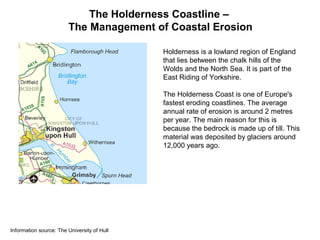
Holderness Coastline - Management
- 1. The Holderness Coastline – The Management of Coastal Erosion Holderness is a lowland region of England that lies between the chalk hills of the Wolds and the North Sea. It is part of the East Riding of Yorkshire. The Holderness Coast is one of Europe's fastest eroding coastlines. The average annual rate of erosion is around 2 metres per year. The main reason for this is because the bedrock is made up of till. This material was deposited by glaciers around 12,000 years ago. Information source: The University of Hull
- 2. The Holderness Coast is one of Europe's fastest eroding coastlines. The average annual rate of erosion is around 2 metres per year. This is around 2 million tonnes of material every year. Under lying the Holderness Coast is bedrock made up of Cretaceous Chalk. However, in most place this is covered by glacial till deposited over 18,000 years ago. It is this soft boulder clay that is being rapidly eroded. The Holderness Coast is a great case study to use when examining coastal processes and the features associated with them. The area contains 'text book' examples of coastal erosion and deposition. The exposed chalk of Flamborough provides examples of erosion, features such as caves, arches and stacks. The soft boulder clay underlying Hornsea provides clear evidence of the erosional power of the sea. Mappleton is an excellent case study of an attempt at coastal management. Spurn Point provides evidence of longshore drift on the Holderness Coast. It is an excellent example of a spit. Around 3% of the material eroded from the Holderness Coast is deposited here each year.
- 3. How might the geology of the area affect the shape of the coastline? What processes are acting upon this coastline? Geology Map of Holderness Altitude Map of Holderness
- 4. What processes are acting upon this coastline? The Holderness Coastline is made up of soft boulder clays (tills) left after the retreat of the Devensian ice sheets about 12 000 years ago. They can be seen on the coast, being rapidly eroded by the sea. To look at, they are a mass of brown clay containing pieces of rock (erratics) brought here by the glaciers from Scandinavia, Scotland, the Lake District and Northeast England. These soft, recent deposits sit on a platform of chalk which slopes away gently to the east. Erratics in till at Mappleton
- 5. What processes are acting upon this coastline? Erosion of the Holderness cliffs is a cyclic, four stage process: 1. The soft Boulder Clay cliffs become saturated with rain water and lose their strength. 2. The cliff is too steep and fails either as a block of material or as a slurry slide 3. Cliff failure reduces the angle and prevents further erosion but … 4. Large waves from the North East remove the debris in longshore drift to the South and the cliff oversteepens, rain falls and the cycle begins again.
- 6. The order of this presentation… 1. Flamborough Head. 2. Mappleton 3. Aldbrough 4. Withernsea 5. Kilnsea 6. Spurn Head
- 7. 1. Flamborough Head The chalk of Flamborough is a resistant rock that provides examples of erosion, features such as caves, arches and stacks. The chalk has formed a headland.
- 8. 2. Mappleton Situated approximately 3km south of Hornsea lies the village of Mappleton. Supporting approximately 50 properties, the village has been subject to intense erosion at a rate of 2.0m per year, resulting in the access road being only 50m from the cliff edge at its closest point. Mappleton lies upon unconsolidated till (boulder clay). This material was deposited by glaciers during the last ice age 12,000 years ago.
- 9. Geology Mappleton lies upon unconsolidated till. This material was deposited by glaciers during the last ice age 18,000 years ago. Coastal Features The two rock groynes at Mappleton have helped develop wide and steep sandy beaches. Coastal Management In 1991 almost £2 million was spent on two rock groynes and a rock revetment to protect Mappleton and the B1242 coastal road. Blocks of granite were imported from Norway for the sea defences. The purpose of the two rock groynes was to trap beach material. As the result of the coastal management a substantial beach accumulated between the groynes halting erosion.
- 10. Mappleton Mappleton is an excellent case study of an attempt at coastal management. In 1991 two rock groynes and a rock revetment made from huge blocks of Scandinavian rock were built. As a consequence a substantial beach accumulated between the groynes halting erosion (picture 1 below). However, further south the rate of erosion has increased significantly (picture 2 below). This is because material which is being carried south is not being replaced (it is trapped within the groynes). Therefore there is no beach to protect the cliffs. Even during a neap tide ( a tide which is 30% less than the average tidal range) the sea reaches the base of the soft cliffs and erosion occurs. 1 Cliffs to the north. Sea defences mean that the beach has grown and the cliffs are stable (look at the grass growing!) 2 Cliffs to the south. The sea defences don’t protect this area and the land is retreating rapidly.
- 11. Mappleton Northern section Defences = Beach build up Southern section No defences = Beach erosion
- 12. 3. Aldbrough Aldbrough is a small settlement to the south of Mappleton. Where Mappleton had substantial sea defences built, Aldbrough has none. The cliffs here are rapidly eroding. Some residents think that the sea defences at Mappleton has made things worse. Why would they think this?
- 13. Aldbrough
- 14. 4. Withernsea This settlement attracts tourists, so substantial sea defences have been constructed to maintain the beach. How many sea defences can you see in this picture?
- 15. Withernsea – how does it all work?
- 16. 5. Kilnsea The old settlement of Kilnsea has now been completely lost. Sea defences were built here in the early 1900s to protect the Godwin Battery - a defensive gun emplacement and the rail-head for a light railway to further military installations on Spurn point. The sea defences are now crumbling and erosion is progressing rapidly.
- 17. Kilnsea Old map of Kilnsea Current aerial photo of Kilnsea
- 18. 6. Spurn Head The area known as Spurn forms the southern extremity of the Holderness coast and includes the unique feature of Spurn Head, a sand and shingle spit 5.5km long, reaching across the mouth of the Humber. Spurn is made up of the material which has been transported along the Holderness Coast. This includes sand, sediment and shingle. Spurn Point provides evidence of longshore drift on the Holderness Coast. It is an excellent example of a spit. How would sea defences along the coastline affect Spurn?
- 19. Spurn Head 1. The material eroded from the Holderness cliffs is swept southwards. 2. North easterly waves move the coarser sands and gravel down towards the mouth of the Humber 3. The finer sands and clays are swept offshore and continue southwards towards the Wash. 4. Spurn Head ‘hangs like a rudder’ for six kilometres off the end of Holderness, built by the sands and gravels eroded from the cliffs and transported south by longshore drift 5. In the past Spurn Head seems to have grown and been washed away in a regular cycle, slowly moving towards the east to keep pace with the erosion of the Holderness cliffs. 6. For over 100 years the position of Spurn has been fixed by artificial sea defences. These defences are now falling into disrepair and the sea is starting to erode parts of the peninsula once again.
- 20. Spurn Head Spurn Head changes position. Most of the spit has flexible road surfaces, which are like mats that can be picked up and moved following major storms. There is plenty of evidence of this movement. Former railway tracks that were built to move building materials along Spurn (for the building of Bull Fort in the Humber Estuary) now appear to lead into the sea.
- 21. Spurn Head Is Spurn eroding? The end of Spurn is fairly stable. This is due to it’s size and the presence of deep rooted plants. The rest of Spurn erodes and moves constantly. There are some groynes to protect it, but these are very old now.
- 22. Spurn Head Is it important to protect access to Spurn Point? Full time lifeboat men live here with their families. The Humber estuary is very busy with large ships. It is one of the most dangerous estuaries in Europe, so pilots guide boats in and out. Their base is on Spurn for quick access to sea. The pilots do not live on Spurn. Spurn is also important for birds and wildlife.
- 23. Locational Context Study Area Sandsend to Scarboroug h Subcell What is a sediment cell? Today coastlines are managed as complete systems, as Sediment cells, within which is a self- contained cycle of erosion, transport and deposition of sediment.
- 24. What is the aim of a SMP? • To provide the basis for sustainable coastal defence policies within a sediment cell and to set objectives for the future management of the coastline. • SMP’s set out a strategy for coastal defence for specified lengths of coast identified as sediment cells. They are funded mostly by DeFRA, the Environment Agency and local councils.
- 25. Strategic Coastal Defence Options in the past • Largely piecemeal • Local defence schemes • Only protect areas immediately threatened • Serious knock on effects downshore e.g. groynes or revetments starve beaches downshore of sediment and actually accelerate erosion in these areas. Building sea walls may also reduce sediment inputs, degrading beaches and mudflats and threatening increased erosion and coastal flooding
- 26. Strategic Coastal Defence Options Today Coastal defence schemes today are not haphazard! A great deal of care and scientific research goes into planning their type and location. The 4 options are:- 1) Do nothing 2) Hold the existing defence line by maintaining or improving the standard of protection 3) Advance the existing defence line 4) Retreat the existing defence line
- 27. Hard engineering strategies Rip Rap GroyneAccropodesRecurved sea wall Gabions Revetment
- 28. Damaged gabions forming a public safety hazard and releasing non-indigenous cobbles onto the beach.
- 29. Soft engineering strategies Geo-textiles Beach nourishmentCliff regrading Drainage pipesManaged retreat
- 30. Broader Implications 1 • 23% total land area lies within 10km of the coast • 16.9 million people live within the coastal zone • Land use: - 33% pasture - 25% arable - 7% woodland - 2% heathland - 3% cliffs, beaches and mudflats - 30% buildings, roads, recreation facilities • 40% UK manufacturing industry lies close to the coast
- 31. Broader Implications 2 • Sea defences around the UK coast cost £300 million to maintain annually • There have been a number of spectacular cliff falls in recent years e.g. Holbeck Hall Hotel in Scarborough (see next slide) • On the Holderness coast erosion rates have reached 11m per year. In Suffolk 8.5 metres per year • Estimates suggest that by 2027 an area the size of Jersey will have been lost on the east coast of the UK alone!
- 32. Holbeck Hall Hotel landslide, Scarborough. June 3rd & 4th 1993
- 33. Holbeck Hall Hotel, Scarborough
- 34. Holbeck Hall Hotel, Scarborough
- 35. Holbeck Hall Hotel, Scarborough
- 36. Holbeck Hall Hotel, Scarborough
- 38. Images of Scarborough prior to Defence Work starting April 2002
- 39. Overtopping caused Marine Drive to be closed 35 times per year!
- 40. The pier is a listed structure first built in 1732. Seaward wall in extremely poor condition
- 41. Marine drive sea wall in a very poor condition
- 42. Marine drive sea wall in a very poor condition
- 43. Accropode armoured revetment to seriously reduce risk of overtopping
- 44. Scarborough today after £33million spent on coastal defence 2002 2007
- 45. Scarborough today after £33million spent on coastal defence 2002 2007
- 46. Scarborough today after £33million spent on coastal defence 2002 2007
- 47. Scarborough today after £33million spent on coastal defence 2002 2007
- 48. The future? Oil terminal Wind turbines Lifeboat Station Humber Pilots Many key industries, farms and homes lie within 50 meters of the coastline. 1. Should they be saved? 2. What effects would saving these have on other areas of the coastline? 3. Who should pay?
