Modeling static loads in gtstrudl
•
3 recomendaciones•2,270 vistas
How to work with Static Loads in GTSTRUDL
Denunciar
Compartir
Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Recomendados
Sandia 2014 Wind Turbine Blade Workshop- LothSandia 2014 Wind Turbine Blade Workshop- Loth

Sandia 2014 Wind Turbine Blade Workshop- LothSandia National Laboratories: Energy & Climate: Renewables
Más contenido relacionado
Similar a Modeling static loads in gtstrudl
Sandia 2014 Wind Turbine Blade Workshop- LothSandia 2014 Wind Turbine Blade Workshop- Loth

Sandia 2014 Wind Turbine Blade Workshop- LothSandia National Laboratories: Energy & Climate: Renewables
Similar a Modeling static loads in gtstrudl (18)
Aircraft wing design and strength, stiffness and stability analysis by using...

Aircraft wing design and strength, stiffness and stability analysis by using...
The use of Fuse Connectors in Cold-Formed Steel Drive-In Racks, Thesis Presen...

The use of Fuse Connectors in Cold-Formed Steel Drive-In Racks, Thesis Presen...
CFD Analysis for Computing Drag force on Various types of blades for Vertical...

CFD Analysis for Computing Drag force on Various types of blades for Vertical...
Explanatory Examples on Ductile Detailing of RC Buildings.pdf

Explanatory Examples on Ductile Detailing of RC Buildings.pdf
19910001020 comparison of nastran analysis with gvt results of uh-60 a

19910001020 comparison of nastran analysis with gvt results of uh-60 a
prioritising the load considering economy of parallel transformer

prioritising the load considering economy of parallel transformer
Último
Último (20)
Connector Corner: Accelerate revenue generation using UiPath API-centric busi...

Connector Corner: Accelerate revenue generation using UiPath API-centric busi...
Apidays New York 2024 - The Good, the Bad and the Governed by David O'Neill, ...

Apidays New York 2024 - The Good, the Bad and the Governed by David O'Neill, ...
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
Apidays Singapore 2024 - Building Digital Trust in a Digital Economy by Veron...

Apidays Singapore 2024 - Building Digital Trust in a Digital Economy by Veron...
Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher

Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher
"I see eyes in my soup": How Delivery Hero implemented the safety system for ...

"I see eyes in my soup": How Delivery Hero implemented the safety system for ...
Strategies for Unlocking Knowledge Management in Microsoft 365 in the Copilot...

Strategies for Unlocking Knowledge Management in Microsoft 365 in the Copilot...
Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME

Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME
Strategize a Smooth Tenant-to-tenant Migration and Copilot Takeoff

Strategize a Smooth Tenant-to-tenant Migration and Copilot Takeoff
Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...

Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...
Apidays New York 2024 - The value of a flexible API Management solution for O...

Apidays New York 2024 - The value of a flexible API Management solution for O...
Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)

Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)
Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business

Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business
Axa Assurance Maroc - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Axa Assurance Maroc - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Modeling static loads in gtstrudl
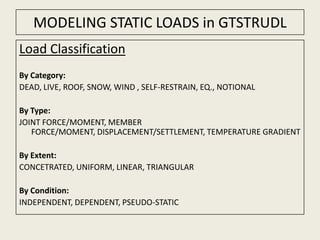
- 1. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Load Classification By Category: DEAD, LIVE, ROOF, SNOW, WIND , SELF-RESTRAIN, EQ., NOTIONAL By Type: JOINT FORCE/MOMENT, MEMBER FORCE/MOMENT, DISPLACEMENT/SETTLEMENT, TEMPERATURE GRADIENT By Extent: CONCETRATED, UNIFORM, LINEAR, TRIANGULAR By Condition: INDEPENDENT, DEPENDENT, PSEUDO-STATIC
- 2. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Classes of Static Loadings (Table 9.1-2, Analysis Guide)
- 3. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Independent Static Loadings DEAD LOADING Command (Section 9.4.2, Analysis Guide) DEAD LOAD ‘DL’ ‘DEAD’ DIRECTION –Y MEMBERS 1 TO 5 Need to be deleted and redefined if members properties change
- 4. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Independent Static Loadings SELF WEIGHT LOADING Command (Section 9.4.1.1, Analysis Guide) SELF WEIGHT LOAD ‘SW’ ‘SELF WEIGHT’ DIRECTION –Y ALL MEMBERS Computed during the Stiffness Analysis process. For immediate computation use
- 5. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Independent Static Loadings LOADING Command (Section 9.3, Analysis Guide) LOADING 1 ‘MACHINE LOADS’ Creates a new Independent Static Loading Condition, which will contain a set of Applied Static Loading Types Use CHANGES mode to Add, Modify, or to Delete Applied Static Loading Types. Use DELETIONS mode to remove an entire Static Loading Condition
- 6. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Applied Static Loading Types JOINT LOADS Command (Section 9.5, Analysis Guide) JOINT LOADS 1 TO 11 BY 2 FORCE Y 5.3 Z -9.1 250 ‘ABC’ ‘JT-13’ FORCE Z 19.8 MOMENT X 10.0 To add, or modify use the CHANGES mode of the LOADING Command.
- 7. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Applied Static Loading Types JOINT DISPLACEMENTS Command (Section 9.6, Analysis Guide) JOINT DISPLACEMENTS 1 5 7 19 DISPLACEMENT Y -1.5 250 ‘ABC’ ‘JT-13’ DISPL X 1.4 Y -0.5 ROTZ 3.5 To add, or modify use the CHANGES mode of the LOADING Command.
- 8. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Applied Static Loading Types MEMBER LOADS Command (Section 9.7, Analysis Guide) MEMBER LOADS 10 TO 20 MOMENT Z CONC FR M -25 L 0.3 1 TO 5 FORCE X GLOBAL UNIFORM FR W -1.2 / W -2.0 LA 0.0 LB 0.5 5 TO 9 FORCE Y LINEAR WA -1.0 WB -0.5 LA 0.2 LB 3.5
- 9. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Applied Static Loading Types MEMBER TEMPERATURE LOAD Command (Section 9.8, Analysis Guide) MEMBER TEMPERATURE LOADS 10 TO 20 AXIAL 30 1 TO 5 AXIAL 20 BENDING Z 20
- 10. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Applied Static Loading Types MEMBER DISTORTIONS Command (Section 9.9, Analysis Guide) MEMBER DISTORTIONS ‘B1’ ‘B2’ CONCENTRATED FR L 1.0 DISPLACEMENT X -1.5
- 11. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Other Independent Static Loadings AREA LOAD Command (Section 9.15, Analysis Guide) AREA LOAD 2 ‘TRIB A’ DIRECTION Y ELEVATION 12.0 LIMITS X 0.0 30.0 Z 0.0 60.0 EXCEPT LIMITS X 10.0 20.0 – Z 15.0 25.0 VALUE 10.0 TWO WAY END AREA LOAD
- 12. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Other Independent Static Loadings FORM LOAD Command (Section 10.1, Analysis Guide) FORM LOAD ‘DESIGN1’ ‘DESIGN LOAD 1’ FROM ‘DL’ 1.4 ‘LL’ 1.6 Needed for Non-Linear analysis May affect computation time for linear analysis Applied Static Loading Types can be added using the CHANGES mode. May be recomputed using
- 13. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Other Independent Static Loadings FORM NOTIONAL LOAD Command (Section 10.1.3, Analysis Guide) FORM NOTIONAL LOAD ‘NX_LL’ ‘HORIZONTAL NOTIONAL LOADS’ – FROM ‘LL’ 1.0 GRAVITY AXIS Y NLDIRECTION X NLFACTOR 0.002 – JOINTS EXISTING AISC 13 Requirement Does not get updated after updating Self Weight loads
- 14. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Dependent Static Loadings LOADING COMBINATION Command (Section 10.2.1, Analysis Guide) LOADING COMBINATION 200 ‘DESIGN LOAD 200’ – SPECIFICATIONS ‘LL’ 1.6 ‘DL’ 1.4 ‘WIND’ -1.0 Results updated right after Stiffness Analysis. Use COMBINE Command to compute results if the loading combination is created after the Stiffness Analysis has been performed. (Section 10.2.3, Analysis Guide)
- 15. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Dependent Static Loadings CREATE LOADING COMBINATION Command (Section 10.2.2, Analysis Guide) CREATE LOADING COMBINATION 200 ‘DESIGN LOAD 200’ ABSOLUTE – SPECIFICATIONS ‘LL’ 1.6 ‘DL’ 1.4 ‘WIND’ -1.0 Cannot be used before Stiffness Analysis has been performed. All of the Loadings used in the Specification must have computed results.
- 16. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Using the Shell
- 17. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Using the Shell
- 18. MODELING STATIC LOADS in GTSTRUDL Using GTMenu