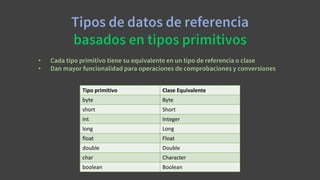
El documento describe las clases de envoltorio o wrappers en Java que corresponden a los tipos primitivos. Cada tipo primitivo como byte, short, int, long, float, double, char y boolean tiene una clase asociada (Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Float, Double, Character, Boolean) que proporciona funcionalidad adicional como métodos para conversiones, comprobaciones y representación como objetos. Se describen los métodos más importantes de cada una de estas clases de envoltorio.