Apache Solr es un servidor de búsqueda full-text basado en Apache Lucene, que permite implementar sistemas de búsqueda, repositorios digitales y recomendaciones. El documento ofrece una guía sobre la instalación, configuración y mantenimiento de Apache Solr, incluyendo detalles sobre componentes, estructuras de directores y formatos de indexación. También se aborda la personalización del análisis de consultas y los métodos de indexación de datos.





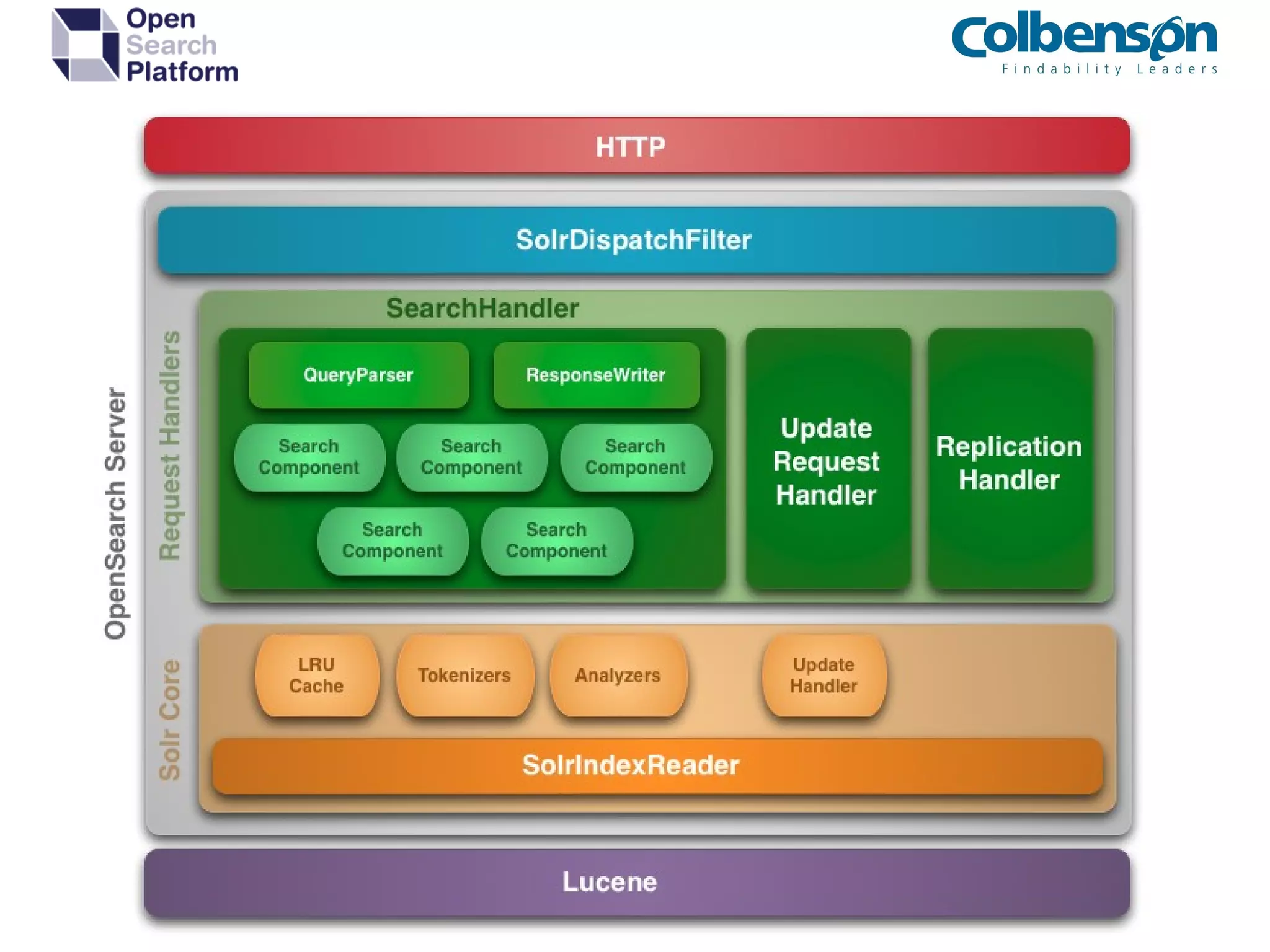

















![Consultando el índice: avanzada Selección del RequestHandler qt : http://host:8983/opensearch/select?q=Pilar%20rojo&start=0&rows=10& qt=dismax Path : http://host:8983/opensearch /dismax ?q=Pilar%20rojo&start=0&rows=10 Utilización de sintáxis de consulta avanzada phrase slopping : “jakarta apache”~10 fuzzy queries : sony~0.9 wildcarding : c?sa OR casa* range queries : ["" to *] term boosting : apache^3 Utilización de SearchComponents Faceting : Búsqueda paramétrica (folding de Amazon, eBay, etc) Highlight : Resaltado de los términos que concuerdan de la búsqueda Spellcheck : Sugerencias de búsqueda con corrección ortográfica MoreLikeThis : Documentos relacionados a partir de uno que actúa de patrón.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formacionglobaliza-110916020539-phpapp02/75/Curso-Formacion-Apache-Solr-25-2048.jpg)