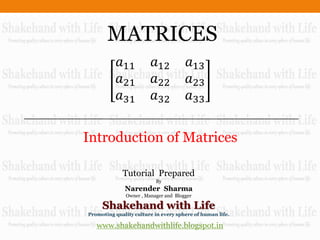
Introduction of matrices
- 1. MATRICES 𝑎11 𝑎12 𝑎13 𝑎21 𝑎22 𝑎23 𝑎31 𝑎32 𝑎33 Introduction of Matrices Tutorial Prepared By Narender Sharma Owner , Manager and Blogger Shakehand with Life Promoting quality culture in every sphere of human life. www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 2. Index Matrices 2 S. No. Topic Page No. 1 Definition of Matrices 3-4 2 Notation of Matrices 5 3 Order of Matrices 6 4 Types of Matrices 7-11 5 Trace of Matrices 12 6 Equality of Two Matrices 13 7 MCQ‟s for Exercise 14-15 8 Answer Key 16 www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 3. Definition of Matrix Matrices 3 A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. In other words, a set of „m‟, „n‟ numbers arranged in the form of rectangular array of m rows and n column is called m×n matrix read as „m‟ by „n‟ matrix. Horizontal lines a11 a12 a13 … … … . . A = a21 a22 a23 … … … . . m×n Vertical a31 a32 a33 … … … . . lines We can understand matrix by the fig. shown above, which shows a mess of vertical and horizontal lines. The crossing points of vertical and horizontal lines are the position of elements of matrix. In above fig there are 9 crossing points which can be find out by multiplying no. of horizontal and vertical lines i.e. 3 × 3 = 9. www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 4. Matrices 4 The numbers a11, a12 ……..etc are called elements of the matrix A. „m‟ is the numbers of rows and „n‟ is number of column. 2 3 4 e.g. A= 5 4 6 3×3 2 4 3 www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 5. Notation of Matrices Matrices 5 • Matrices are denoted by capital letters A, B, C or X , Y , Z etc. • Its elements are denoted by small letters a, b, c ….. etc. • The elements of the matrix are enclosed by any of the brackets i.e. , , . • The position of the elements of a Matrix is indicated by the subscripts attached to the element. e.g. 𝑎13 indicates that element „a‟ lies in first row and third column i.e. first subscript denotes row and second subscript denote column. Element Indicate Row 𝑎1 3 Indicate Column www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 6. Order of Matrices Matrices 6 • The number of rows and columns of a matrix determines the order of the matrix. • Hence , a matrix , having m rows and n columns is said to be of the order m × n ( read as „m‟ by „n‟). • In particular, a matrix having 3 rows and 4 columns is of the order 3 × 4 and it is called a 3 × 4 matrix e.g. 2 3 5 A= is a matrix of order 2 × 3 since there are two rows and three 4 6 7 columns. A = 3 5 7 is a matrix of order 1 × 3 since there are one row and three columns. 5 A = 6 is a matrix of order 3 × 1 since there are three rows and one 8 column. www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 7. Types of Matrices Matrices 7 Rectangular Square Diagonal Scalar Matrix Matrix Matrix Matrix Column Row Null Unit Matrix Matrix Matrix Matrix Upper Lower Triangular Triangular Sub Matrix Matrix Matrix www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 8. Matrices 8 Rectangular Matrix : A matrix in which the number of rows and columns are not equal is called a rectangular matrix e.g. , 2 4 5 A= 2 × 3 is rectangular matrix of order 2×3 4 6 7 Square Matrix : A matrix in which the number of rows is equal to the number of columns is called a square matrix e.g. Principal Diagonal 2 3 4 𝐴= 3 2 5 7 8 5 Note : The elements 2, 2 , 5 in the above matrix are called diagonal elements and the line along which they lie is called the principal diagonal www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 9. Matrices 9 Diagonal Matrix : A square matrix in which all diagonal elements are non- zero and all non-diagonal elements are zeros is called a diagonal matrix e.g. 2 0 0 𝐴= 0 2 0 is a diagonal matrix of 3 × 3 0 0 5 Scalar Matrix : A diagonal matrix in which diagonal elements are equal (but not equal to 1), is called a scalar matrix e.g. 2 0 0 𝐴= 0 2 0 is a scalar matrix of 3 × 3 0 0 2 Identity (or Unit) Matrix : A square matrix whose each diagonal element is unity and all other elements are zero is called and Identity (or Unit) Matrix. An Identity matrix of order 3 is denoted by I3 or simply by I. www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 10. Matrices 10 e.g. 1 0 0 I3 = 0 1 0 is a unit matrix of order 3 0 0 1 Null (Zero) Matrix : A matrix of any order (rectangular or square) whose each of its element is zero is called a null matrix (or a Zero matrix) and is denoted by O. e.g. 0 0 0 0 0 O= and O = are null matrices of order 2 × 2 and 2 × 3 0 0 0 0 0 respectively. Row Matrix : A matrix having only one row and any number of columns is called a row matrix (or a row vector) e.g. 𝐴= 1 2 3 is a row matrix of order 1 × 3 www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 11. Matrices 11 Column Matrix : A matrix having only one column and any number of rows is called a column matrix (or a column vector) e.g. 1 A = 3 is a column matrix or order 3 × 1 6 Upper Triangular and Lower Triangular Matrix: A square matrix is called an upper triangular matrix if all the elements below the principal diagonal are zero and it is said to be lower triangular matrix if all the elements above the principal diagonal are zero e.g. UTM 2 3 4 LTM 5 0 0 𝐴= 0 1 5 , 𝐵= 8 7 0 0 0 7 4 3 1 Sub Matrix : A matrix obtained by deleting some rows or column or both of a given matrix is called its sub matrix. e.g. 2 3 4 2 3 𝐴 = 5 1 5 , Now is a sub matrix of given matrix A. The sub 3 9 3 9 7 matrix obtained by deleting 2nd row and 3rd column of matrix A. www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 12. Trace of Matrix Matrices 12 The sum of all the elements on the principal diagonal of a square matrix is called the trace of the matrix. It is denoted by tr. A . a11 a12 a13 If A= a21 a22 a23 then a31 a32 a33 trace of A = tr.A = 𝑎11 + 𝑎22 + 𝑎33 2 3 4 e.g. A = 5 1 5 , then 3 9 7 trace of A = tr. A =2+1+7=10 www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 13. Equality of Two Matrices Matrices 13 Two matrices „A‟ and „B‟ are said to be equal if only if they are of the same order and each element of „A‟ is equal to the corresponding element of „B‟. Given a11 a12 a13…….. b11 b12 b13……… A = a21 a22 a23…….. m×n and B = b21 b22 b23……… x×y a31 a32 a33…….. b31 b32 b33……… The above two matrices will be equal if and only if No. of rows and column of A and B are equal i.e. m=x and n=y. Each element of A is equal to the corresponding element of B i.e. a11 =b11 , a12 = b12 , a13 = b13 ……… and so on 𝑎 𝑏 3 4 Let 𝐴 = and 𝐵 = , according to the condition of equality of 𝑐 𝑑 5 6 matrices both matrices have same order i.e. 2 × 2 but the 2nd necessary condition is a=3, b=4, c=5 , d= 6 www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 14. MCQ’s for Excercise Matrices 14 1. If in a given matrix the rows are 2 and the column are 3 then maximum no. of elements in this matrix are A) 4 B) 6 C) 8 D) 10 2. Element a32 is belongs to which row and column in a given matrix A A) 2nd row, 3rd column B) 3rd row , 2nd column C) can’t decide D) None of the above 2 4 5 5 7 3. What is the order of given matrix 7 5 7 8 1 9 0 3 2 4 A) 3 × 5 B) 5 × 3 C) 3 × 3 D) 5 × 5 4. A matrix which do not have equal no. of rows and columns called A) Square Matrix B) Triangular Matrix C) Scalar Matrix D) Rectangular Matrix 5. A matrix in which the rows and columns are equal in no. is called A) Square Matrix B) Triangular Matrix C) Scalar Matrix D) Rectangular Matrix 6. In a Diagonal matrix all the elements on the principal diagonal can’t be equal to A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 15. Matrices 15 7. In a scalar matrix all the diagonal elements are A) Equal to one B) Equal but greater than one C) Not equal D) None of the above 8. In a Unit matrix A) All element are zero B) All elements are one C) Diagonal elements zero rest are one D) Diagonal elements are one rest are zero 9. In a given matrix all elements below principal diagonal are zero , the matrix is A) Upper triangular matrix B) Lower triangular matrix C) Diagonal Matrix D) Scalar Matrix 10. In a given matrix all elements above principal diagonal are zero , the matrix is A) Upper triangular matrix B) Lower triangular matrix C) Diagonal Matrix D) Scalar Matrix a11 a12 a13 11. Given A = a21 a22 a23 then tr. A will be a31 a32 a33 A) 𝑎11 + 𝑎12 + 𝑎13 B) 𝑎11 + 𝑎22 + 𝑎33 C) 𝑎31 + 𝑎22 + 𝑎13 D) 𝑎21 + 𝑎22 + 𝑎23 12. Which one is true about the necessary condition for equality of two matrices A) Order of two matrices are same B) Corresponding elements of the two matrices are same C) Both A and B D) None of the above www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
- 16. Answer Key Matrices 16 S.No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Ans. B B A D A A S.No. 7 8 9 10 11 12 Ans. B D A B B C To get free copy of this tutorial E mail: shakehandwithlife@gmail.com Mention your name, place , profession with Subject : “Tutorial - Introduction of Matrices” For more E- Tutorial , Notes , Books, previous solved papers, Educational and motivational articles , and related documents Visit : www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in Like us on Facebook Page : Shakehand with Life www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.in
