Neurobiological considerations Valeria Caicedo
•Descargar como PPTX, PDF•
0 recomendaciones•777 vistas
Considerations on Sencond language acquisitions
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
SLA ,Learning Theories , Second language Aquisition

SLA ,Learning Theories , Second language Aquisition
Language acquisition fisrt language acquisition;age and acquisition

Language acquisition fisrt language acquisition;age and acquisition
Cognitive language acquisition theories presentation

Cognitive language acquisition theories presentation
Similar a Neurobiological considerations Valeria Caicedo
Similar a Neurobiological considerations Valeria Caicedo (20)
PAGTUTULAD AT PAGKAKAIBA NG UNA AT PANGALAWANG WIKA-final.pptx

PAGTUTULAD AT PAGKAKAIBA NG UNA AT PANGALAWANG WIKA-final.pptx
Language Development in Early childhood by Emma Jefferies and Jeb Stevens

Language Development in Early childhood by Emma Jefferies and Jeb Stevens
Comparing and contrasting first and second language acquisition john

Comparing and contrasting first and second language acquisition john
Linguistic and literacy development of children and adolescents

Linguistic and literacy development of children and adolescents
Más de Vale Caicedo
Más de Vale Caicedo (8)
Principles of language learning and teaching ana v. caicedo

Principles of language learning and teaching ana v. caicedo
Principles of language learning and teaching ana v. caicedo

Principles of language learning and teaching ana v. caicedo
Último
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Último (20)
Sensory_Experience_and_Emotional_Resonance_in_Gabriel_Okaras_The_Piano_and_Th...

Sensory_Experience_and_Emotional_Resonance_in_Gabriel_Okaras_The_Piano_and_Th...
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
Exploring_the_Narrative_Style_of_Amitav_Ghoshs_Gun_Island.pptx

Exploring_the_Narrative_Style_of_Amitav_Ghoshs_Gun_Island.pptx
HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx

HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Neurobiological considerations Valeria Caicedo
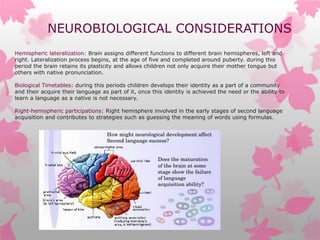
- 1. NEUROBIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Hemispheric lateralization: Brain assigns different functions to different brain hemispheres, left and right. Lateralization process begins, at the age of five and completed around puberty. during this period the brain retains its plasticity and allows children not only acquire their mother tongue but others with native pronunciation. Biological Timetables: during this periods children develops their identity as a part of a community and their acquire their language as part of it, once this identity is achieved the need or the ability to learn a language as a native is not necessary. Right-hemispheric participations: Right hemisphere involved in the early stages of second language acquisition and contributes to strategies such as guessing the meaning of words using formulas.
- 2. COGNITIVE CONSIDERATIONS Stages of intellectual development in child: Sensory stage (birth to two) Preoperational stage (ages two to seven) Operational stage (ages seven to sixteen) Concrete operational stage (ages seven to eleven) Formal operational stage (ages eleven to sixteen) Since puberty a person becomes capable of abstraction, formal thinking that transcends the specific experience and insight, from this age we need explanations about language, which creates a barrier to the free learning As the child matures into adulthood, the left hemisphere becomes more dominant than the right hemisphere. that dominance contributes to a tendency to over-analyze and be too intellectual focused on the task of learning a second language, which does not occur in children Cognition is developed as a process of moving from state of doubt and uncertainty (imbalance) to the stages of resolution and security (Balanced-brio)
- 3. AFFECTIVE CONSIDERATIONS We are influenced by emotions: Inhibitions Language ego Second identity Attitudes Peer pressure Ego language is the identity of a person is also based on the language spoken, when puberty starts emotional, physical, and cognitive changes lead to a defensive mechanism in which the ego language becomes protector and defense. The language, which now has become an integral part of one's identity, is threatened, and therefore a context that is developed must be willing to make a fool in the fight by trial and error to speak and understand the second language. Negative attitudes can affect the success in learning a language, if an adult is averse or have bad attitude towards culture, or people who speak an specific language, learning process to acquire a second language will be affected.
- 4. LINGUISTIC CONSIDERATIONS Bilingualism: coordinate bilingualism, compound bilingualism. The acquisition of two languages in bilingual children is slightly slower than the acquisition of the first language, but bilingual children are better in concept formation and have greater mental flexibility. Interference between first second languages: linguistic and cognitive processes of learning a second language in young children are generally similar to first language processes; this teaches us that similar strategies and linguistic characteristics are present in the first and second language learning in children. Interference in adults: Adults who learn a second language manifest some of the same types of errors found in children learning their mother tongue. Order of acquisition: children learn a second language using a creative constructions process, just as they do in their first language.
