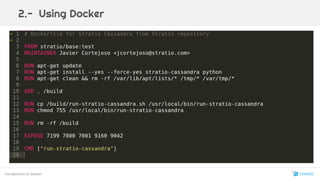
Docker es una tecnología de virtualización a nivel de sistema operativo que permite gestionar contenedores de software, facilitando su creación, distribución y ejecución. Ofrece ventajas para distintos roles, desde desarrolladores hasta ingenieros QA y DevOps, gracias a su capacidad para crear entornos aislados y simplificar el despliegue. Además, se integra con una amplia gama de herramientas y ecosistemas para la orquestación, el monitoreo y la gestión de datos.









![$ docker run --help
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Run a command in a new container
-c, --cpu-shares=0 CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpuset="" CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
-d, --detach=false Detached mode: run the container in the background and print the new container ID
-e, --env=[] Set environment variables
-h, --hostname="" Container host name
-i, --interactive=false Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--link=[] Add link to another container in the form of <name|id>:alias
-m, --memory="" Memory limit (format: <number><optional unit>, where unit = b, k, m or g)
--name="" Assign a name to the container
-P, --publish-all=false Publish all exposed ports to random ports on the host interfaces
-p, --publish=[] Publish a container's port to the host. format: ip:hostPort:containerPort | ip::containerPort |
hostPort:containerPort | containerPort (use 'docker port' to see the actual mapping)
--privileged=false Give extended privileges to this container
--rm=false Automatically remove the container when it exits (incompatible with -d)
-t, --tty=false Allocate a pseudo-TTY
-v, --volume=[] Bind mount a volume (e.g., from the host: -v /host:/container, from Docker: -v /container)
--volumes-from=[] Mount volumes from the specified container(s)
Introduction to Docker
2.- Using Docker
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodocker-150428155551-conversion-gate01/85/Introduction-to-docker-Stratio-16-320.jpg)