Capm scenario identifying the critical path answers
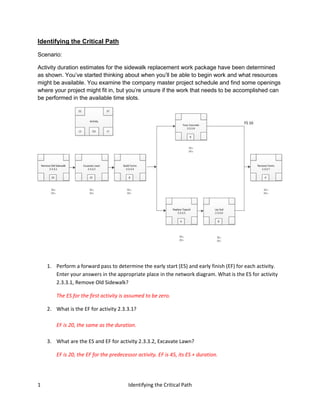
- 1. Identifying the Critical Path Scenario: Activity duration estimates for the sidewalk replacement work package have been determined as shown. You’ve started thinking about when you’ll be able to begin work and what resources might be available. You examine the company master project schedule and find some openings where your project might fit in, but you’re unsure if the work that needs to be accomplished can be performed in the available time slots. 1. Perform a forward pass to determine the early start (ES) and early finish (EF) for each activity. Enter your answers in the appropriate place in the network diagram. What is the ES for activity 2.3.3.1, Remove Old Sidewalk? The ES for the first activity is assumed to be zero. 2. What is the EF for activity 2.3.3.1? EF is 20, the same as the duration. 3. What are the ES and EF for activity 2.3.3.2, Excavate Lawn? EF is 20, the EF for the predecessor activity. EF is 45, its ES + duration. 1 Identifying the Critical Path
- 2. 4. Calculate the ES and EF for the remaining activities. Why is the ES for activity 2.3.3.5 the same as the ES for activity 2.3.3.4? They both have the same predecessor activity (2.3.3.3). 5. How do you calculate the ES for the last activity, 2.3.3.7? The ES for the last activity is calculated by taking the EF from 2.3.3.4 and adding the 16-hour finish-to-start lag for the concrete to cure. 6. What does your network diagram look like with a forward pass? 7. Perform a backward pass to determine the late start (LS) and late finish (LF) for each activity. Enter your answers in the appropriate place in the network diagram. What is the LF for activity 2.3.3.7, Remove Forms? The LF for the last activity is the same as its EF, which is 81. 8. Why is the LF for activity 2.2.3.4, Pour Concrete, the same as its EF? The activity is on the critical path. 9. Why is the LF for activity 2.3.3.6, Lay Sod, higher than the LS for activity 2.3.3.4, Pour Concrete? There is a 16-hour lag between the finish activity 2.3.3.4, Pour Concrete, and the start of actifity 2.3.3.7, Remove Forms. 2 Identifying the Critical Path
- 3. 10. What does your completed diagram look like with a backward pass? 11. Determine the float for this network. Which activities have total float in this network? How much float do they have? Activities 2.3.3.5 and 2.3.3.6 are the only activities with total float because they are not on the critical path. Each has a total float of 10 hours (LF-EF or LS-ES). 12. Does that mean that those activities can each flex their start or finish time by the total float hours? No. The 10 hours of total float are shared by the two activities. If activity 2.3.3.5 is delayed for eight hours, there will only be two hours of float left for activity 2.3.3.6. 13. Which activities have free float? Only activity 2.3.3.6, Lay Sod, has free float, because it’s the only activity that can safely be delayed without delaying the ES of the subsequent activity, which is on the critical path. 14. How much free float does that activity have? Activity 2.3.3.6 has 10 hours of free float, which is the same as its total float. However, activity 2.3.3.5 does not have free float. The activity shares the 10 hours of total float with activity 2.3.3.6. 3 Identifying the Critical Path
- 4. 15. What would happen to the free float of that activity if its concurrent activity used up the hours of total float? It would go to zero, so activity 2.3.3.6 would no longer have any float. 16. What is the critical path? There are two possible paths through the activities. The total duration nodes 2.3.3.1 + 2.3.3.2 + 2.3.3.3 + 2.3.3.5 + 2.3.3.6 + 2.3.3.7 = 71. The total duration for nodes 2.3.3.1 + 2.3.3.2 + 2.3.3.3 + 2.3.3.4 + 2.3.3.7 = 81 counting the 16-hour lag for the concrete curing, so that is the critical path. 17. What will happen to the total time if it takes 12 hours to pour the concrete? Activity 2.3.3.4, Pour Concrete, has an estimated duration of eight hours and is on the critical path. So if the actual duration of that activity increases by four hours, the total time will also increase by four hours. 18. What will happen to the total time if it takes 10 hours to lay the sod? Activity 2.3.3.6, Lay Sod, is not on the critical path. So if the actual duration of that activity increases by two hours, the total time will not be affected. 19. What will happen to the total time if it takes 20 hours to lay the sod? The critical path will change, and total time will increase to 83 hours. 4 Identifying the Critical Path
