Food chain
•Descargar como DOCX, PDF•
51 recomendaciones•49,744 vistas
Food chain and food web
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
Destacado
Destacado (18)
FERMENTATIONS , PHOTOSYNTHESIS & NITROGEN FIXATION 

FERMENTATIONS , PHOTOSYNTHESIS & NITROGEN FIXATION
Similar a Food chain
Similar a Food chain (20)
Food Chain and Food Web (Ecosystem) EVS, B. Pharmacy 1st Year, Sem-II

Food Chain and Food Web (Ecosystem) EVS, B. Pharmacy 1st Year, Sem-II
Ecoystem complex and interaction of living organisms

Ecoystem complex and interaction of living organisms
Más de Vidya Kalaivani Rajkumar
Más de Vidya Kalaivani Rajkumar (20)
Último
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Parvati Darshan 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Girls Waiting For You To Fuck
Booking Contact Details
WhatsApp Chat: +91-6297143586
pune Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus they look fabulously elegant; making an impressionable.
Independent Escorts pune understands the value of confidentiality and discretion - they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together.
We provide -
01-may-2024(v.n)
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Parvati Darshan 6297143586 Call Hot I...

Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Parvati Darshan 6297143586 Call Hot I...Call Girls in Nagpur High Profile
(NEHA) Call Girls Navi Mumbai Call Now: 8250077686 Navi Mumbai Escorts Booking Contact Details WhatsApp Chat: +91-8250077686 Navi Mumbai Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus, they look fabulously elegant, making an impression. Independent Escorts Navi Mumbai understands the value of confidentiality and discretion; they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together. We provide: (NEHA) Call Girls Navi Mumbai Call Now 8250077686 Navi Mumbai Escorts 24x7

(NEHA) Call Girls Navi Mumbai Call Now 8250077686 Navi Mumbai Escorts 24x7Call Girls in Nagpur High Profile Call Girls
Último (20)
GENUINE Babe,Call Girls IN Chhatarpur Delhi | +91-8377877756

GENUINE Babe,Call Girls IN Chhatarpur Delhi | +91-8377877756
VIP Model Call Girls Uruli Kanchan ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting From ...

VIP Model Call Girls Uruli Kanchan ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting From ...
Call Girls Jejuri Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking

Call Girls Jejuri Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Parvati Darshan 6297143586 Call Hot I...

Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Parvati Darshan 6297143586 Call Hot I...
Call Now ☎️🔝 9332606886 🔝 Call Girls ❤ Service In Muzaffarpur Female Escorts ...

Call Now ☎️🔝 9332606886 🔝 Call Girls ❤ Service In Muzaffarpur Female Escorts ...
Call Girls Ramtek Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking

Call Girls Ramtek Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking
Call Girls Service Pune ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 8005736733 Cal...

Call Girls Service Pune ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 8005736733 Cal...
Verified Trusted Kalyani Nagar Call Girls 8005736733 𝐈𝐍𝐃𝐄𝐏𝐄𝐍𝐃𝐄𝐍𝐓 Call 𝐆𝐈𝐑𝐋 𝐕...

Verified Trusted Kalyani Nagar Call Girls 8005736733 𝐈𝐍𝐃𝐄𝐏𝐄𝐍𝐃𝐄𝐍𝐓 Call 𝐆𝐈𝐑𝐋 𝐕...
VIP Model Call Girls Charholi Budruk ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting Fro...

VIP Model Call Girls Charholi Budruk ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting Fro...
VIP Model Call Girls Hadapsar ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting From 5K to...

VIP Model Call Girls Hadapsar ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting From 5K to...
Proposed Amendments to Chapter 15, Article X: Wetland Conservation Areas

Proposed Amendments to Chapter 15, Article X: Wetland Conservation Areas
(NEHA) Call Girls Navi Mumbai Call Now 8250077686 Navi Mumbai Escorts 24x7

(NEHA) Call Girls Navi Mumbai Call Now 8250077686 Navi Mumbai Escorts 24x7
VIP Model Call Girls Wagholi ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting From 5K to ...

VIP Model Call Girls Wagholi ( Pune ) Call ON 8005736733 Starting From 5K to ...
CSR_Module5_Green Earth Initiative, Tree Planting Day

CSR_Module5_Green Earth Initiative, Tree Planting Day
Call Girls Moshi Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking

Call Girls Moshi Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking
Sector 18, Noida Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified

Sector 18, Noida Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified
Food chain
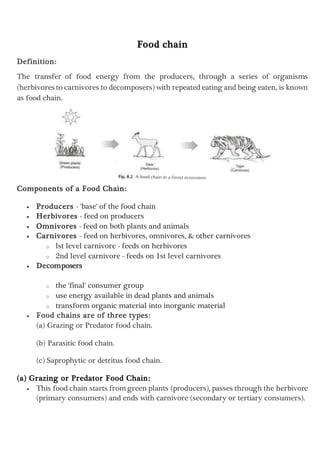
- 1. Food chain Definition: The transfer of food energy from the producers, through a series of organisms (herbivores to carnivores to decomposers) with repeated eating and being eaten, is known as food chain. Components of a Food Chain: Producers - 'base' of the food chain Herbivores - feed on producers Omnivores - feed on both plants and animals Carnivores - feed on herbivores, omnivores, & other carnivores o lst level carnivore - feeds on herbivores o 2nd level carnivore - feeds on 1st level carnivores Decomposers o the 'final' consumer group o use energy available in dead plants and animals o transform organic material into inorganic material Food chains are of three types: (a) Grazing or Predator food chain. (b) Parasitic food chain. (c) Saprophytic or detritus food chain. (a) Grazing or Predator Food Chain: This food chain starts fromgreen plants (producers), passes through the herbivore (primary consumers) and ends with carnivore (secondary or tertiary consumers).
- 2. Autotroph→ Herbivore→ Primary Carnivore →Secondary Carnivore→ Tertiary Carnivore → Decomposer etc. E.g. of aquatic ecosystem Phytoplankton →Zooplankton→ Fish→ Hawk E.g. of grassland ecosystem Grass→Rabbit→Fox→Wolf→Tiger Grass→ Grasshopper→ Frog→Snake→Hawk (b) Parasitic food chain: In this type of food chain either the producer or the consumer is parasitized. So the food passes to the smaller organism. The energy transfer through this kind of food chain is not significant. Producer→ Herbivores→ Parasite→ Hyper parasites Trees→ Fruit eating birds→ Lice and bugs→ Bacteria and fungi (c) Saprophytic or Detritus Food chain: This type of food chain starts from dead organic matter of decaying animals and plant bodies to the micro-organisms and then to detritus feeding organism and to other predators. The food chain depends mainly on the entry of organic matter produced in another system. The organism of the food chain includes algae, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, insects, nematodes etc.
- 3. Significance of Food Chains and Food webs 1. They help in maintaining the ecological balance. 2. They help in understanding the feeding relations among organisms. 3. Energy flow and nutrient cycling take place through them. 4. The movement of sometoxic substances (like DDT) in the ecosystem, sprayed to kill the pests and insects, through the various trophic levels, their accumulation at the highest trophic level, etc. can be studied(bio magnification). Food web Food web can be defined as, "a network of food chains which are interconnected at various tropic levels, so as to forma number of feeding connections amongstdifferentorganisms of a biotic community". It is also known as consumer-resource system. All the food chains are interconnected and overlapping within an ecosystem and they make up a food web. Important facts • A node represents an individual species, or a group of related species or different stages of a single species. • A link connects two nodes. Arrows represent links, and always go from prey to predator. • The lowest tropic level are called basal species. • The highest tropic level are called top predators.
- 4. • Movement of nutrients is cyclic but of energy is unidirectional and non-cyclic. Types of food web representation Different food webs • Soil food web • Aquatic food web • Food web in forest • Food web of grassland • Food web in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem • These food webs simply indicate a feeding relationship. TOPOLOGICAL WEBS • Bio-energetic webs, or flow webs, include information on the strengthof the feeding interaction. FLOW WEBS • In interactionthe arrows show how one group influences another. INTERACTION WEB
- 5. Significance of food web
- 6. Food webs are important tools in understanding that plants are the foundation of all ecosystems and food chains. Food webs aid in the understanding of natural selection. Food webs are helpful in explaining how disruptions in populations due to over- hunting, poaching, global warming and habitat destruction result in food scarcities leading to extinction Trophic level Definition: The levels of a food chain (food pyramid) is called Trophic levels. The trophic level of an organism is the level it holds in a food pyramid. The sun is thesourceof all the energy in foodchains. Green plants, usually the first level of any food chain, absorb some of the Sun’s light energy to make their own food by photosynthesis. Green plants (autotrophs) are therefore known as ‘Producers’ in a food chain. The second level of the food chains is called the Primary Consumer. These consume the green plants. Animals in this group are usually herbivores. Examples include insects, sheep, caterpillars and even cows. The third in the chain are Secondary Consumers. Theseusually eat up the primary consumers and other animal matter. They are commonly called carnivores and examples include lions, snakes and cats. The fourthlevel is called TertiaryConsumers.Theseareanimals that eat secondary consumers. Quaternary Consumers eat tertiary consumers. At the top of the levels are Predators.
- 7. Predators feed on preys. A prey is an animal that predators hunt to kill and feed on. Predators include owls, snakes, wild cats, crocodiles and sharks. Humans can also be called predators. When any organism dies, detrivores (like vultures, worms and crabs) eat them up. The rest are broken down by decomposers (mostly bacteria and fungi), and the exchange of energy continues. Decomposers start the cycle again. Energy flow The Sun is the principal source of energy input to biological systems. The Earth receives 2 main types of energy from the Sun: light (solar)and heat.
- 8. Photosynthetic plants and some bacteria can trap light energy and convertit into chemical energy. Non-cyclical nature of energy flow Heterotrophic organisms obtain their energy by eating plants or animals that have eaten plants. So all organisms, directly or indirectly, get their energy from the Sun. The energy is passed from one organism to another in a food chain but, unlike water and elements such as carbon and nitrogen, energy does not return in a cycle. Energy give out by organisms is lost to the environment. Energy is lostat each level in the food chain, as in the examples below. Energy lost through the process of respiration (as heat) Energy used up for movement (to search for food, find a mate, escape from predators…). Warm-blood animals (birds and mammals) maintain a standard blood temperature – they lose heat to the environment. Warm-blood animals lose heat energy in faeces and urine. Some of the material in the organism being eaten is not usedby the consumer, for example a locust does not eat the roots of maize, and some of the parts eaten are not digestible. On average, about 90% of the energy is lost at each level in a food chain. This means that in long food chains, very little of the energy entering the chain through the producer is available to the top carnivore. So there tend to be small numbers of top carnivores. The food chain below shows how energy reduces through the chain. It is based on maize obtaining 100 units of energy. maize ---> locust ---> lizard ---> snake 100 units 10 units 1 unit 0.1 unit
- 9. On shorter food chains, less energy is lost.
