Biosci 1
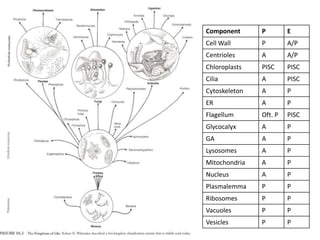
- 1. Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Component P E Cell Wall P A/P Centrioles A A/P Chloroplasts PISC PISC Cilia A PISC Cytoskeleton A P ER A P Flagellum Oft. P PISC Glycocalyx A P GA A P Lysosomes A P Mitochondria A P Nucleus A P Plasmalemma P P Ribosomes P P Vacuoles P P Vesicles P P
- 2. Endosymbiont Hypothesis - Proposed by Lynn Margulis from Boston University AUTOTROPHIC HETEROTROPHIC EUKARYOTES EUKARYOTES
- 5. SYMBIOTIC THEORY The first multicellular organisms occurred from symbiosis of different species of single-celled organisms, each with different roles.
- 6. CELLULARIZATION OR SYNCYTIAL THEORY A single unicellular organism could have developed internal membrane partitions around each of its nuclei.
- 7. COLONIAL THEORY (proposed by Haeckel in 1874) Symbiosis of many organisms of the same species led to multicellular organism.
- 8. PARAZOANS (no true tissues) – sponges/porifers PHYLUM PORIFERA (L. porus, pore + fera, to bear)
- 9. CHARACTERISTICS OF PHYLUM PORIFERA 1. Assymetrical or radially symmetrical
- 10. Verongia
- 11. Verongia
- 12. Adocia
- 13. CHARACTERISTICS OF PHYLUM PORIFERA 1. Assymetrical or radially symmetrical 2. Presence of the cell types: pinacocytes, mesenchyme cells, and choanocytes
- 14. THREE CELL TYPES a. PINACOCYTES – flat cells that line the outer surface of a sponge POROCYTES – specialized pinacocytes that form contractile tubes responsible for the regulation of water circulation in the organism b. CHOANOCYTES or COLLAR CELLS – flagellated cells that have collarlike ring of microvilli surrounding a flagellum Functions 1. Creation of water currents by flagellar movement 2. Filtration of microscopic food particles from the water 3. has reproductive function in that choanocytes have the ability to form sperm and egg cells c. MESENCHYME CELLS – found in the mesohyl (between the pinacocyte and the choanocyte layers. Mesenchyme cells include amoeboid cells that are specialized for reproduction, secreting skeletal elements, transporting food, storing food, and forming contractile rings around openings in the sponge wall.
- 16. CHARACTERISTICS OF PHYLUM PORIFERA 1. Assymetrical or radially symmetrical 2. Presence of the cell types: pinacocytes, mesenchyme cells, and choanocytes 3. Central cavity, or series of branching chambers, through which water is circulated during filter feeding
- 22. CHARACTERISTICS OF PHYLUM PORIFERA 1. Assymetrical or radially symmetrical 2. Presence of the cell types: pinacocytes, mesenchyme cells, and choanocytes 3. Central cavity, or series of branching chambers, through which water is circulated during filter feeding 4. No tissues or organs (parazoans)
- 23. PHYLUM CNIDARIA Characteristics: 1. Individuals are either solitary or colonies 2. Of two basic body types a. polyp or hydranth – with a tubular body having one end closed and attached and the other with central mouth usually surrounded by soft tentacles b. medusa – free swimming adult with gelatinous body of umbrella shape, margined with tentacles, and having the mouth on a central projection of the concave surface
- 24. Cyanea arctica Having tentacles up t0 33 feet long
- 25. Sea anemones range from a few millimeters to 1 meter in diameter
- 28. PHYLUM CNIDARIA Characteristics: 3. Symmetry radial or biradial about an oral-aboral axis; no head or segmentation 4. Body of two layers of cells, an external epidermis and an inner gastrodermis, with varying amount of mesoglea in between 5. Cnidarians are characterized with the presence of nematocysts (stinging capsules); nematocysts are found either in both layers. 6. All are aquatic and nearly all are marine
- 30. Chlorohydra viridissima Has symbiotic zoochlorellae in its inner cells Hydra oligactis Has slender stalks and long tentacles
- 31. EPITHELIOMUSCULAR CELLS – cells having a bulbous outer portion and an elongate base containing a contractile fibril placed against the mesoglea. These cells are responsible for the shortening or contraction of hydra principally during movement. GLAND CELLS – tall cells that secrete a sticky mucus by which hydras attach to objects in the water. These cells can also produce gas bubble. INTERSTITIAL CELLS - - small, round and undifferentiated cells with large nuclei, found between the bases of epidermal cells. They have the potential to produce all other cell types. Such as cnidocytes and gametes. CNIDOCYTIC CELLS – specialized cells that contain the unique cnidarian stinging apparatus, the nematocyst.
- 32. NEMATOCYSTS are used for defense, locomotion or food capture. a. Abundant in the tentacles, some occur throughout the epidermis, except on basal disk
- 33. Obelia
- 35. Tubularia
- 39. 00863f28 Pelagia
- 41. Chironex fleckeri or Order Cubomedusae
- 46. Aurelia strobila Strobilation – type of transverse fission that involves horizontal constrictions from around the body and deepen so that the organism resembles a pile of minute saucers with fluted borders, the edge of each being formed into eight double lobes.
- 47. Strobilating polyp and ephyra
- 49. Metridium
- 53. Ephiactis
- 54. Boloceroides
- 55. Cerianthus
