REGLAS GRAMATICALES.pdf
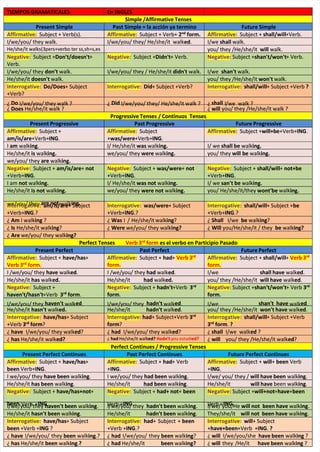
- 1. TIEMPOS TIEMPOS GRAMATICALES GRAMATICALES En En INGLES INGLES Simple /Affirmative Tenses Simple /Affirmative Tenses Present Present Simple Simple Past Past Simple Simple = = la la acción acción ya ya termino termino Future Future Simple Simple Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Verb(s). Subject + Verb(s). Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Verb+ Subject + Verb+ 2 2nd nd form. form. Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + shall/will shall/will+Verb. +Verb. I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they walk. walk. I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they/ they/ He/she/it He/she/it walk walked ed. I/we . I/we shall shall walk. walk. He/she/it walks(3pers+verbo ter ss,sh=s,es He/she/it walks(3pers+verbo ter ss,sh=s,es you/ they /He/she/it you/ they /He/she/it will will walk. walk. Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject +Don't/doesn't Don't/doesn't+ + Verb. Verb. Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject +Didn't Didn't+ Verb. + Verb. Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject +shan't/won't shan't/won't+ Verb. + Verb. I/we/you/ they I/we/you/ they don't don't walk. walk. I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they / / He/she/it He/she/it didn didn' 't t walk. walk. I/we I/we shan't shan't walk. walk. He/she/it He/she/it doesn't doesn't walk. walk. you/ you/ they they /He/she/it /He/she/it won't won't walk. walk. Interrogative: Interrogative: Do/Does Do/Does+ Subject + Subject +Verb? +Verb? Interrogative: Interrogative: Did Did+ Subject +Verb? + Subject +Verb? Interrogative: Interrogative: shall/will shall/will+ Subject +Verb + Subject +Verb ? ? ¿ ¿ Do Do I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they walk walk ? ? ¿ ¿ Did Did I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they/ they/ He/she/it He/she/it walk walk ? ? ¿ ¿ shall shall I I/we /we walk walk ? ? ¿ ¿ Does Does He/she/it He/she/it walk walk ? ? ¿ ¿ will will you/ they /He/she/it walk ? you/ they /He/she/it walk ? Progressive Progressive Tenses / Tenses / Continuos Continuos Tenses Tenses Present Progressive Present Progressive Past Progressive Past Progressive Future Progressive Future Progressive Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + am/is/are am/is/are+Verb+ +Verb+ING ING. . Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject Subject + +was/were was/were+Verb+ +Verb+ING ING. . Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject +will+be will+be+Verb+ +Verb+ING ING. . I I am am walk walking ing. . I/ I/ He/she/it He/she/it was was walk walking. ing. I/ I/ we we shall be shall be walk walking. ing. He/she/it He/she/it is is walk walking. ing. we/you/ we/you/ they they were were walk walking. ing. you/ you/ they they will be will be walk walking. ing. we/you/ they we/you/ they are are walk walking. ing. Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + am/is/are am/is/are+ + not not +Verb+ +Verb+ING ING. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + was/were was/were+ + not not +Verb+ +Verb+ING ING. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + shall/will shall/will+ + not+be not+be +Verb+ +Verb+ING ING. . I am I am not not walk walking. ing. I/ I/ He/she/it He/she/it was not was not walk walking. ing. I/ I/ we we san't be san't be walk walking. ing. He/she/it He/she/it is is not not walk walking. ing. we/you/ we/you/ they they were not were not walk walking. ing. you/ you/ He/she/it/they He/she/it/they wont'be wont'be walk walking. ing. we/you/ they we/you/ they are not are not walk walking. ing. Interrogative: Interrogative: am/is/are am/is/are+ Subject + Subject +Verb+ +Verb+ING ING.? .? Interrogative: Interrogative: was/were was/were+ Subject + Subject +Verb+ +Verb+ING ING.? .? Interrogative: Interrogative: shall/will shall/will+ Subject + + Subject +be be +Verb+ +Verb+ING ING.? .? ¿ ¿ Am Am I walk I walking ing ? ? ¿ ¿ Was Was I I / He/she/it / He/she/it walk walking ing? ? ¿ ¿ Shall Shall I/we I/we be be walk walking ing? ? ¿ ¿ Is Is He/she/it walk He/she/it walking ing? ? ¿ ¿ Were Were we/you/ they walk we/you/ they walking? ing? ¿ ¿ Will Will you/He/she/it / they you/He/she/it / they be be walk walking? ing? ¿ ¿ Are Are we/you/ they walk we/you/ they walking? ing? Perfect Tenses Perfect Tenses Verb 3 Verb 3rd rd form form es el verbo en Participio Pasado es el verbo en Participio Pasado Present Perfect Present Perfect Past Perfect Past Perfect Future Perfect Future Perfect Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + have/has have/has+ + Verb Verb 3 3rd rd form form. . Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + had had+ + Verb 3 Verb 3rd rd form. form. Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + shall/will shall/will+ + Verb 3 Verb 3rd rd form. form. I /we/you/ they I /we/you/ they have have walk walked ed. . I I /we/you/ /we/you/ they they had had walk walked ed. I/we . I/we shall have shall have walk walked ed. . He/she/it He/she/it has has walk walked. ed. He/she/it He/she/it had had walk walked. ed. you/ you/ they they /He/she/it /He/she/it will have will have walk walked ed. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + haven't/hasn't haven't/hasn't+Verb +Verb 3 3rd rd form form. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + hadn't hadn't+Verb +Verb 3 3rd rd form form. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject +shan't/won't shan't/won't+ Verb + Verb 3 3rd rd form form. . I/we/you/ they I/we/you/ they haven't haven't walk walked ed. . I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they hadn't hadn't walk walked ed. I/we . I/we shan't shan't have have walk walked ed. . He/she/it He/she/it hasn't hasn't walk walked. ed. He/she/it He/she/it hadn't hadn't walk walked ed. . you/ you/ they they /He/she/it /He/she/it won't have won't have walk walked ed. . Interrogative: Interrogative: have/has have/has+ Subject + Subject +Verb +Verb 3 3rd rd form form? ? Interrogative: Interrogative: had had+ Subject+Verb + Subject+Verb 3 3rd rd form form? ? Interrogative: Interrogative: shall/will shall/will+ Subject +Verb + Subject +Verb 3 3rd rd form form. . ? ? ¿ ¿ have have I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they walk walked ed? ? ¿ ¿ had had I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they walk walked ed? ? ¿ ¿ shall shall I/we walk I/we walked ed ? ? ¿ ¿ has has He/she/it walk He/she/it walked? ed? ¿ ¿ had had He/she/it walk He/she/it walked? ed? Hadn't Hadn't you estudi you estudied? ed? ¿ ¿ will will you/ you/ they they /He/she/it /He/she/it walk walked ed? ? Perfect Continues / Progressive Tenses Perfect Continues / Progressive Tenses Present Perfect Continues Present Perfect Continues Past Perfect Continues Past Perfect Continues Future Perfect Continues Future Perfect Continues Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + have/has have/has+ + been been Verb+ Verb+ING ING. . Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + had had+ Verb + Verb + +ING ING. . Affirmative: Affirmative: Subject + Subject + will will+ + been been Verb Verb + +ING ING. . I we/you/ they I we/you/ they have been have been walk walking ing. . I I we/you/ we/you/ they they had had been been walk walking ing. . I/we/ I/we/ you/ you/ they they / / will have been will have been walk walking ing. . He/she/it He/she/it has been has been walk walking ing. He/she/it . He/she/it had had been been walk walking ing. He/she/it . He/she/it will have will have been walk been walking ing. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + have/has+not have/has+not+ + been been Verb + Verb +ING ING. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject + had+ not had+ not+ + been been Verb + Verb +ING ING. . Negative: Negative: Subject + Subject +will+not will+not+ +have have+ +been been Verb Verb + +ING ING. . I/we/you/ they I/we/you/ they haven't haven't been been walk walking ing. . I/we/you/ I/we/you/ they they hadn't hadn't been been walk walking ing. . I/we/ I/we/ you/He you/He will will not not been been have have walk walking ing. . He/she/it He/she/it hasn't hasn't been been walk walking ing. He/she/it . He/she/it hadn't hadn't been been walk walking ing. They/she/it . They/she/it will will not not been been have have walk walking ing. . Interrogative: Interrogative: have/has have/has+ Subject + Subject been been +Verb +Verb + +ING ING ? ? Interrogative: Interrogative: had had+ Subject + + Subject + been been +Verb +Verb + +ING ING.? .? Interrogative: Interrogative: will will+ Subject + Subject + +have+been have+been+Verb + +Verb +ING ING. . ? ? ¿ ¿ have have I/we/you/ they I/we/you/ they been been walk walking ing.? .? ¿ ¿ had had I/we/you/ they I/we/you/ they been been walk walking ing? ? ¿ ¿ will will I/we/you/she I/we/you/she have been have been walk walking ing ? ? ¿ ¿ has has He/she/it He/she/it been been walk walking ing. .? ? ¿ ¿ had had He/she/it He/she/it been been walk walking? ing? ¿ ¿ will will they /He/it they /He/it have been have been walk walking ing ? ?
- 2. TIEMPOS TIEMPOS GRAMATICALES GRAMATICALES EN EN INGLES INGLES Verb Verb Tenses Tenses 1. 1. Affirmative 2. Affirmative 2. Negative 3. Negative 3. Interrogative Interrogative Present simple Present simple They They have have a a car. car. They They don't don't have a car. have a car. Do Do They have a car? They have a car? Present continuous Present continuous He is Read He is Reading ing now. now. He He is isn't n't Read Reading ing now. now. is is He He Read Reading ing now? now? Present perfect Present perfect We We have been have been there. there. We We haven't haven't been been there. there. Have Have We We been been there? there? Present perfect continuous Present perfect continuous You You have been have been work working ing hard. hard. You You've been 've been work working ing hard. hard. Have Have You You been been work working ing hard? hard? Past simple Past simple They They saw saw a a movie. movie. They They didn't didn'tsaw a movie. saw a movie. Did Did They They see see a movie? a movie? Past continuous Past continuous It It was was snowing. snowing. It It wa was sn't n't snow snowing ing. . was was It snow It snowing ing? ? Past perfect Past perfect They They had had left left for for France. France. They They hadn't hadn't left for France. left for France. had had They left for France? They left for France? Past perfect continuous Past perfect continuous She She had been had been wait waiting ing for for him. him. She She hadn't been hadn't been wait waiting ing for for him. him. had had She She been been wait waiting ing for for him? him? Future simple Future simple It It will will snow snow this this Winter. Winter. It It won't won't snow this Winter. snow this Winter. will will It snow this Winter? It snow this Winter? Future continuous Future continuous She She will will be travel be traveling ing. She . She won't won't be travel be traveling ing. . will will She be travel She be traveling ing? ? Future perfect Future perfect He He will will have arriv have arrived ed. He . He won't won't have arriv have arrived ed. . will will He have arriv He have arrived ed? ? Future perfect continuous Future perfect continuous You will You will have been have been work working ing. You . You won't won't have been have been work working ing. . will will You You have been have been work working ing? ? Conditional Conditional I I would would fly fly there. there. I I wouldn't wouldn't fly there. fly there. would would I fly there? I fly there? Conditional continuous Conditional continuous They They would be would be sleep sleeping ing now. now. They They wouldn't wouldn't be sleep be sleeping ing now. now. would would They They be be sleep sleeping ing now? now? Conditional perfect Conditional perfect She She would have been would have been there. there. She She wouldn't wouldn't have been have been there. there. would would She She have been have been there? there? Future be going to Future be going to She She's going to 's going to get get married. married. She She's going to 's going to get married. get married. Is Is She She going to going to get married? get married? TIEMPOS TIEMPOS GRAMATICALES GRAMATICALES EN EN ESPAÑOL ESPAÑOL Verb Verb Tenses Tenses 1. 1. Affirmative 2. Affirmative 2. Negative 3. Negative 3. Interrogative Interrogative Present simple Present simple Tienen Tienen un un coche. coche. Ellos Ellos no no tienen tienen un un coche. coche. ¿Tienen ¿Tienen un un coche? coche? Present continuous Present continuous Él Él está está leyendo leyendo ahora. ahora. Él Él no no está está leyendo leyendo ahora. ahora. está está leyendo leyendo él él ahora? ahora? Present perfect Present perfect Hemos Hemos estado estado allí. allí. No No hemos hemos estado estado allí. allí. Nos Nos hemos hemos estado estado allí? allí? Present perfect continuous Present perfect continuous Usted ha estado trabajando Usted ha estado trabajando duro. duro. Usted ha estado trabajando Usted ha estado trabajando duro. duro. ¿Ha estado trabajando duro? ¿Ha estado trabajando duro? Past simple Past simple Vieron Vieron una una película. película. Ellos Ellos didn'tsaw didn'tsaw una una película. película. ¿Vieron ¿Vieron una una película? película? Past continuous Past continuous Estaba Estaba nevando. nevando. No No estaba estaba nevando. nevando. Se Se estaba estaba nevando? nevando? Past perfect Past perfect Ellos Ellos se se habían habían ido ido a a Francia. Francia. No No habían habían ido ido a a Francia. Francia. Si Si hubieran hubieran salido salido de de Francia? Francia? Past perfect continuous Past perfect continuous Había estado esperando por Había estado esperando por él. él. No No había había estado estado esperando. esperando. Ella Ella había había estado estado esperando esperando por él? por él? Future simple Future simple Nevará Nevará este este invierno. invierno. No No lo lo hará hará nieve nieve este este invierno. invierno. Se hará nieve este invierno? Se hará nieve este invierno? Future continuous Future continuous Ella Ella va va a a viajar. viajar. Ella Ella no no va va a a viajar. viajar. Ella Ella va va a a viajar? viajar? Future perfect Future perfect Se Se habrá habrá llegado. llegado. No No habrá habrá llegado. llegado. Él Él se se ha ha llegado? llegado? Future perfect continuous Future perfect continuous Usted Usted ha ha estado estado trabajando. trabajando. Usted Usted no no ha ha estado estado trabajando. trabajando. tendrá Usted ha estado tendrá Usted ha estado trabajando? trabajando? Conditional Conditional Me Me gustaría gustaría volar volar allí. allí. Yo Yo no no volar volar allí. allí. Me Me gustaría gustaría volar volar allí? allí? Conditional continuous Conditional continuous Estarían Estarían durmiendo durmiendo ahora. ahora. No No estarían estarían durmiendo durmiendo ahora. ahora. ¿Estarían durmiendo ahora? ¿Estarían durmiendo ahora? Conditional perfect Conditional perfect Ella Ella habría habría estado estado allí. allí. Ella Ella no no habría habría estado estado allí. allí. Ella Ella podría podría haber haber estado estado allí? allí? Future be going to Future be going to Ella Ella va va a a casarse. casarse. Ella Ella va va a a casarse. casarse. Ella Ella se se va va a a casar? casar?
- 3. 1 reglas gramaticales presente simple pasado 1 reglas gramaticales presente simple pasado que están en el video los t que están en el video los tiempos gramaticales. iempos gramaticales.
- 4. VOZ PASIVA SEGÚN EL TIEMPO GRAMATICAL VOZ PASIVA SEGÚN EL TIEMPO GRAMATICAL Cómo entender la Voz pasiva en Inglés FÁCILMENTE Cómo entender la Voz pasiva en Inglés FÁCILMENTE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=080leytixWE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=080leytixWE Voz Pasiva Inglés (en TODOS los TIEMPOS VERBALES) Voz Pasiva Inglés (en TODOS los TIEMPOS VERBALES) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mv41eq-mgis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mv41eq-mgis INGLÉS. 33- PASIVA. Passive Voice. Inglés para hablantes de español. Tutorial INGLÉS. 33- PASIVA. Passive Voice. Inglés para hablantes de español. Tutorial https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tPTV5VmnQwY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tPTV5VmnQwY Voz Pasiva en Inglés (Passive Voice) Voz Pasiva en Inglés (Passive Voice) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7fOAjRovgNc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7fOAjRovgNc VOZ PASIVA SEGÚN EL TIEMPO GRAMATICAL VOZ PASIVA SEGÚN EL TIEMPO GRAMATICAL Se utiliza el verbo TOBE según el tiempo gramatical y el verbo se coloca en el participio pasado o en la 3 Se utiliza el verbo TOBE según el tiempo gramatical y el verbo se coloca en el participio pasado o en la 3 Forma Forma TIEMPO TIEMPO GRAMATICAL GRAMATICAL VOZ VOZ ACTIVA ACTIVA VOZ VOZ PASIVA PASIVA 1 PRESENT 1 PRESENT SIMPLE SIMPLE The little girl The little girl buys buys candies. candies. La niña La niña compra compra dulces. dulces. Candies Candies are bought are bought by the little girl. by the little girl. Dulces Dulces son comprados son comprados por la niña. por la niña. 1 PRESENT 1 PRESENT SIMPLE SIMPLE I I take take the taxi. the taxi. yo yo tomo tomo el taxi. el taxi. the taxi the taxi is taken is taken by me by me El taxi El taxi es tomado es tomado por mi por mi 2 2 PAST PAST SIMPLE- SIMPLE- PASADO PASADO SIMPLE. SIMPLE. France France gave gave the Statue of liberty to America. the Statue of liberty to America. Francia Francia le dio le dio la estatua de la libertad a U.S.A. la estatua de la libertad a U.S.A. The Statue of liberty The Statue of liberty WAS GIVEN WAS GIVEN to America by to America by France. France. La estatua de la libertad La estatua de la libertad FUE DADA FUE DADA a U.S.A por a U.S.A por Francia. Francia. 2 2 PAST PAST SIMPLE- SIMPLE- PASADO PASADO SIMPLE. SIMPLE. He He crashed crashed the car. the car. El El choco choco el auto. el auto. The car The car WAS CRASHED WAS CRASHED by him. by him. El auto El auto FUE CHOCADO FUE CHOCADO por el. por el. 3 FUTURE 3 FUTURE SIMPLE SIMPLE He He will buy will buy a new guitar. a new guitar. El El comprara comprara una nueva guitarra. una nueva guitarra. A new guitar A new guitar will be bought will be bought by him. by him. Una nueva guitarra Una nueva guitarra sera comprada sera comprada por el. por el. 4 PRESENT 4 PRESENT CONTINUOS CONTINUOS He He is painting is painting the house. the house. el el esta pintando esta pintando la casa. la casa. the house the house is being painted is being painted by him. by him. La casa La casa esta siendo pintada esta siendo pintada por el. por el. 5 PAST 5 PAST CONTINUOS CONTINUOS They They were writing were writing a song. a song. ellos ellos estaban escribiendo estaban escribiendo una cancion. una cancion. A song A song was being written was being written by them. by them. Una cancion Una cancion estaba siendo escrita estaba siendo escrita por ellos. por ellos. 6 PRESENT 6 PRESENT PERFECT PERFECT We We have visited have visited our mom. our mom. Hemos visitado Hemos visitado a nuestra madre. a nuestra madre. Our mom Our mom has been visited has been visited by us. by us. Nuestra mama Nuestra mama ha sido visitada ha sido visitada por nosotros. por nosotros. 7 PAST 7 PAST PERFECT PERFECT When the police came, they When the police came, they had stolen had stolen the the bank. bank. Cuando la policia llego, Cuando la policia llego, ellos habian ellos habian robado robado el banco. el banco. The bank The bank had been stolen had been stolen when the police when the police came. came. El banco El banco habia sido robado habia sido robado cuando la policia cuando la policia llego. llego.
- 6. 2016 julio 2 - 2016 julio 2 - PRESENT SIMP PRESENT SIMPLE VS PRESENT CON LE VS PRESENT CONTINUOS TINUOS 1. The train always 1. The train always leaves leaves (leave) on time. (leave) on time. 2. 'What's the matter? Why 2. 'What's the matter? Why are you crying are you crying(cry/you)?' (cry/you)?' 3. That's strange. They 3. That's strange. They are not watching are not watching (not to watch) TV. (not to watch) TV. 4. He 4. He does not speak does not speak (not to speak) very good English. (not to speak) very good English. 5. Please be quiet! I 5. Please be quiet! I am doing am doing (do) my homework. (do) my homework. 6. Where 6. Where do they live do they live (live/they)? (live/they)? 7. Listen! John 7. Listen! John is playing is playing music! (play) music! (play) 8. I never 8. I never go go (go) to the swimming pool. (go) to the swimming pool. 9. Harold Black's a famous pianist. He 9. Harold Black's a famous pianist. He gives gives (give) two or (give) two or three concerts every week. three concerts every week. 10. He 10. He travels travels (travel) a lot and this week he's in New York. (travel) a lot and this week he's in New York. 11. Today he 11. Today he is staying is staying (stay) at an expensive hotel. (stay) at an expensive hotel. 12. He's at his hotel now. He 12. He's at his hotel now. He is having is having (have) breakfast in (have) breakfast in the dining-room. the dining-room. 13. He 13. He is drinking is drinking (drink) a cup of coffee and he (drink) a cup of coffee and he is is reading reading (read) a newspaper. (read) a newspaper. 14. Harold's always very busy. He 14. Harold's always very busy. He plays plays (play) the piano (play) the piano regularly. regularly. 15. He 15. He practises practises (practise) for four hours every day. (practise) for four hours every day. 16. He 16. He goes goes (go) to bed late and he always (go) to bed late and he always gets up gets up (get (get up) early. up) early. 18. But he sometimes 18. But he sometimes gets dressed gets dressed (get dressed) too (get dressed) too quickly, quickly, 19. and this morning he 19. and this morning he is wearing is wearing (wear) one blue sock (wear) one blue sock and one red sock! and one red sock! 1. El tren siempre 1. El tren siempre deja deja (licencia) a tiempo. (licencia) a tiempo. 2. "¿Cuál es el problema? ¿Por qué 2. "¿Cuál es el problema? ¿Por qué lloras lloras (grito / usted)? ' (grito / usted)? ' 3. Eso es extraño. Ellos 3. Eso es extraño. Ellos no están viendo no están viendo (no mirar) de (no mirar) de televisión. televisión. 4. El 4. El no habla no habla (por no hablar) muy bien Inglés. (por no hablar) muy bien Inglés. 5. Por favor, silencio! Que 5. Por favor, silencio! Que estoy haciendo estoy haciendo (hacer) la tarea. (hacer) la tarea. 6. ¿Dónde 6. ¿Dónde viven viven (en vivo / ellos)? (en vivo / ellos)? 7. Escucha! John 7. Escucha! John está reproduciendo está reproduciendo música! (jugar) música! (jugar) 8. Nunca 8. Nunca voy voy (ir) a la piscina. (ir) a la piscina. 9. Harold Negro es un pianista famoso. Él 9. Harold Negro es un pianista famoso. Él da da (da) dos o tres (da) dos o tres conciertos cada semana. conciertos cada semana. 10. El 10. El viaja viaja (de viaje) mucho y esta semana está en Nueva (de viaje) mucho y esta semana está en Nueva York. York. 11. Hoy en día 11. Hoy en día se hospeda se hospeda (estancia) en un hotel caro. (estancia) en un hotel caro. 12. Está en su hotel ahora. 12. Está en su hotel ahora. Él Él está teniendo está teniendo (tener) un (tener) un desayuno en el comedor. desayuno en el comedor. 13. Él 13. Él está bebiendo está bebiendo (bebida) una taza de café y que (bebida) una taza de café y que está está leyendo leyendo (leer) un periódico. (leer) un periódico. 14. Harold es siempre muy concurrida. Él 14. Harold es siempre muy concurrida. Él juega juega (juego) el (juego) el piano con regularidad. piano con regularidad. 15. El 15. El practica practica (práctica) durante cuatro horas todos los (práctica) durante cuatro horas todos los días. días. 16. 16. Va Va (ir) a la cama tarde y que siempre (ir) a la cama tarde y que siempre se levanta se levanta (levantarse) temprano. (levantarse) temprano. 18. Sin embargo, a veces 18. Sin embargo, a veces se viste se viste (vestirse) demasiado (vestirse) demasiado rápido, rápido, 19. y esta mañana él 19. y esta mañana él está usando está usando (desgaste) un calcetín (desgaste) un calcetín azul y un calcetín rojo! azul y un calcetín rojo! 1. Put the verbs into the correct tense (present simple or present continuos). 1. Put the verbs into the correct tense (present simple or present continuos). Harold Black's a famous pianist. He Harold Black's a famous pianist. He gives gives two or two or three concerts every week. three concerts every week. He He travels travels a lot and this week he's in New York. a lot and this week he's in New York. Today he Today he is staying is staying at an expensive hotel. at an expensive hotel. He's at his hotel now. He He's at his hotel now. He is having is having breakfast in the breakfast in the dining-room. dining-room. He He is drinking is drinking a cup of coffee and he a cup of coffee and he is reading is reading a a newspaper. newspaper. Harold's always very busy. He Harold's always very busy. He plays plays the piano the piano regularly. regularly. He He practices practices for four hours every day. for four hours every day. He He goes goes to bed late and he always to bed late and he always gets up gets up early. early. But he sometimes But he sometimes gets dressed gets dressed too quickly, and too quickly, and this morning this morning he he is wearing is wearing one blue sock and one one blue sock and one red sock! red sock! Harold Negro es un Harold Negro es un pianista famoso. Él pianista famoso. Él da da dos o tres dos o tres conciertos cada semana. conciertos cada semana. Él Él viaja viaja mucho y esta semana está en Nueva York. mucho y esta semana está en Nueva York. Hoy en día Hoy en día se hospeda se hospeda en un hotel caro. en un hotel caro. Está en su hotel ahora. Él Está en su hotel ahora. Él está teniendo está teniendo un un desayuno en el comedor. desayuno en el comedor. Él Él está bebiendo está bebiendo una taza de café y que una taza de café y que está está leyendo un periódico. leyendo un periódico. Harold es siempre muy concurrida. Harold es siempre muy concurrida. Toca Toca el piano el piano con regularidad. con regularidad. Él Él practica practica durante cuatro horas todos los días. durante cuatro horas todos los días. Se acuesta tarde y que siempre se levanta Se acuesta tarde y que siempre se levanta temprano. temprano. Pero a veces Pero a veces se viste se viste con demasiada rapidez, y esta con demasiada rapidez, y esta mañana él mañana él está usando está usando un calcetín azul y un un calcetín azul y un calcetín rojo! calcetín rojo!
- 7. Present progressive (present Present progressive (present continuous): continuous): It is used when the action is done while you are talking. It is used when the action is done while you are talking. The present progressive i The present progressive is formed with s formed with 'to be' in the 'to be' in the present tense+the present participle of the verb. present tense+the present participle of the verb. Here are some examples: Here are some examples: 1. Look! he 1. Look! he's 's sleeping sleeping. . 2. Somebody 2. Somebody is waiting is waiting for you. for you. 3. What 3. What are are you you looking looking at? at? 4. What 4. What are are you you looking looking for? for? 5. What 5. What is is she she doing doing? - She must ? - She must be working be working in the in the garden. garden. 6. He 6. He is writing is writing a new novel. a new novel. 7. I 7. I am reading am reading a good book. a good book. 8. Don't take this book, I 8. Don't take this book, I'm reading 'm reading it! it! The present simple : The present simple : 1) It is used for facts that are true now and later: 1) It is used for facts that are true now and later: Examples: Examples: a. Spring a. Spring begins begins on March 21st. on March 21st. b. The Earth b. The Earth revolves revolves round the Sun. round the Sun. c. He c. He plays plays the piano. the piano. 2) It may express a repetition or a habit: 2) It may express a repetition or a habit: Examples: Examples: a. We a. We have have tea at 4. tea at 4. b. She b. She goes goes to London twice a month. to London twice a month. Compare these two sentences: Compare these two sentences: He wears glasses because he is short-sighted. Why isn't he He wears glasses because he is short-sighted. Why isn't he wearing wearing them today? them today? He He's learning 's learning his lessons. He always his lessons. He always learns learns them at the them at the last minute. last minute. Presente progresivo Presente progresivo (presente): (presente): Se utiliza cuando la acción se realiza mientras está Se utiliza cuando la acción se realiza mientras está hablando. hablando. El presente progresivo se forma con "ser" en presente + el El presente progresivo se forma con "ser" en presente + el participio presente del verbo. participio presente del verbo. Aquí hay unos ejemplos: Aquí hay unos ejemplos: 1. Mira! Él 1. Mira! Él está durmiendo está durmiendo. . 2. Alguien 2. Alguien está esperando está esperando. . 3. ¿Qué 3. ¿Qué estás mirando estás mirando? ? 4. ¿Qué 4. ¿Qué estás buscando estás buscando? ? 5. ¿Qué 5. ¿Qué está haciendo está haciendo? - Ella debe ? - Ella debe estar trabajando estar trabajando en el en el jardín. jardín. 6. 6. Está escribiendo Está escribiendo una nueva novela. una nueva novela. 7. 7. Estoy leyendo Estoy leyendo un buen libro. un buen libro. 8. No tome este libro, lo 8. No tome este libro, lo estoy leyendo estoy leyendo! ! El presente simple : El presente simple : 1) Se utiliza para 1) Se utiliza para los hechos que son verdad ahora y los hechos que son verdad ahora y más adelante: más adelante: Ejemplos: Ejemplos: a. La primavera a. La primavera comienza comienza el 21 de marzo. el 21 de marzo. b. La Tierra b. La Tierra gira gira alrededor del Sol alrededor del Sol c. Él c. Él toca toca el piano. el piano. 2) Se puede expresar una repetición o 2) Se puede expresar una repetición o un hábito: un hábito: Ejemplos: Ejemplos: a. a. Tenemos Tenemos el té a las 4. el té a las 4. b. Ella b. Ella va va a Londres dos veces al mes. a Londres dos veces al mes. Comparar estas dos frases: Comparar estas dos frases: Lleva gafas porque es miope. ¿Por qué no se les Lleva gafas porque es miope. ¿Por qué no se les lleva lleva hoy hoy en día? en día? Está aprendiendo Está aprendiendo sus lecciones. Siempre las sus lecciones. Siempre las aprende aprende en en el último minuto. el último minuto.
- 8. The present continuous. The present continuous. What's the rule? What's the rule? Present actions/situations Present actions/situations We use the present continuous tense when we talk about We use the present continuous tense when we talk about something which is happening something which is happening or or in progress at the time in progress at the time of speaking of speaking (but not necessarily exactly at the time). (but not necessarily exactly at the time). Example Example "Is John here?" "Is John here?" "Yes, he's next door, checking the accounts." "Yes, he's next door, checking the accounts." Be careful! Here is a list of Be careful! Here is a list of verbs not normally used in verbs not normally used in the continuous form: the continuous form: want. want. need. prefer. need. prefer. like. love. like. love. hate. hate. belong. belong. see. see. hear. hear. know. know. realise. recognise. suppose. believe. understand. forget. realise. recognise. suppose. believe. understand. forget. remember. seem. remember. seem. Future arrangements Future arrangements The most common use of the present continuous tense is to The most common use of the present continuous tense is to talk about the future. talk about the future. Example Example "I'm flying to Rome next Tuesday." "I'm flying to Rome next Tuesday." The speaker/writer indicates that a future event has been The speaker/writer indicates that a future event has been arranged (in this case, the flight to Rome has been booked). arranged (in this case, the flight to Rome has been booked). Test it out! Test it out! Present simple or Pres Present simple or Present Continuous? ent Continuous? 1. I always 1. I always play play tennis on Fridays. tennis on Fridays. 2. He 2. He is finishing is finishing his report. He will bring it into the office his report. He will bring it into the office when it is complete. when it is complete. 3. "My parents phoned me this morning.They 3. "My parents phoned me this morning.They are enjoying are enjoying themselves in the Seychelles. Champagne every night! In themselves in the Seychelles. Champagne every night! In fact, they don't want to leave." fact, they don't want to leave." 4. We 4. We prefer prefer to entertain our guests in a local restaurant to entertain our guests in a local restaurant rather than the canteen. Although it is expensive, we can rather than the canteen. Although it is expensive, we can talk freely there. talk freely there. 5. I 5. I know know the answer to your problem. Get a new computer. the answer to your problem. Get a new computer. 6. "Where is John?" "In his office 6. "Where is John?" "In his office waiting waiting for an important for an important telephone call." telephone call." 7. I can't make the meeting tomorrow. I 7. I can't make the meeting tomorrow. I am interviewing am interviewing the the applicants for the sales manager's job. applicants for the sales manager's job. 8. My brother 8. My brother works works for Shink Inc. which makes bathroom for Shink Inc. which makes bathroom fittings. fittings. 9. Who 9. Who is talking is talking to Bill? Is it the new secretary? to Bill? Is it the new secretary? 10. The new contract 10. The new contract seems seems fine to me. However, could you fine to me. However, could you just check it through once more? just check it through once more? El presente continuo. El presente continuo. ¿Cual es la regla? ¿Cual es la regla? acciones presentes / situaciones acciones presentes / situaciones Usamos el presente continuo cuando hablamos de Usamos el presente continuo cuando hablamos de algo algo que está sucediendo que está sucediendo o o en curso en el momento de en curso en el momento de hablar hablar (pero no necesariamente exactamente en el (pero no necesariamente exactamente en el momento). momento). Ejemplo Ejemplo "¿Es John aquí?" "¿Es John aquí?" "Sí, está al lado, la comprobación de las cuentas." "Sí, está al lado, la comprobación de las cuentas." ¡Ten cuidado! Aquí está una lista de ¡Ten cuidado! Aquí está una lista de verbos que no verbos que no suelen utilizarse en forma continua: suelen utilizarse en forma continua: querer. necesitar. preferir. me gusta. amor. odio. pertenecer querer. necesitar. preferir. me gusta. amor. odio. pertenecer a. a. ver. ver. oír. oír. saber. saber. darse cuenta de. reconocer. suponer. creer. entender. darse cuenta de. reconocer. suponer. creer. entender. olvidar. recuerda. parecer. olvidar. recuerda. parecer. Futuros acuerdos Futuros acuerdos El uso más común del tiempo presente continuo es para El uso más común del tiempo presente continuo es para hablar sobre el futuro. hablar sobre el futuro. Ejemplo Ejemplo "Estoy volando a Roma el próximo martes." "Estoy volando a Roma el próximo martes." El hablante / escritor indica que un evento futuro ha sido El hablante / escritor indica que un evento futuro ha sido arreglado (en este caso, el vuelo a Roma ha sido arreglado (en este caso, el vuelo a Roma ha sido reservado). reservado). Probarlo! Probarlo! ¿Presente simple o presente continuo? ¿Presente simple o presente continuo? 1. Siempre 1. Siempre juego juego de tenis de los viernes. de tenis de los viernes. 2. Él 2. Él está terminando está terminando su informe. Él traerá a la oficina su informe. Él traerá a la oficina cuando se ha completado. cuando se ha completado. 3. "Mis padres me llamaron por teléfono esta mañana. Ellos 3. "Mis padres me llamaron por teléfono esta mañana. Ellos están disfrutando están disfrutando de sí mismos en las Seychelles. de sí mismos en las Seychelles. Champagne todas las noches! De hecho, ellos no quieren Champagne todas las noches! De hecho, ellos no quieren salir." salir." 4. 4. Preferimos Preferimos entretener a nuestros clientes en un entretener a nuestros clientes en un restaurante local en lugar de la cantina. A pesar de que es restaurante local en lugar de la cantina. A pesar de que es caro, podemos hablar libremente allí. caro, podemos hablar libremente allí. 5. 5. Sé Sé la respuesta a su problema. Obtener un equipo nuevo. la respuesta a su problema. Obtener un equipo nuevo. 6. "¿Dónde está Juan?" "En su oficina 6. "¿Dónde está Juan?" "En su oficina esperando esperando una una llamada importante." llamada importante." 7. No puedo hacer que la reunión de mañana. Estoy 7. No puedo hacer que la reunión de mañana. Estoy entrevistando entrevistando a los solicitantes de trabajo del gerente de a los solicitantes de trabajo del gerente de ventas. ventas. 8. Mi hermano 8. Mi hermano trabaja trabaja para Shink Inc., que hace que los para Shink Inc., que hace que los accesorios de baño. accesorios de baño. 9. ¿Quién 9. ¿Quién está hablando está hablando con Bill? ¿Es la nueva secretaria? con Bill? ¿Es la nueva secretaria? 10. El nuevo contrato 10. El nuevo contrato parece parece bien a mí. Sin embargo, bien a mí. Sin embargo, ¿podrías comprobarlo a través una vez más? ¿podrías comprobarlo a través una vez más?
- 9. Present Simple or Present Present Simple or Present Continuous? - Exercise 2 Continuous? - Exercise 2 Put the verb in brackets in the correct form (present simple Put the verb in brackets in the correct form (present simple or present continuous). or present continuous). Next week, my friends and I are Next week, my friends and I are going going camping in the camping in the woods. woods. I I am organizing am organizing the food, because I the food, because I like like cooking. cooking. Dave Dave has has a big car with a trailer, so he a big car with a trailer, so he is planning is planning the the transportation. transportation. Sam Sam is bringing is bringing the tent the tent — — he he goes goes camping every year, camping every year, so he so he has has a great tent and lots of other equipment. a great tent and lots of other equipment. My wife My wife thinks thinks we're crazy. we're crazy. She likes holidays in comfortable hotels, so she She likes holidays in comfortable hotels, so she is taking is taking a a trip to Paris instead. trip to Paris instead. +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Next week, my friends and I are Next week, my friends and I are going (go) going (go) camping in the camping in the woods. woods. I I am organizing (organize) am organizing (organize) the food, because I the food, because I like (like) like (like) cooking. cooking. Dave Dave has (have) has (have) a big car with a trailer, so he a big car with a trailer, so he is planning is planning (plan) (plan) the transportation. the transportation. Sam Sam is bringing (bring) is bringing (bring) the tent the tent — — he he goes (go) goes (go) camping camping every year, so he every year, so he has (have) has (have) a great tent and lots of other a great tent and lots of other equipment. equipment. My wife My wife thinks (think) thinks (think) we're crazy. we're crazy. She She likes (like) likes (like) holidays in comfortable hotels, so she is holidays in comfortable hotels, so she is taking (take) taking (take) a trip to Paris instead. a trip to Paris instead. ¿Presente simple o presente ¿Presente simple o presente continuo? - Ejercicio 2 continuo? - Ejercicio 2 Poner el verbo entre paréntesis en la forma correcta Poner el verbo entre paréntesis en la forma correcta (presente simple o presente continuo). (presente simple o presente continuo). La próxima semana, mis La próxima semana, mis amigos y yo amigos y yo vamos a vamos a acampar en acampar en el bosque. el bosque. Estoy organizando Estoy organizando la comida, porque me la comida, porque me gusta gusta cocinar. cocinar. Dave Dave tiene tiene un gran coche con un remolque, por lo que un gran coche con un remolque, por lo que es la es la planificación planificación del transporte. del transporte. Sam Sam está trayendo está trayendo la tienda - que la tienda - que va va de camping cada de camping cada año, por lo que año, por lo que tiene tiene una gran tienda de campaña y un una gran tienda de campaña y un montón de otros equipos. montón de otros equipos. Mi esposa Mi esposa piensa piensa que estamos locos. que estamos locos. A ella le gustan las vacaciones confortables hoteles, por lo A ella le gustan las vacaciones confortables hoteles, por lo que que es hacer es hacer un viaje a París en su lugar. un viaje a París en su lugar. +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ La próxima semana, mis amigos y yo vamos de La próxima semana, mis amigos y yo vamos de camping camping (GO) (GO) en el bosque. en el bosque. Estoy organizando (organizar) Estoy organizando (organizar) la comida, porque la comida, porque me me gusta (como) gusta (como) la cocción. la cocción. Dave Dave ha (tener) ha (tener) un gran coche con un remolque, por lo que un gran coche con un remolque, por lo que es la es la planificación (plan) planificación (plan) el transporte. el transporte. Sam Sam está trayendo (traer) está trayendo (traer) de la carpa - que de la carpa - que vaya (ir) vaya (ir) acampar todos los años, por lo que acampar todos los años, por lo que tiene (tener) tiene (tener) una gran una gran tienda de campaña y un montón de otros equipos. tienda de campaña y un montón de otros equipos. Mi esposa Mi esposa cree (piensa) cree (piensa) que estamos locos. que estamos locos. A ella le A ella le gusta (como) gusta (como) vacaciones en hoteles confortables, vacaciones en hoteles confortables, por lo que ella por lo que ella está tomando (tomar) está tomando (tomar) un viaje a París en su un viaje a París en su lugar. lugar.
- 10. Present Present Perfect Perfect or or Past Past Simple? - Exercise 1 Simple? - Exercise 1 Put the verb in brackets in the correct form (present perfect Put the verb in brackets in the correct form (present perfect or past simple). or past simple). 1. that man 1. that man has worked has worked in London in London since since 2003. 2003. 2. we 2. we went went to a concert to a concert yesterday yesterday. (go). . (go). 3. she 3. she had had lunch 2 hours lunch 2 hours ago ago. . 4. he 4. he has studied has studied for 2 hours. (study). for 2 hours. (study). 5. ¿ 5. ¿ have have you you finished finished your homework your homework yet yet?. (finish). ?. (finish). 6. I 6. I haven’t seen haven’t seen that film that film yet yet. (not see). . (not see). 7. John 7. John went went to the cinema to the cinema last Saturday last Saturday. (go). . (go). 8. I 8. I have never eaten have never eaten Chinese food, but Chinese food, but I’d I’d like like to try it. to try it. (never ate /or /have never eaten ). (never ate /or /have never eaten ). 9. I 9. I never ate never ate Chinese food when I Chinese food when I lived lived in in China. China. (never (never ate /or /have never eaten ). ate /or /have never eaten ). 10. he 10. he studied studied for 2 hours for 2 hours yesterday yesterday. (study) . (study) +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ PRESENT PERFECT: PRESENT PERFECT: for for since since yet yet already already even even PRESENT PERFECT OR PAST SIMPLE: PRESENT PERFECT OR PAST SIMPLE: never never PAST SIMPLE: PAST SIMPLE: yesterday yesterday last __________ last __________ ______ ago ______ ago ¿Presente ¿Presente Perfecto Perfecto o o pasado pasado simple? - Ejercicio 1 simple? - Ejercicio 1 Poner el verbo entre paréntesis en la forma correcta Poner el verbo entre paréntesis en la forma correcta (presente perfecto o pasado simple). (presente perfecto o pasado simple). 1. que el hombre 1. que el hombre ha trabajado ha trabajado en Londres en Londres desde desde 2003. 2003. 2. 2. fuimos fuimos a un concierto de a un concierto de ayer ayer. (ir). . (ir). 3. 3. almorzó almorzó hace hace 2 horas. 2 horas. 4. 4. ha estudiado ha estudiado durante durante 2 2 horas. horas. (estudiar). (estudiar). 5. ¿ 5. ¿Ha terminado Ha terminado su tarea su tarea todavía todavía ?. (terminar). ?. (terminar). 6. 6. No he visto No he visto esa película esa película todavía todavía. . (no (no ver). ver). 7. Juan 7. Juan fue fue al cine el al cine el sábado pasado sábado pasado. (ir). . (ir). 8. 8. Nunca he comido Nunca he comido comida china, pero comida china, pero me gustaría me gustaría probarlo. (Nunca comió / o / nunca han comido). probarlo. (Nunca comió / o / nunca han comido). 9. 9. Nunca se comió Nunca se comió la comida china la comida china cuando vivía cuando vivía en en China. (Nunca comió / o / nunca han comido). China. (Nunca comió / o / nunca han comido). 10. 10. Estudió Estudió durante 2 horas durante 2 horas ayer ayer. (estudiar) . (estudiar) +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ PRESENTE PERFECTO: PRESENTE PERFECTO: para para ya que ya que todavía todavía ya ya incluso incluso PERFECTO PRESENTE O PASADO SIMPLE: PERFECTO PRESENTE O PASADO SIMPLE: Nunca Nunca PASADO SIMPLE: PASADO SIMPLE: ayer ayer último __________ último __________ hace ______ hace ______
- 11. Lista de conectores lingüísticos en Lista de conectores lingüísticos en inglés inglés 1. INTRODUCCIÓN 1. INTRODUCCIÓN Los Los conectores lingüísticos conectores lingüísticos, también denominados , también denominadospalabras de transición palabras de transición, son conjunciones , son conjunciones adverbiales que facilitan y apoyan el lenguaje hablado y adverbiales que facilitan y apoyan el lenguaje hablado y escrito. Se utilizan para comenzar oraciones, escrito. Se utilizan para comenzar oraciones, conectar ideas o argumentos y concluir discursos. Por conectar ideas o argumentos y concluir discursos. Por su importancia para su importancia para mejorar nuestro inglé mejorar nuestro inglés s, , a a continuación veremos una lista de continuación veremos una lista de los conectores más importantes los conectores más importantes organizados por categorías. organizados por categorías. Espero que os resulte útil. Espero que os resulte útil. 2. CONECTORES LINGÜÍSTICO EN INGLÉS POR CATEGORÍAS 2. CONECTORES LINGÜÍSTICO EN INGLÉS POR CATEGORÍAS 2.1. Hablando sobre el presente, la 2.1. Hablando sobre el presente, la actualidad actualidad Hoy en día Hoy en día: Nowadays : Nowadays Actualmente Actualmente: Currently, at present, at the : Currently, at present, at the present time, now, these days, in this day and present time, now, these days, in this day and age age 2.2. Hablando sobre el pasado 2.2. Hablando sobre el pasado Hace mucho tiempo Hace mucho tiempo: A long time ago : A long time ago En la antiguedad En la antiguedad: In ancient times : In ancient times Hace poco tiempo Hace poco tiempo: Not long ago : Not long ago En tiempos pasados En tiempos pasados: In former times : In former times Antiguamente Antiguamente: Formerly : Formerly En los viejos tiempos En los viejos tiempos: In the old days : In the old days 2.3. Dando un ejemplo o una 2.3. Dando un ejemplo o una razón adicional razón adicional Además Además: in addition, what’s more, : in addition, what’s more, besides, besides, furthermore, furthermore, moreover moreover Además de esto Además de esto: Besides this : Besides this También También: Also, besides : Also, besides Es más Es más: Moreover : Moreover Lo que es más Lo que es más: What’s more : What’s more 2.4. Diciendo la verdad 2.4. Diciendo la verdad Para decir la verdad, para ser sincero Para decir la verdad, para ser sincero: : To tell the truth To tell the truth En realidad, a decir verdad En realidad, a decir verdad: In fact : In fact Realmente, en realidad Realmente, en realidad: Actually* : Actually* *NOTA: Actually no debe confundirse con *NOTA: Actually no debe confundirse con “actualmente”. Para tal fin “actualmente”. Para tal fin es más común utilizar es más común utilizar los ejemplos del apartado 2.1. los ejemplos del apartado 2.1. 2.5. Dando información en contra de las 2.5. Dando información en contra de las expectativas expectativas Sin embargo, no obstante Sin embargo, no obstante: However, : However, nevertheless, all the same, still nevertheless, all the same, still Aún así Aún así: Even so : Even so A pesar de que, a pesar de todo A pesar de que, a pesar de todo: : notwithstanding, all the same, still, notwithstanding, all the same, still, regardless regardless 2.6. Mostrando el lado positivo y negativo de 2.6. Mostrando el lado positivo y negativo de un asunto un asunto Afortunadamente, por fortuna Afortunadamente, por fortuna: : Fortunately, happily Fortunately, happily Felizmente, alegremente Felizmente, alegremente: Happily : Happily Desafortunadamente, Desafortunadamente, desgraciadamente desgraciadamente: Unfortunately, sadly : Unfortunately, sadly Tristemente Tristemente: Sadly : Sadly 2.7. Aportando similitudes y diferencias 2.7. Aportando similitudes y diferencias Igualmente Igualmente: Likewise : Likewise Del mismo modo Del mismo modo: In the same way, : In the same way, similarly similarly Por otra parte, por otro lado Por otra parte, por otro lado: On the : On the other hand, in contrast other hand, in contrast De todos modos De todos modos: Anyway : Anyway 2.8. Declarando que algo es cierto 2.8. Declarando que algo es cierto o o probablemente cierto probablemente cierto Obviamente, evidentemente Obviamente, evidentemente: Obviously : Obviously Indudablemente Indudablemente: Undoubtedly : Undoubtedly Seguramente Seguramente: Surely : Surely Verdaderamente, en realidad, en Verdaderamente, en realidad, en efecto efecto: Indeed : Indeed Claramente, aparenetemente, al Claramente, aparenetemente, al parecer parecer: Apparently : Apparently Posiblemente Posiblemente: Possibly : Possibly 2.9. Mostrando una conclusión, 2.9. Mostrando una conclusión, consecuencia o un resultado directo consecuencia o un resultado directo Por lo tanto, Por lo tanto, por consiguiente por consiguiente: : Therefore Therefore Consecuentemente, por consiguiente Consecuentemente, por consiguiente: : Consequently Consequently En consecuencia, así En consecuencia, así: Thus, as a result : Thus, as a result
- 12. MODAL VERBS MODAL VERBS Qué es un modal verb Qué es un modal verb Empecemos por el principio. Un verbo modal es Empecemos por el principio. Un verbo modal es un grupo especial de verbos auxiliares. Es decir, un grupo especial de verbos auxiliares. Es decir, auxilian/complementan a otro verbo otorgándole nuevos sentidos. Son diferentes de la mayoría de otros auxilian/complementan a otro verbo otorgándole nuevos sentidos. Son diferentes de la mayoría de otros verbos en inglés en 4 aspectos. verbos en inglés en 4 aspectos. Las 4 claves para identificar un Las 4 claves para identificar un verbo modal verbo modal I. Infinitivos sin “to” I. Infinitivos sin “to” Después de los verbos modales, usamos infinitivos sin “to”. Después de los verbos modales, usamos infinitivos sin “to”. Mientras que después del resto de verbos, Mientras que después del resto de verbos, los usamos siempre con “to”. los usamos siempre con “to”. – – Can I use your phone? ( y no Can I to use…) Can I use your phone? ( y no Can I to use…) En cambio, sí lo En cambio, sí lo usamos en usamos en – – I want to use her phone. I want to use her phone. Más ejemplos con verbos modales: Más ejemplos con verbos modales: – – Joe can’t swim. Joe can’t swim. – – I may be out tonight. I may be out tonight. Por el contrario los Por el contrario los verbos que no son modales: verbos que no son modales: – – I’d like to go home. I’d like to go home. – – Joe seems to have a cold. Joe seems to have a cold. II. Sin -s II. Sin -s Los verbos modales no tienen -s en la tercera persona del singular (la forma he/she/it). El resto de Los verbos modales no tienen -s en la tercera persona del singular (la forma he/she/it). El resto de verbos sí. verbos sí. – – John can speak Korean (y no John cans…). En cambio, John can speak Korean (y no John cans…). En cambio, sí lo usamos en sí lo usamos en – – John knows my father. John knows my father. Más ejemplos con verbos modales: Más ejemplos con verbos modales: – – Barbara may be late. Barbara may be late. – – This must be your coat. This must be your coat. Por el contrario, los verbos que no son Por el contrario, los verbos que no son modales: modales: – – Ann seems to be ill. Ann seems to be ill. – – The cat wants to go out The cat wants to go out III. Sin do III. Sin do Las preguntas y las oraciones negativas con modal verbs van sin el Las preguntas y las oraciones negativas con modal verbs van sin el “do“. Con el r “do“. Con el resto de verbos, sí lo esto de verbos, sí lo empleamos. empleamos. – – Can you help me? (y no Do you can help me?). En cambio, sí lo Can you help me? (y no Do you can help me?). En cambio, sí lo usamos en usamos en – – Do you know my friend Do you know my friend Jeremy? Jeremy? Otro ejemplo (con una oración negativa): Otro ejemplo (con una oración negativa): – – You must not tell Philip. You must not tell Philip. Por el contrario, con un verbo no modal: Por el contrario, con un verbo no modal: – – Sally doesn’t cook very well. Sally doesn’t cook very well. IV. Sin infinitivo ni participios IV. Sin infinitivo ni participios Los verbos modales no tienen forma de inf Los verbos modales no tienen forma de infinitivo o participio: to initivo o participio: to can, musted. En su lugar, empleamos can, musted. En su lugar, empleamos otros verbos: otros verbos: Por ejemplo, el infinitivo de can equivale a Por ejemplo, el infinitivo de can equivale a – –> be able to; y el de must > be able to; y el de must– –> have to. > have to. Conclusión Conclusión En esta primera aproximación a los modal En esta primera aproximación a los modal verbs tienes que quedarte con cuáles son (el verbs tienes que quedarte con cuáles son (el cuadro del cuadro del principio) y con las 4 principio) y con las 4 diferencias que los hacen especiales. Cuando leas en inglés, fíjate en diferencias que los hacen especiales. Cuando leas en inglés, fíjate en los modal los modal verbs. Si aún no ti verbs. Si aún no tienes un libro que te enganche, hace poco publicamos un post en enes un libro que te enganche, hace poco publicamos un post en el que te el que te recomendamos varios según tu nivel de lectura. recomendamos varios según tu nivel de lectura.