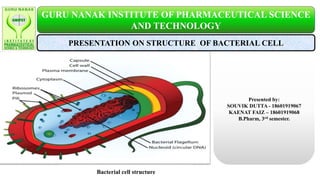
Bacterial cell
- 1. PRESENTATION ON STRUCTURE OF BACTERIAL CELL Presented by: SOUVIK DUTTA - 18601919067 KAENAT FAIZ – 18601919068 B.Pharm, 3rd semester. Bacterial cell structure GURU NANAK INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- 2. • Introduction. • Occurrence and distribution. • Size and shape of bacteria. • Structure of bacteria. • Cell wall. • Capsule and plasma membrane. • Cytoplasm. • Nuclear material. • Plasmid and episome. • Flagella and pili or fimbriae. • Applications of bacteria. • Conclusion. CONTENT
- 3. • Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic organisms. • Their cell wall is rigid and made of peptidoglycan, also called murein or mucopeptide. • Food reserve is in the form of glycogen or fat globules. • An organized nucleus is absent. Instead, a double-stranded DNA lies coiled inside the cytoplasm. It is called nucleoid. • Cell organelles- like mitochondria, chloroplasts, Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex are absent. • Respiratory enzymes are located on the inner surface of cell membrane. • They have various modes of nutrition including photoautotrophic, chemoautotrophic, saprophytic and parasitic types. • Sexual mode of reproduction is completely absent however parasexual mode of reproduction such as transformation, transduction and conjugation does occur. INTRODUCTION
- 4. • Bacteria constitute a highly specialized group of one-celled organisms. They occur everywhere-in soil, in water and in air. • The features which contribute to their universal distribution are: Extremely simple structure. Small size and consequent large surface-to-volume ratio. Resistance of vegetative cells to adverse environmental factors. Formation of highly resistant endospores. Diversity in their mode of nutrition. OCCURRENCE AND DISTRIBUTION
- 5. • Bacteria are the smallest of all known cellular organisms. • The bacillus form are up to10 microns in length an 0.2-1 micron in diameter. • Beggiotoa mirabilis is the largest bacterium. It is 16-45 μ in diameter. • Bacillus butschlii is considered to be the longest bacterium with a length of approximately 80 μm. • Dialister pneumosintes is probably the smallest bacterium known. • Bacteria posses the following shapes: Cocci-They are oval or spherical in shape.eg-Staphylococcus Bacilli- They are rod shaped bacteria with or without flagella.eg- Streptobacillus Spirilla-They are coiled like a cork screw.eg-Spirillum Vibrio-They are motile , comma-like with a flagellum.eg-Vibrio cholerae SIZE AND SHAPE OF BACTERIA
- 6. • Under an electron microscope following structures are involved in a bacterial cell: 1. Cell wall 2. Capsule or mucilage sheath 3. Plasma membrane 4. Cytoplasm 5. Nuclear material 6. Plasmids and Episomes 7. Flagella 8. Pili or Fimbriae STRUCTURE OF BACTERIA Bacterial cell structure
- 7. • The cell wall of bacteria is made up of peptidoglycan, lipids and some inorganic salt. • The peptidoglycan present in the cell wall has two portion- peptide portion and the amino sugar portion. • The peptide portion consists of amino acids like L-alanine, D- alanine, D-glutamic acid,etc. • The amino sugar portion of peptidoglycan consists of- N-acetyl glucosamine(NAG) and N-acetyl muramic acid(NAM) • Th two types of bacteria i.e., Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria differs on the basis of their cell wall component. • Gram negative bacteria has Lipopolysacchharide in their cell wall. 1. CELL WALL
- 8. CAPSULE • It is actually called glycocalyx, which can be of two types- Capsule and Slime layer. • It is composed of polysaccharides and serves as an additional protective layer. • The bacteria with a capsule are called capsulated bacteria. • The capsule provides protection to bacteria cells from phages, toxic chemicals, desiccation, etc. 2.CAPSULE AND PLASMA MEMBRANE PLASMA MEMBRANE • Structurally it is almost like that of eukaryotes but sterols like cholesterol is absent. • Instead a similar type of compound called hopanoids are present which provides membrane stability. • The bacterial cell gets modified or invaginated to form infoldings like Mesosomes-central and peripheral Desmosomes
- 9. • It lacks cyclosis due to the lack of microfilaments. • It contains the following structures or organelles: Ribosome It helps in protein synthesis with the help of m-RNA It is non-membranous cell organelle and mainly exist as polyribosome. Chromatophores- Aggregates of photosynthetic pigment. Inclusion bodies or ergestic substances-It can be of the following types: Reserve food Metachromatic granules Gas vacuole or pseudo vacuole Magnetosome 4.CYTOPLASM
- 10. • The nuclear material is visible as a light-colored region known as nucleoid • It is also known as prochromosome, genophore or incipient nucleus • The nucleoid is not surrounded by any envelope and lack histone protein • The basic polyamines are present which helps in compacting the nucleoid DNA • Nucleoid is actually covalently closed circular double stranded DNA (ccc ds DNA) • Nucleoid possess genes which are important for the survival of a bacterium 5.NUCLEAR MATERIAL Bacterial cell
- 11. • Bacterial cells also contain some extra-chromosomal DNA which are autonomous and self-replicatory called plasmids. • Plasmids replicate independent of the main chromosome. • In some bacteria, plasmids contain important gene-like fertility factors(F factor), resistance factors(R factors), • Plasmid provides some extra benefits to a bacterium • Bacteria can live without a plasmid. • The plasmid which integrate into the main chromosome are called episomes. 6.PLASMID AND EPISOME Fig: Genome and plasmid in a bacterial cell
- 12. FLAGELLA These are fine, thread-like, protoplasmic appendages. • It extends through the cell wall and the slimy layer of the flagellated bacterial cells. • These helps the bacteria to swim about in the liquid medium. • A bacterial flagellum can be divided into three parts: Basal body. Hook and Filament. • It is said to possess the typical 9+2 microtubular organization. 7.FLAGELLA AND PILI OR FIMBRIAE PILI OR FIMBRIAE • Hollow thread-like structure originating from the plasma membrane. • Helps in attachment of bacteria to a surface or epithelial cells. • Sex pili is involved in conjugation process. Fig: Bacterial flagellum
- 13. • Role of bacteria in sewage treatment: The bacteria helps in decomposition of solid matter of sewage into semi-solid sludge. • Methanogenic bacteria are used for the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter of sewage’ • Role of bacteria in medicines: Bacteria are used for the preparation of serums, vaccines, antibiotics and vitamins. • Role of bacteria in Energy production: Biogas are produced but the anaerobic bacteria which are used for lighting of homes and streets. • Bacteria are used for retting of fibres of flax, hemp and jute. • Bacteria are used in fermentation processes for the production of methanol, lactic acid, etc. • Bacteria such as Rhizobium acts as nitrogen fixers for the fixation of atmospheric N2 to NO2, NO3, etc. APPLICATIONS OF BACTERIA
- 14. • So, the structure of different parts and organelles of bacteria widely differs from that of eukaryotic cells. • The structure of bacteria is such that mainly it can withstand the harsh conditions of the environment. • They lack well defined nucleus and also does not have membrane bound organelles. • They mainly perform asexual mode of reproduction like binary fission. • They are widely used in food, pharmaceuticals industries and in agriculture. • They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. • They have rapid growth and reproduction at optimum environmental condition. CONCLUSION
- 15. • Prescott’s microbiology by Mc Graw Hill, Tenth Edition. Page no.-42-79 • NCERT, Head Publication Division by Ashok Srivastava, First Edition. Page no.-127-129 • Srijan biology for ISC School, Class 11 by Veer Bala Rastogi. Page no.- 3.1-3.5 REFERENCE