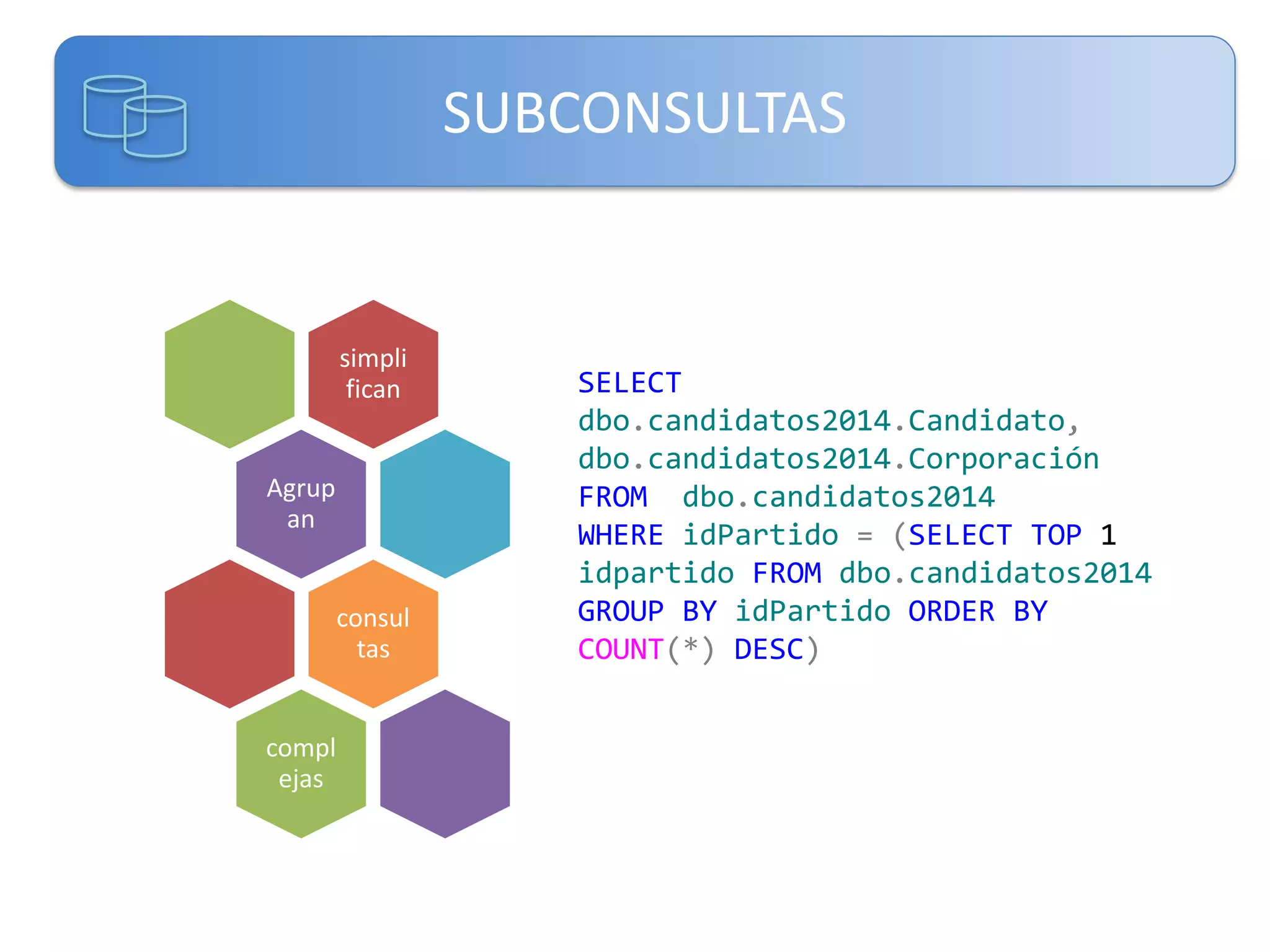
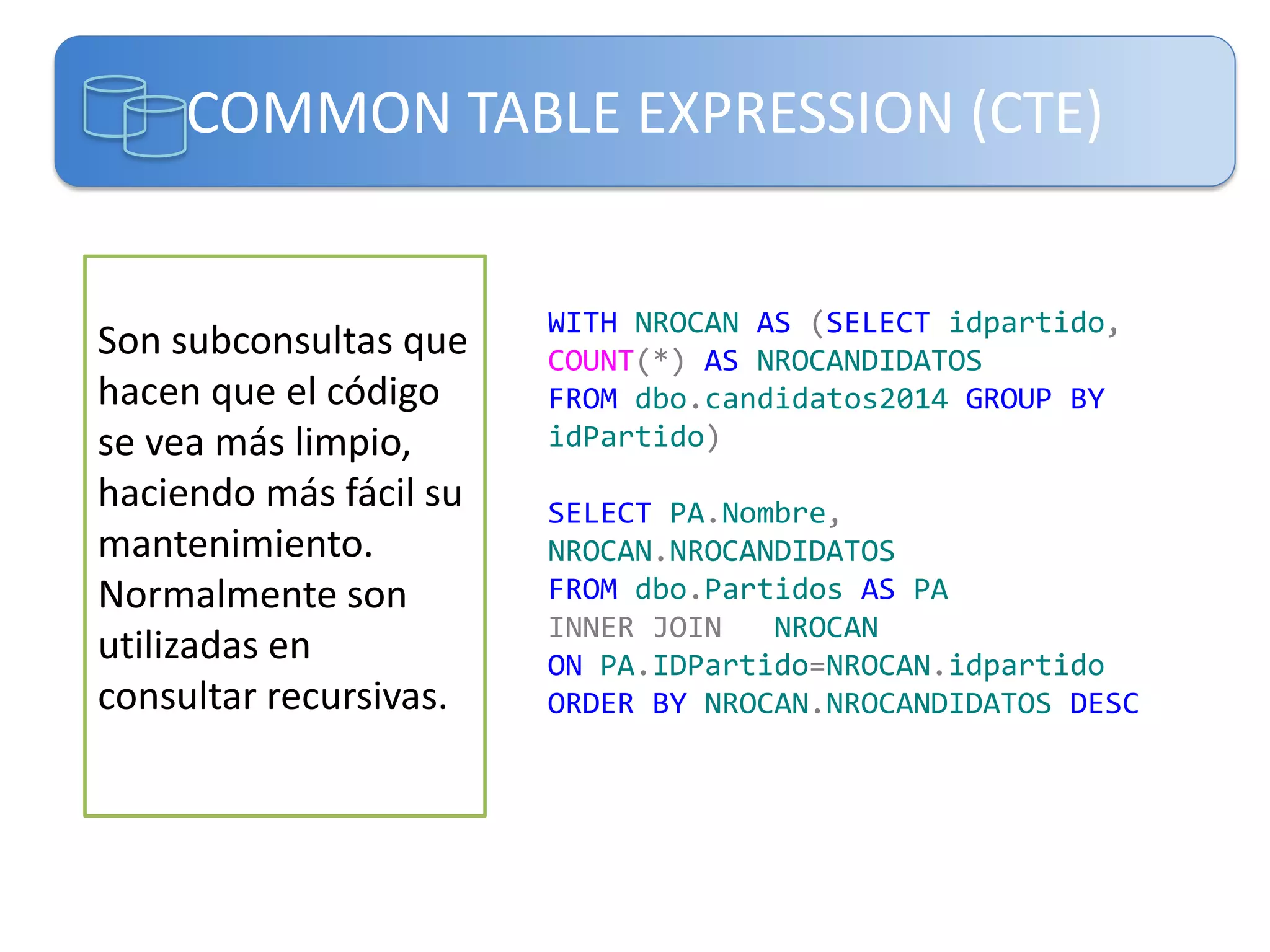
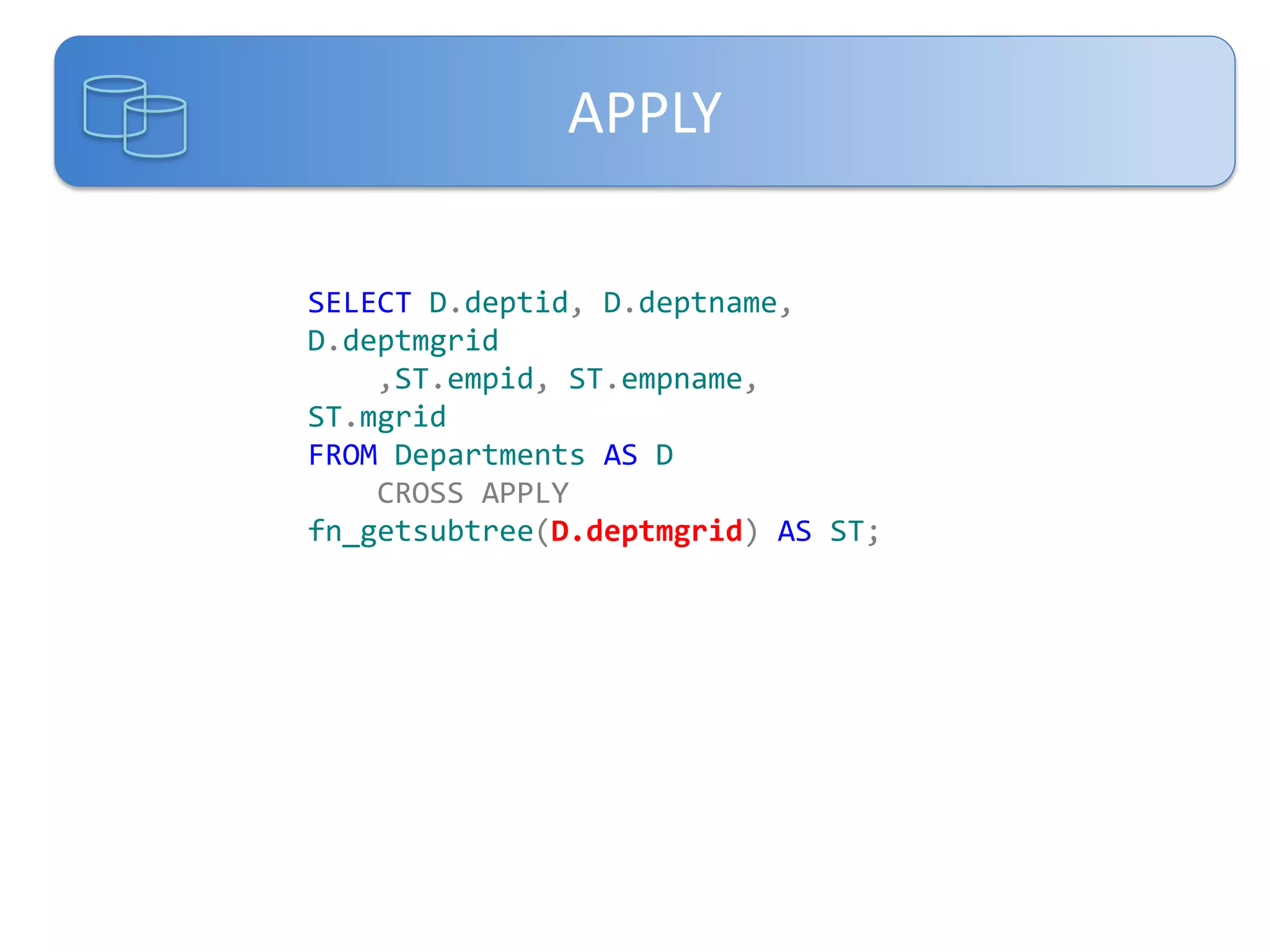
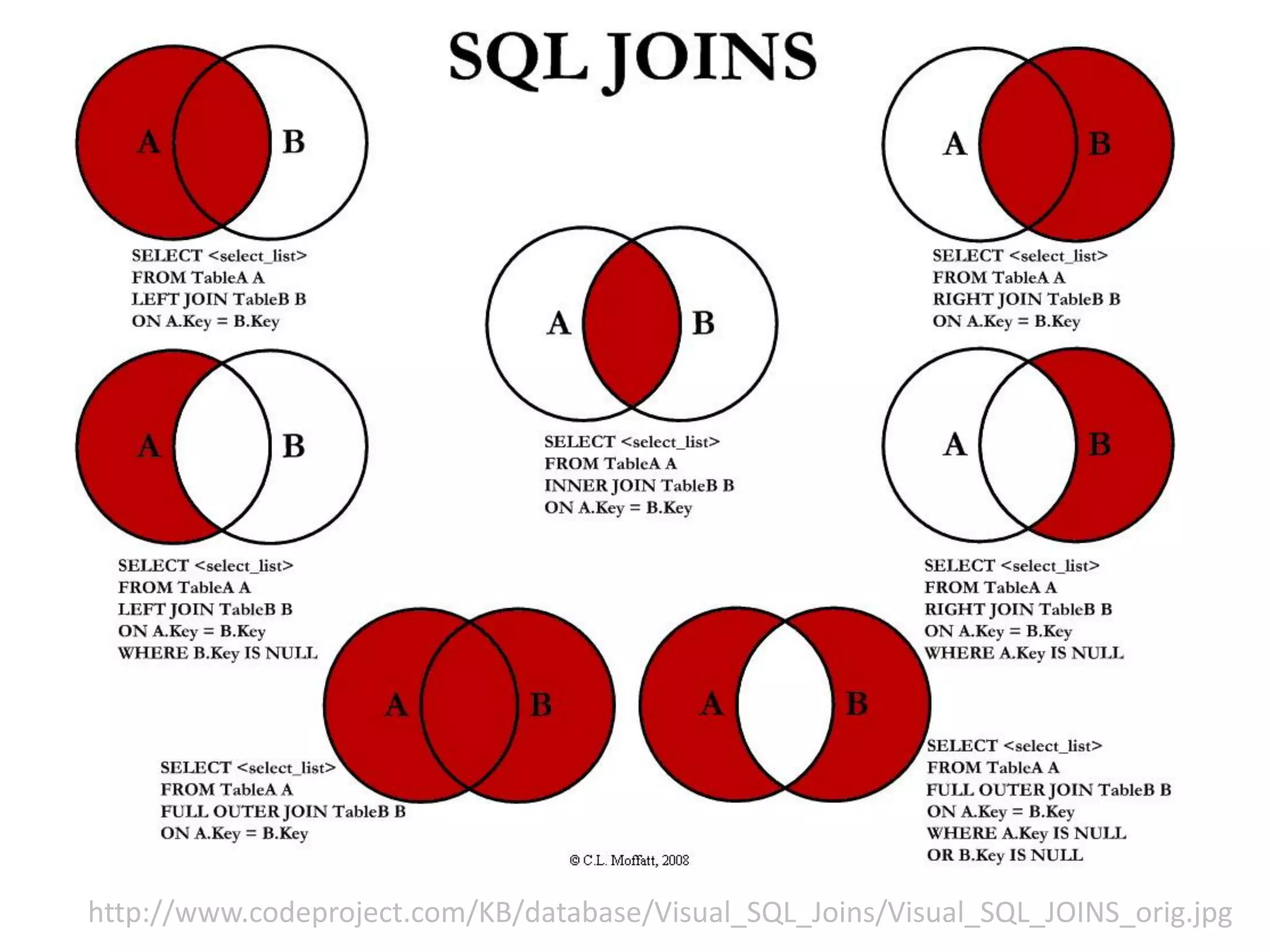
Este documento presenta una introducción a las certificaciones de SQL Server 2012 y al examen 70-461. Cubre temas como combinación de tablas mediante joins, subconsultas y expresiones de tabla comunes. El documento también incluye una agenda con los contenidos del examen 70-461, como creación de objetos de base de datos, modificación de datos, resolución de problemas y optimización.