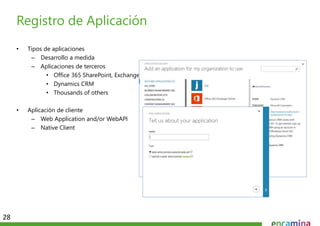
Este documento describe las diferentes formas en que se puede extender Office 365 mediante el desarrollo. Estas incluyen aplicaciones de SharePoint, aplicaciones de Office y aplicaciones en la nube. Las aplicaciones de SharePoint pueden ser alojadas en SharePoint o en un proveedor externo, mientras que las aplicaciones de Office y en la nube interactúan con los servicios de Office 365 como Exchange, OneDrive y SharePoint. El documento también proporciona ejemplos de cómo crear este tipo de aplicaciones y consideraciones importantes como el registro y la autenticación.