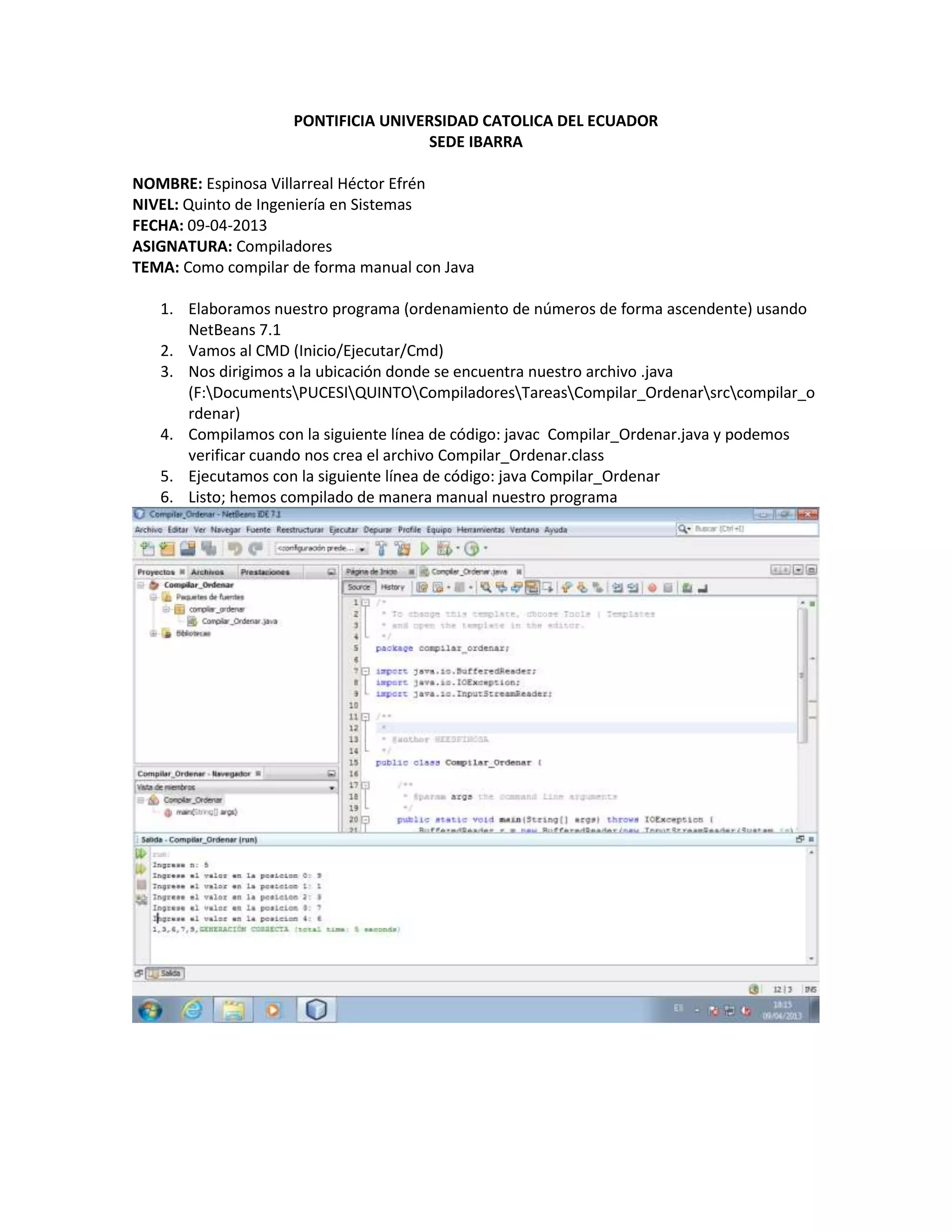
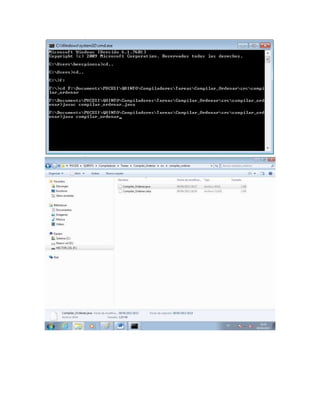
Este documento describe los pasos para compilar un programa Java de forma manual utilizando la línea de comandos. Inicialmente, se crea el programa Java usando NetBeans. Luego, se abre el CMD y se navega hasta la ubicación del archivo .java. Finalmente, se compila el programa usando el comando "javac NombreArchivo.java" y se ejecuta usando "java NombreArchivo". El documento también incluye el código fuente de un programa Java que ordena números de forma ascendente como ejemplo.
![Código fuente de mi programa:
/*
* To change this template, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
//package compilar_ordenar;
importjava.io.BufferedReader;
importjava.io.IOException;
importjava.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
*
* @author HEESPINOSA
*/
public class Compilar_Ordenar {
/**
* @paramargs the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("Ingresenumero: ");
intnumero = Integer.parseInt(r.readLine());
int []x = new int[numero];
for (int i = 0; i <numero; i++) {
System.out.print("El valor de la posicion "+ i +" es: ");
x[i] = Integer.parseInt(r.readLine());
}
intauxiliar;
if(numero%2==0){
for (int i = 0; i < (numero/2); i++) {
for (int j = i; j < (numero/2); j++) {
if(x[i]>x[j]){
auxiliar = x[i];
x[i]=x[j];
x[j]=auxiliar;
}
}
}
for (int i = (numero/2); i <numero; i++) {
for (int j = i; j <numero; j++) {
if(x[i]<x[j]){
auxiliar = x[i];
x[i]=x[j];
x[j]=auxiliar;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compilarmediantedos-130409190307-phpapp01/85/Compilar-mediante-dos-3-320.jpg)
![}
} else{
for (int i = 0; i <numero; i++) {
for (int j = i; j <numero; j++) {
if(x[i]>x[j]){
auxiliar = x[i];
x[i]=x[j];
x[j]=auxiliar;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <numero; i++) {
System.out.print(x[i]+",");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compilarmediantedos-130409190307-phpapp01/85/Compilar-mediante-dos-4-320.jpg)