OBSTRUCTION OF UPPER AIRWAY AND EPISTAXIS.pdf
•
0 recomendaciones•12 vistas
obstruction of upper airway, causes, signs and symptoms, diagnostic evaluation, treatment, prevention, epistaxis definition, causes, symptoms, diagnostic evaluation, management,
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Descargar para leer sin conexión
Recomendados
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
Similar a OBSTRUCTION OF UPPER AIRWAY AND EPISTAXIS.pdf
Similar a OBSTRUCTION OF UPPER AIRWAY AND EPISTAXIS.pdf (20)
Dental Management of Respiratory & Adrenal Disorders

Dental Management of Respiratory & Adrenal Disorders
Cold and flu, its diagnosis and treatment for Pharmacist

Cold and flu, its diagnosis and treatment for Pharmacist
3. Respiratory presentation.pdf medical surgical nursing

3. Respiratory presentation.pdf medical surgical nursing
Pulmonary Complications in pediatric population.pptx

Pulmonary Complications in pediatric population.pptx
Más de Dolisha Warbi
Más de Dolisha Warbi (20)
PYODERMA, IMPETIGO, FOLLICULITIS, FURUNCLES, CARBUNCLES.pdf

PYODERMA, IMPETIGO, FOLLICULITIS, FURUNCLES, CARBUNCLES.pdf
PHOSPHATE – ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA & HYPERPHOSPHATEMIA).pdf

PHOSPHATE – ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA & HYPERPHOSPHATEMIA).pdf
BICARBONATE - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (METABOLIC ACIDOSIS & METABOLIC ALKALOSIS...

BICARBONATE - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (METABOLIC ACIDOSIS & METABOLIC ALKALOSIS...
MAGNESIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPERMAGNESEMIA & HYPOMAGNESEMIA).pdf

MAGNESIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPERMAGNESEMIA & HYPOMAGNESEMIA).pdf
POTASSIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPERKALEMIA & HYPOKALEMIA).pdf

POTASSIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPERKALEMIA & HYPOKALEMIA).pdf
CALCIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPERCALCEMIA & HYPOCALCEMIA).pdf

CALCIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPERCALCEMIA & HYPOCALCEMIA).pdf
SODIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPONATREMIA & HYPERNATREMIA) .pdf

SODIUM - ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE (HYPONATREMIA & HYPERNATREMIA) .pdf
Último
Overview of scleroderma manifestations, organ involvement, brief classifications (limited, diffuse, sine scleroderma). Overview of current treatment options, need for additional therapies. Overview of plan for multi-disciplinary scleroderma center at the University of Chicago. Potential future therapies in the literature at large. Planned trials/future treatment options at the University of Chicago.
For more info about scleroderma and the foundation, head to www.stopscleroderma.org
This talk was presented at the Scleroderma Patient Education Conference on May 4, 2024, hosted by the Scleroderma Foundation of Greater Chicago. Scleroderma: Treatment Options and a Look to the Future - Dr. Macklin

Scleroderma: Treatment Options and a Look to the Future - Dr. MacklinScleroderma Foundation of Greater Chicago
Último (20)
Is preeclampsia and spontaneous preterm delivery associate with vascular and ...

Is preeclampsia and spontaneous preterm delivery associate with vascular and ...
Why invest into infodemic management in health emergencies

Why invest into infodemic management in health emergencies
Final CAPNOCYTOPHAGA INFECTION by Gauri Gawande.pptx

Final CAPNOCYTOPHAGA INFECTION by Gauri Gawande.pptx
Muscle Energy Technique (MET) with variant and techniques.

Muscle Energy Technique (MET) with variant and techniques.
Scientificity and feasibility study of non-invasive central arterial pressure...

Scientificity and feasibility study of non-invasive central arterial pressure...
Arterial health throughout cancer treatment and exercise rehabilitation in wo...

Arterial health throughout cancer treatment and exercise rehabilitation in wo...
Cardiac Impulse: Rhythmical Excitation and Conduction in the Heart

Cardiac Impulse: Rhythmical Excitation and Conduction in the Heart
Cardiovascular Physiology - Regulation of Cardiac Pumping

Cardiovascular Physiology - Regulation of Cardiac Pumping
The POPPY STUDY (Preconception to post-partum cardiovascular function in prim...

The POPPY STUDY (Preconception to post-partum cardiovascular function in prim...
ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx![ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
ANATOMY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT AND MALE [Autosaved] [Autosaved].pptx
Young at heart: Cardiovascular health stations to empower healthy lifestyle b...

Young at heart: Cardiovascular health stations to empower healthy lifestyle b...
End Feel -joint end feel - Normal and Abnormal end feel

End Feel -joint end feel - Normal and Abnormal end feel
Relationship between vascular system disfunction, neurofluid flow and Alzheim...

Relationship between vascular system disfunction, neurofluid flow and Alzheim...
"Central Hypertension"‚ in China: Towards the nation-wide use of SphygmoCor t...

"Central Hypertension"‚ in China: Towards the nation-wide use of SphygmoCor t...
Scleroderma: Treatment Options and a Look to the Future - Dr. Macklin

Scleroderma: Treatment Options and a Look to the Future - Dr. Macklin
Book Trailer: PGMEE in a Nutshell (CEE MD/MS PG Entrance Examination)

Book Trailer: PGMEE in a Nutshell (CEE MD/MS PG Entrance Examination)
OBSTRUCTION OF UPPER AIRWAY AND EPISTAXIS.pdf
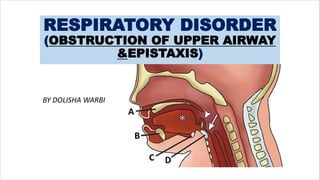
- 1. RESPIRATORY DISORDER (OBSTRUCTION OF UPPER AIRWAY &EPISTAXIS) BY DOLISHA WARBI
- 2. OBSTRUCTION OF UPPER AIRWAY • Upper airway obstruction refers to a condition where there is a partial or complete blockage in the passage through which air flows from the nose and mouth to the lungs. Causes of Upper Airway Obstruction: 1.Foreign Body: Inhaled objects, such as food, small toys, or other items, can block the airway. 2.Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions can cause swelling of the airway, known as angioedema, leading to obstruction. 3.Infections: Infections like croup (common in children) or epiglottitis can cause inflammation and swelling in the upper airway. 4.Trauma: Injury to the neck or face can result in swelling or damage to the structures in the upper airway. 5.Tumors: Growths or tumors in the throat or neck can cause obstruction. 6.Anatomical Abnormalities: Congenital or acquired abnormalities in the airway structure may lead to obstruction
- 3. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: • Cyanosis. • Choking. • Confusion. • Difficulty in breathing. • Gasping for air. • Panic. • Wheezing, crowing, whistling. • Unusual breathing noises. • Changes in consciousness. • Poor expansion of chest. • Tachypnoea. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION: o H/C. o P/E. o Bronchoscopy. o Laryngoscopy. o X-ray o Symptomatic finding.
- 4. Treatment: 1.Heimlich Maneuver (for Foreign Body): In cases where a foreign object is causing the obstruction, the Heimlich maneuver may be performed to dislodge the object. 2.Emergency Medical Assistance: Seek immediate medical attention for any signs of severe airway obstruction. 3.Epinephrine (for Allergic Reactions): In cases of severe allergic reactions causing angioedema, epinephrine may be administered. 4.Intubation or Tracheostomy: In severe cases where the airway is completely blocked, healthcare professionals may need to insert a tube through the mouth (intubation) or create a surgical airway in the neck (tracheostomy) to ensure a clear passage for air. 5.Corticosteroids and Antibiotics: If the obstruction is due to infection or inflammation, medications like corticosteroids and antibiotics may be prescribed. Drugs name - dexamethasone, 1.0 to 1.5 mg/kg, Flunisolide, Theophylline, Erythromycin, Amoxicillin, azithromycin (Zithromax), penicillin etc.
- 6. PREVENTION: ØAvoid smoking. ØEats small bites of food and eat slowly. ØChew thoroughly before Swallowing. ØSupervised children during eating. ØVisit doctor regularly in cases of having any respiratory disorder.
- 7. EPISTAXIS qEpistaxis refers to bleeding from the nose, commonly known as a nosebleed. It is a common condition that can range from a minor annoyance to a potentially serious medical issue. Definition: Epistaxis: Bleeding from the nose. Causes: • Trauma: Injury to the nose, such as a blow or the insertion of a foreign object. • Dry or Irritated Nasal Passages: Dry air, nasal allergies, or irritants can lead to the development of crusts within the nose, making it more susceptible to bleeding. • Nasal Infections: Infections, especially if associated with inflammation, can contribute to nosebleeds. • Nasal Deformities: Structural abnormalities in the nasal passages may increase the risk of bleeding. • Blood Disorders: Conditions such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease can affect blood clotting and contribute to nosebleeds. • Medications: Certain medications, like blood thinners, can increase the likelihood of bleeding.
- 8. Symptoms: 1. Bleeding from the Nose: This is the primary symptom of epistaxis. 2. Blood may flow out through the nostrils or down the back of the throat. 3. May be accompanied by pain, difficulty breathing, or a feeling of pressure in the nose. Diagnostic Evaluation: 1. Clinical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess the patient's medical history and conduct a physical examination. 2. Nasal Endoscopy: In some cases, a small flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) may be used to examine the nasal passages. 3. Blood Tests: If an underlying medical condition is suspected, blood tests may be ordered to evaluate the clotting function.
- 9. Management: • First Aid: • Tilt the head forward to prevent blood from flowing down the throat. • Pinch the nostrils together and breathe through the mouth. • Apply an ice pack to the bridge of the nose. • Topical Agents: Nasal sprays or gels containing vasoconstrictors or clotting agents may be used to stop bleeding. • Cauterization: Sealing the bleeding blood vessels using heat or chemicals. • Nasal Packing: Placing gauze or an inflatable balloon in the nasal cavity to apply pressure and stop bleeding. • Surgical Intervention: In severe or recurrent cases, surgical procedures may be considered to address underlying issues.