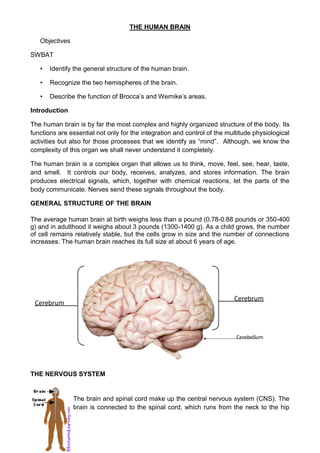
The human brain
- 1. THE HUMAN BRAIN<br />Objectives <br />SWBAT<br />Identify the general structure of the human brain.<br />Recognize the two hemispheres of the brain.<br />Describe the function of Brocca’s and Wernike’s areas. <br />Introduction<br />The human brain is by far the most complex and highly organized structure of the body. Its functions are essential not only for the integration and control of the multitude physiological activities but also for those processes that we identify as “mind”. Although, we know the complexity of this organ we shall never understand it completely. <br />The human brain is a complex organ that allows us to think, move, feel, see, hear, taste, and smell. It controls our body, receives, analyzes, and stores information. The brain produces electrical signals, which, together with chemical reactions, let the parts of the body communicate. Nerves send these signals throughout the body. <br />GENERAL STRUCTURE OF THE BRAIN<br />The average human brain at birth weighs less than a pound (0.78-0.88 pounds or 350-400 g) and in adulthood it weighs about 3 pounds (1300-1400 g). As a child grows, the number of cell remains relatively stable, but the cells grow in size and the number of connections increases. The human brain reaches its full size at about 6 years of age.<br />CerebrumCerebrumCerebellum<br />THE NERVOUS SYSTEM <br />left0The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS). The brain is connected to the spinal cord, which runs from the neck to the hip area. The spinal cord carries nerve messages between the brain and the body.<br />The brain and spinal cord are made up of many cells, including the neurons. Neurons are cells that send and receive electro-chemical signals to and from the brain and nervous system. There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain. <br />The neuron <br />442722015240The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with ranching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conducts the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals transmit the electro-chemical signal across a synapse (the gap between the axon terminal and the receiving cell). <br />Unlike most other cells, once neurons are damaged they cannot regenerate. <br />2976880179070Structure of the brain<br />The brain has three main parts, the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The brain is divided into regions that control specific functions.<br />Moreover, the brain is divided into two hemispheres. The cerebral hemispheres are connected to each other by the corpus callosum. <br />There are four regions: frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe.<br />The Cerebrum is the largest division of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, each of which is divided into four lobes. <br />Longitudinal FissureLeft hemisphere Right hemisphere <br />FOUR LOBES<br />The frontal lobe<br />Broca’s Area – Controls facial neurons, speech, and language comprehension. Located on Left Frontal Lobe. Broca’s Aphasia – Results in the ability to comprehend speech, but the decreased motor ability (or inability) to speak and form words.<br />It is located deep to the Frontal Bone of the skull. It plays an integral role in the following functions/actions:<br />- Memory Formation; Emotions; Decision Making/Reasoning; and Personality<br />Broca’s Area – Controls facial neurons, speech, and language comprehension. Located on Left Frontal Lobe.<br /> Broca’s Aphasia – Results in the ability to comprehend speech, but the decreased motor ability (or inability) to speak and form words.<br />The parietal lobe<br />It plays a major role in the following functions/actions:<br />- Senses and integrated sensation(s); Spatial awareness and perception<br />3. Occipital lobe<br />Its primary function is the: processing, integration, and interpretation of vision and visual stimuli. <br />4. Temporal lobe<br />It plays an integral role in the following functions:<br />Hearing<br />Organization/Comprehension of language<br />Information Retrieval (Memory and Memory Formation)<br />Wernicke’s Area – Language comprehension. Located on the Left Temporal Lobe.<br />- Wernicke’s Aphasia – Language comprehension is inhibited. Words and sentences are not clearly understood, and sentence formation may be inhibited.<br />- Arcuate Fasciculus - A white matter tract that connects Broca’s Area and Wernicke’s Area through the Temporal, Parietal and Frontal Lobes. Allows for coordinated, comprehensible speech. Damage may result in:<br />- Conduction Aphasia - Where auditory comprehension and speech articulation are preserved, but people find it difficult to repeat heard speech.<br /> Wernicke’s Area – Language comprehension. Located on the Left Temporal Lobe.<br />THE HEMISPHERES OF THE BRAIN<br />The brain is divided into two hemispheres that are roughly mirror images of each other. For instance each of the four lobes is present in both hemispheres. Both of them are connected by a band of nerves called the CORPUS CALLOSUM which carries messages back and forth between the two. <br />Each hemisphere is connected to half of the body in a criss-crossed way. That’s to say that the motor cortex of the left hemisphere of the brain controls most of the right side of the body; while the right hemisphere motor cortex controls most of the left side.<br />Thus (in this way), a stroke which damages the right hemisphere will result in numbness and paralysis on the left side of the body.<br />In general, the left and right hemispheres of the brain process information in different ways. We tend to process information using our dominant side. However, the learning and thinking process is improved when both sides of the brain participate in a balanced manner. This means strengthening your less dominant hemisphere of the brain. <br />Left and right hemisphere<br />740410170180Optimistic halfPositive emotions- controlPessimistic halfEmotional perceptions <br />NEUROFUNCTIONAL THEORY (LAMENDELLA) <br />Lamendella defines the scope of a neurofunctional approach as follows: <br />“A neurofunctional perspective on language attempts to characterize the neurolinguistic information processing systems responsible for the development and use of language”.<br />This author points out that those who study SLA based on this theory, tend to point out the importance of the brains in the acquisition and development of the language.<br />According to Hatch, there is no single “black box” for language in the brain. By this he means that it is not possible to identify precisely which areas of the brain are associated with language functioning. <br />Therefore, it is better to speak of the “relative contribution of some areas more than others under certain conditions” according to Seliger.<br />Neurofunctional accounts of SLA have considered the contribution of two areas of the brain: the right hemisphere and the areas of the left hemisphere (in particular those known as Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas which closely associated with the comprehension and production of language).<br />Right hemisphere functioning <br />Associated with right hemisphere functioning is the holistic processing and according to Krashen, this hemisphere is responsible for the storing and processing of formulaic speech. Patters and routines constitute formulaic speech are unanalyzed wholes and as such belong to the gestalt (wholes) perception of the right hemisphere. <br />It has also been suggested that right hemisphere involvement in L2 processing will be more evident in the early non-proficient stages than in later, more advances stages of SLA. (Young learners)<br />Selinger has also suggested that the right hemisphere may also be involved in pattern practice in classroom SLA and he argues that this hemisphere may act as an initial staging mechanism for handling patterns which can then be re-examined later in left hemisphere functioning. If this does not happen, the learner will not be able to utilize the forms that have been drilled in the construction of spontaneous creative speech. This explains the fact that formal language does not appear to facilitate natural language use immediately.<br />Left hemisphere functioning <br />The left hemisphere is associated with creative language use, this includes syntactic and semantic processing and the motor operations involved in speaking and writing. However, it is not clear where these functions are localized. <br />There are two main areas associated with language.<br />5416551751965 LEFT One-at-a time processing.Sequential: A to B to C.Looks at details.Receptive to verifiable aspects of the world.A splitter (distinction is important).Talks, and talks and talks.Knows “how” Lineal thinking RIGHT All-at-once processingSimultaneousLook at the whole Receptive to qualitative aspects of the world (feelings)A lumper (conecctedness is important, puts everything together) Mute ,uses pictures not words.Knows “what”Majestic thinking SIGN MINDDESIGN MIND22225104775BROCA’S AREAWERNICKE’S AREAThis area is located just anterior to the motor cortex which controls movements of the lips, tongue, jaw, and vocal cords.Damage to this area results in slow and laboured speech, but is does not affect comprehension.This area partially surrounds the auditory cortex.Damage to this area results in speech that is fluent but also meaningless, and it also affects comprehension of language(spoken and written).<br />Linear Vs. Holistic Processing<br />The left side of the brain processes information in a linear manner. It processes from part to whole. It takes pieces, lines them up, and arranges them in a logical order; then it draws conclusions. <br />The right brain however, processes from whole to parts, holistically. It starts with the answer. It sees the big picture first, not the details. If you are right-brained, you may have difficulty following a lecture unless you are given the big picture first. <br />Sequential Vs. Random Processing<br />In addition to thinking in a linear manner, the left brain processes in sequence. The left brained person is a list maker. If you are left brained, you would enjoy making master schedules and daily planning. You complete tasks in order and take pleasure in checking them off when they are accomplished. <br />By, contrast, the approach of the right-brained student is random. If you are right-brained, you may move quickly from one task to another. You will get just as much done, but perhaps without having addressed priorities. An assignment may be late or incomplete, not because you weren't working but because you were working on something else. Because the right side of the brain is color sensitive, you might try using colors to learn sequence, making the first step green, the second blue, the last red. <br />Symbolic Vs. Concrete Processing<br />The left brain has no trouble processing symbols, such as letters, words, and mathematical notations. The left brained person tends to be comfortable with linguistic and mathematical problems. Left-brained students will probably just memorize vocabulary words or math formulas. <br />The right brain, on the other hand, wants things to be concrete. The right brain person wants to see, feel, or touch the real object. They prefer to see words in context, to see how the formula works. To use your right brain, create opportunities for hands-on activities, use something real whenever possible. You may also want to draw out a math problem or illustrate your notes.<br />Logical Vs. Intuitive Processing<br />The left brain processes in a linear, sequential, logical manner. When you process on the left side, you use information piece by piece to solve a math problem or work out a science experiment. When you read and listen, you look for the pieces so that you can draw logical conclusions. <br />If you process primarily on the right side of the brain, you use intuition. You may know the right answer to a math problem but not be sure how you got it. You may have to start with the answer and work backwards. In writing, it is the left brain that pays attention to mechanics such as spelling, agreement, and punctuation. But the right side pays attention to coherence and meaning; that is, your right brain tells you it quot; feelsquot; right.<br />Verbal Vs. Nonverbal Processing<br />Left brain students have little trouble expressing themselves in words. <br />Right brain students may know what they mean, but often have trouble finding the right words. <br />Men’s and women’s learning styles and capacities<br />What Cortical Region of the brain would these doctors be stimulating?<br />Bibliography<br />Understanding Psychology” –Fourth Edition, Random House School Division.<br />“Biology” Chapter 43 – Integration and control IV: The vertebrate Brain. Helena Curtis & N. Sue Barnes.<br />“Theories of Second Language Acquisition” – Rod Ellis<br />“The Human Brain” - Harvard University LS/HHMI High School Science - Multiple Diagrams of the Human Brain. outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/teachers/Summer05/.../Human_brain.ppt <br />www.bbc.co.uk - BBC homepage – the brain<br />
