Lista de programas
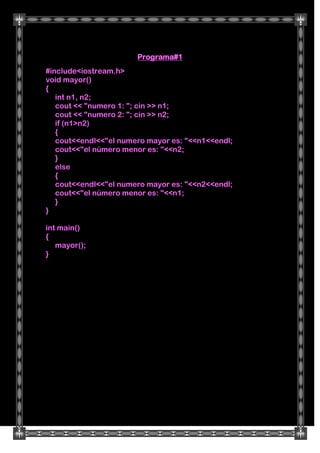
- 1. Programa#1<br />#include<iostream.h>void mayor(){ int n1, n2; cout << quot; numero 1: quot; ; cin >> n1; cout << quot; numero 2: quot; ; cin >> n2; if (n1>n2) { cout<<endl<<quot; el numero mayor es: quot; <<n1<<endl; cout<<quot; el número menor es: quot; <<n2; } else { cout<<endl<<quot; el numero mayor es: quot; <<n2<<endl; cout<<quot; el número menor es: quot; <<n1; }}int main(){ mayor();} <br />Programa#2<br />#include<iostream.h>void mayor(int n1, int n2){ if (n1>n2) { cout<<endl<<quot; el numero mayor es: quot; <<n1<<endl; cout<<quot; el numero menor es: quot; <<n2; } else { cout<<endl<<quot; el numero mayor es: quot; <<n2<<endl; cout<<quot; el numero menor es: quot; <<n1; }}int main(){ int n1, n2; cout << quot; numero 1: quot; ; cin >> n1; cout << quot; numero 2: quot; ; cin >> n2; mayor(n1, n2);}<br />Programa#3<br />#include<iostream.h>int mayor (){ int n1, n2,r; cout << quot; numero 1: quot; ; cin >> n1; cout << quot; numero 2: quot; ; cin >> n2; if (n1>n2) { r=n1; } else { r=n2; } return r;}int main(){ int r; r=mayor(); cout<<endl<<quot; el numero mayor es: quot; <<r;}<br />Programa#4<br />#include<iostream.h>int mayor(int n1, int n2){ int r; if (n1>n2) { r=n1; } else { r=n2; } return r;}int menor(int n1, int n2){ int m; if (n1<n2) { m=n1; } else { m=n2; } return m;}int main(){ int n1, n2, r,m; cout << quot; numero 1: quot; ; cin >> n1; cout << quot; numero 2: quot; ; cin >> n2; r = mayor(n1, n2); m=menor(n1,n2); cout <<endl<< quot; el numero mayor es: quot; << r<<endl; cout << quot; el número menor es: quot; << m;}<br />En la forma adicional quedaría de la siguiente manera<br />#include<iostream.h>int mayor(int n1, int n2){ int r; if (n1>n2) { r=n1; } else { r=n2; } return r;}int menor(int n1, int n2){ int m; if (n1<n2) { m=n1; } else { m=n2; } return m;}int main(){ int n1, n2; cout << quot; numero 1: quot; ; cin >> n1; cout << quot; numero 2: quot; ; cin>> n2; cout <<endl<< quot; el numero mayor es quot; << mayor(n1, n2)<<endl; cout << quot; el numero menor es quot; << menor(n1, n2);} <br />