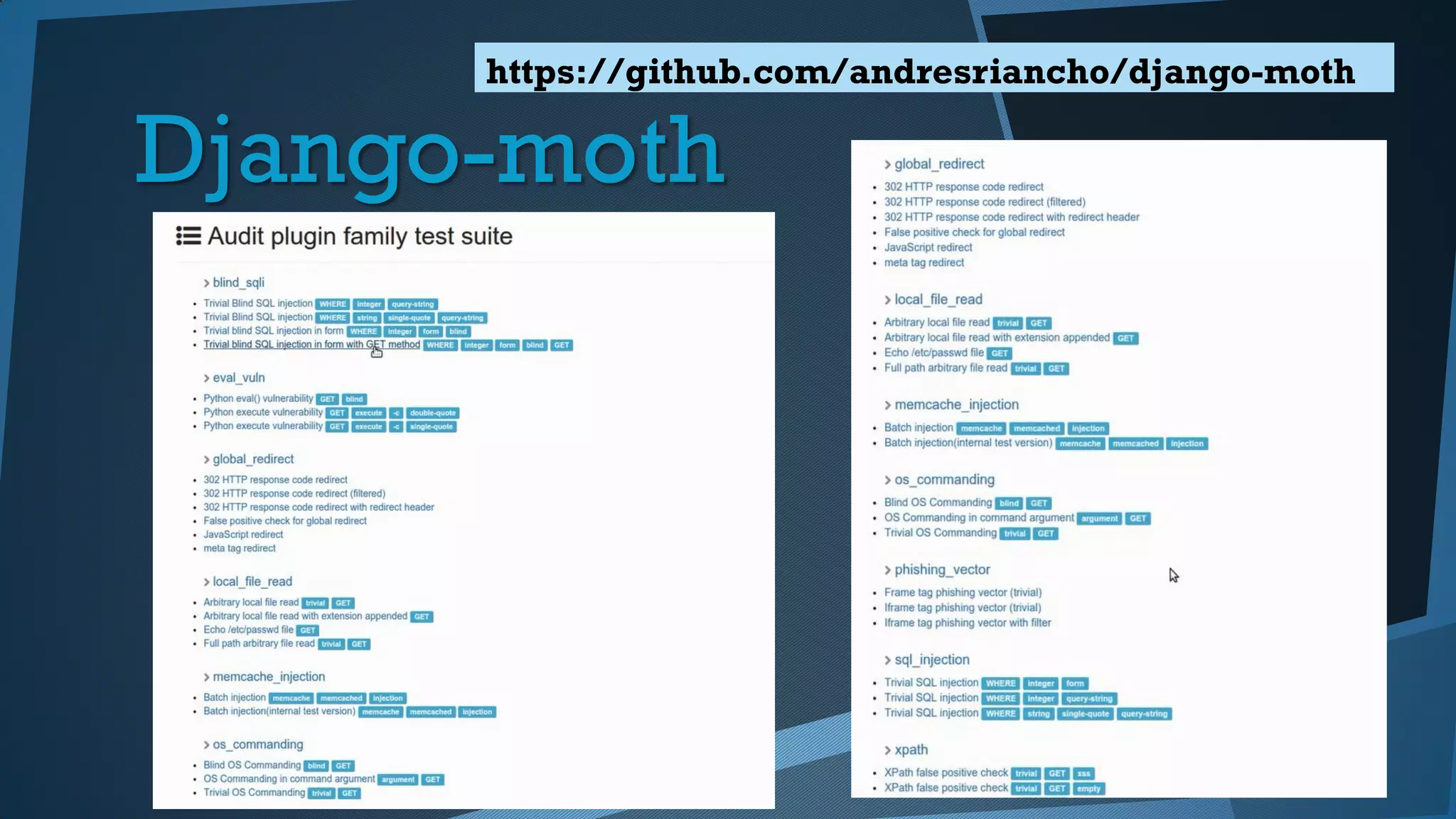
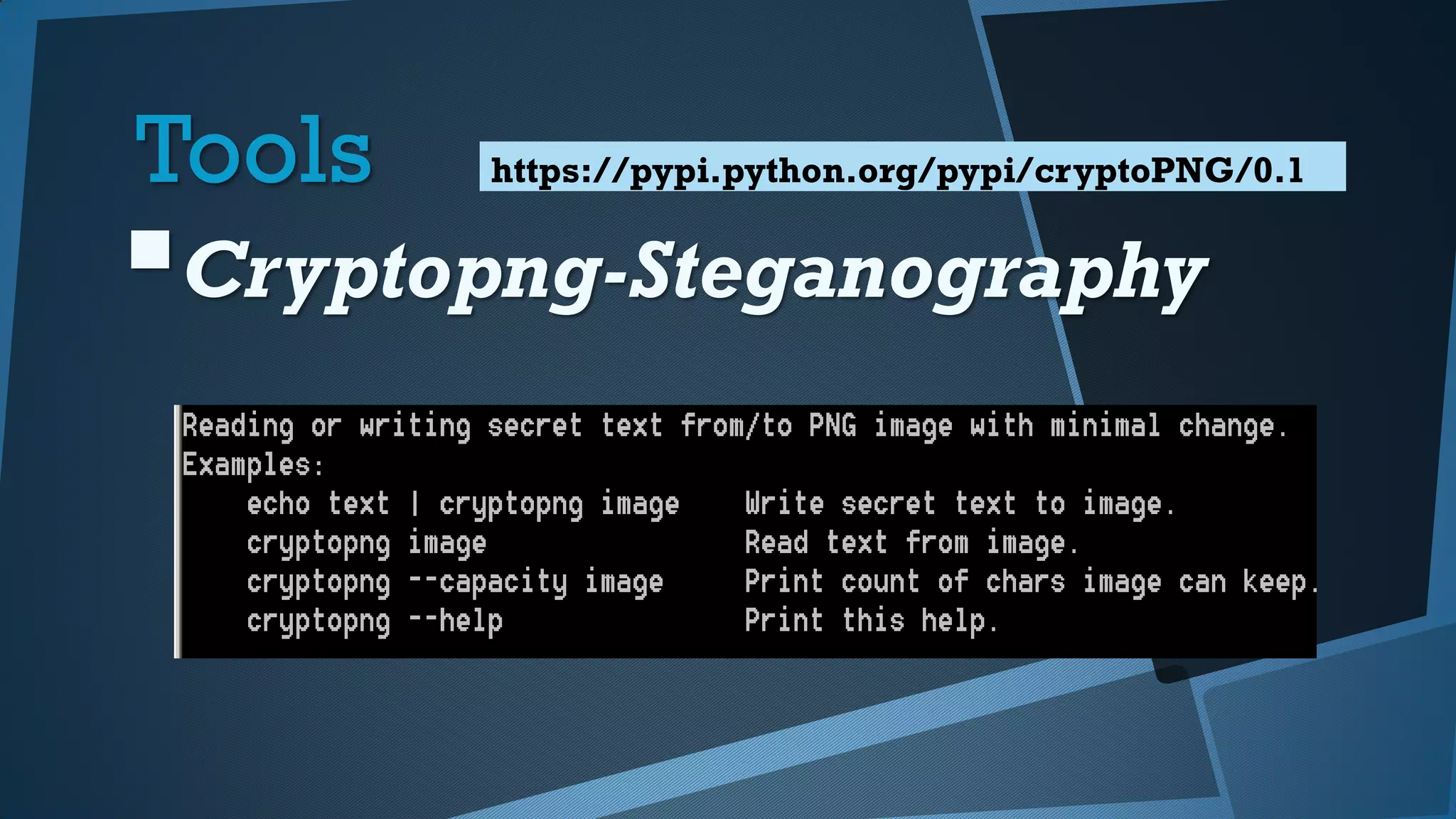
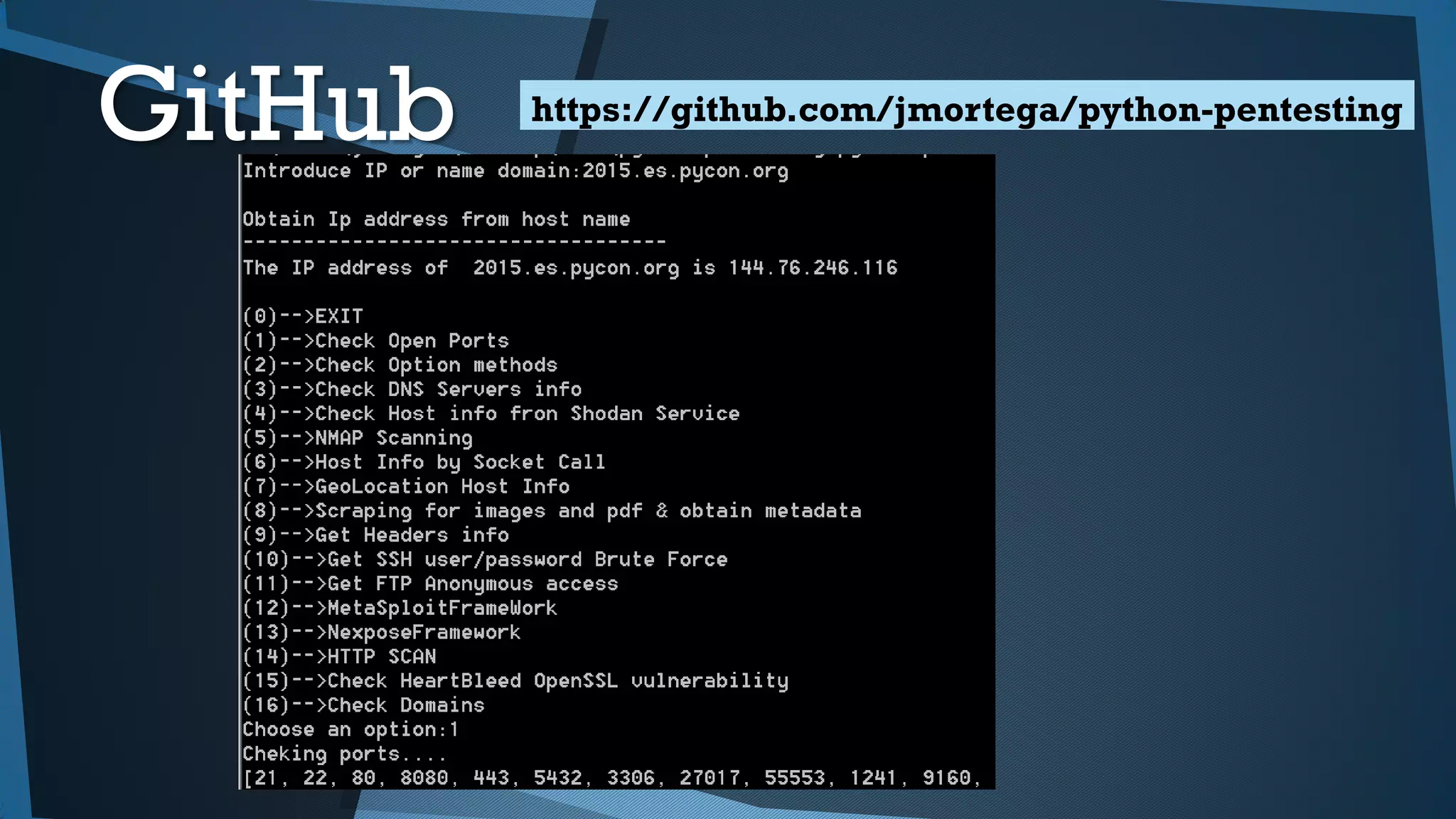
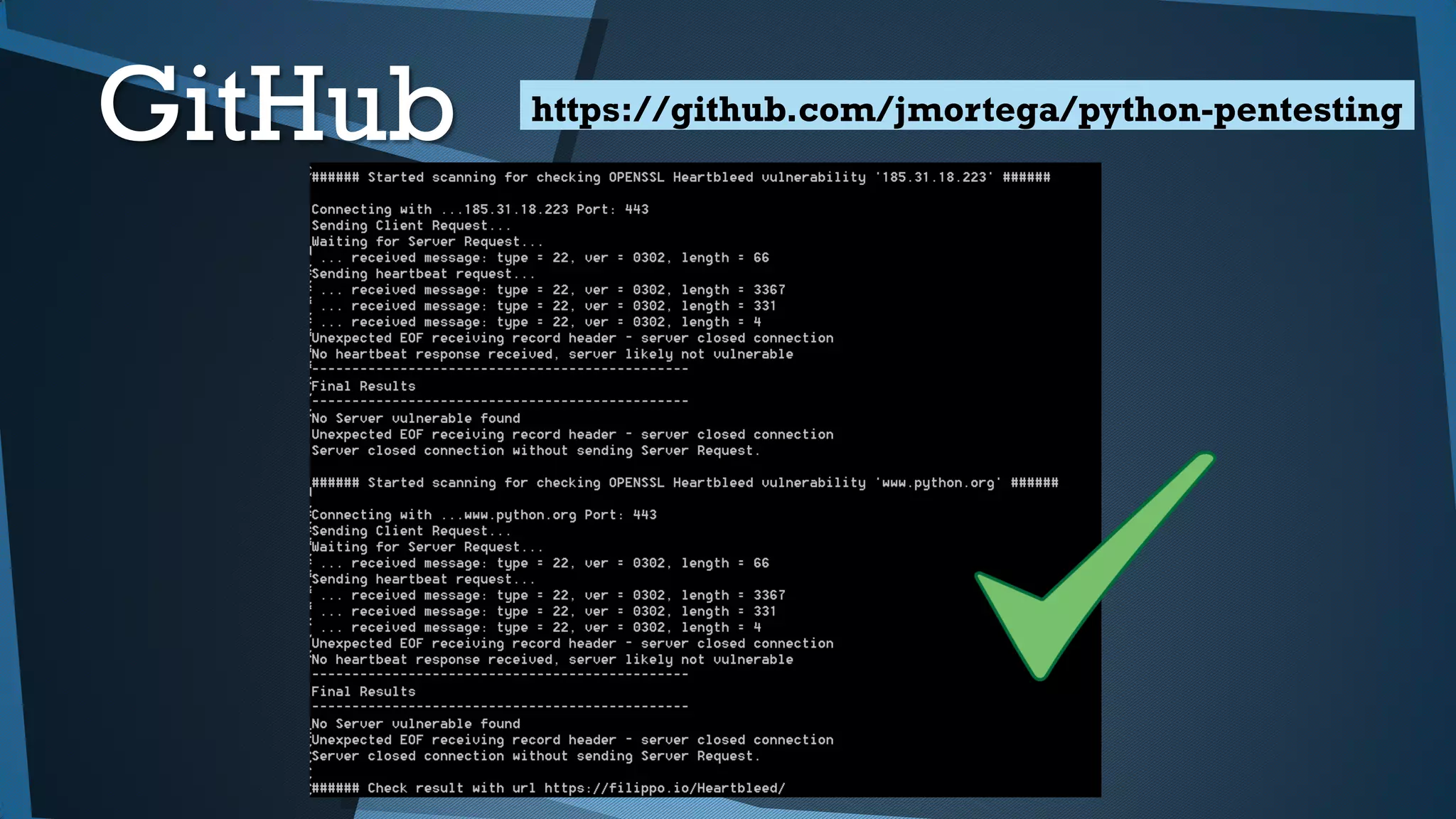
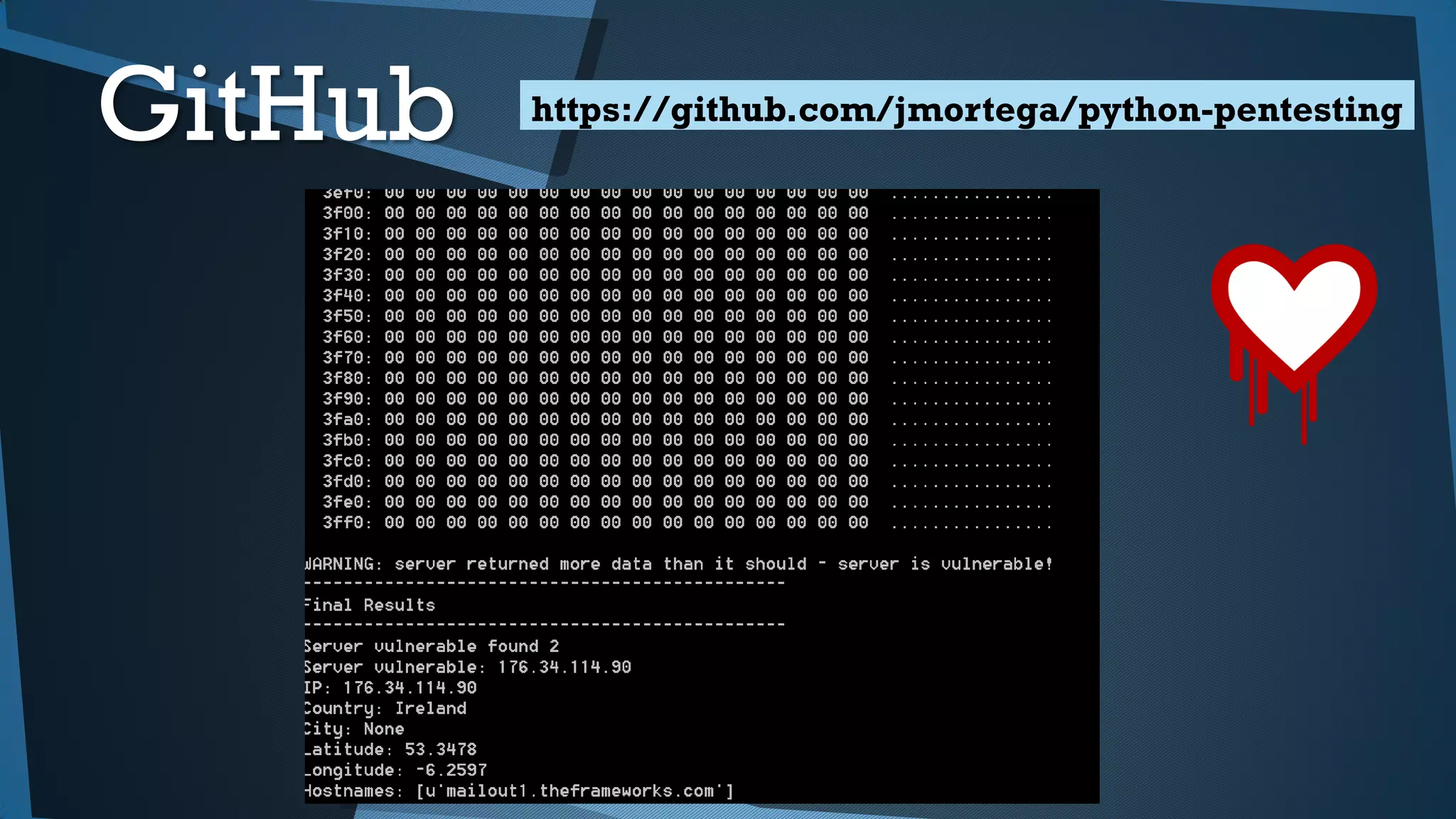
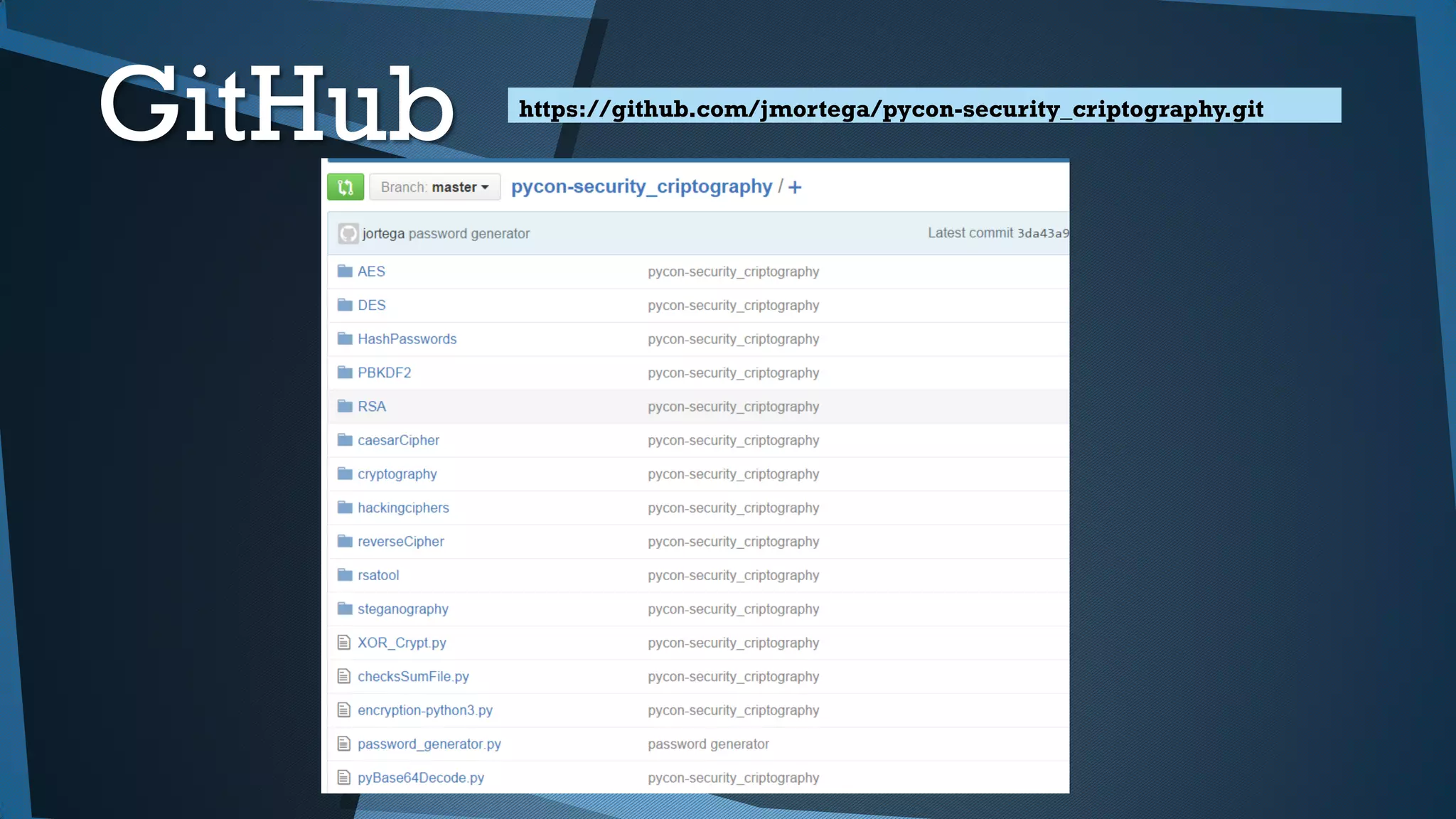
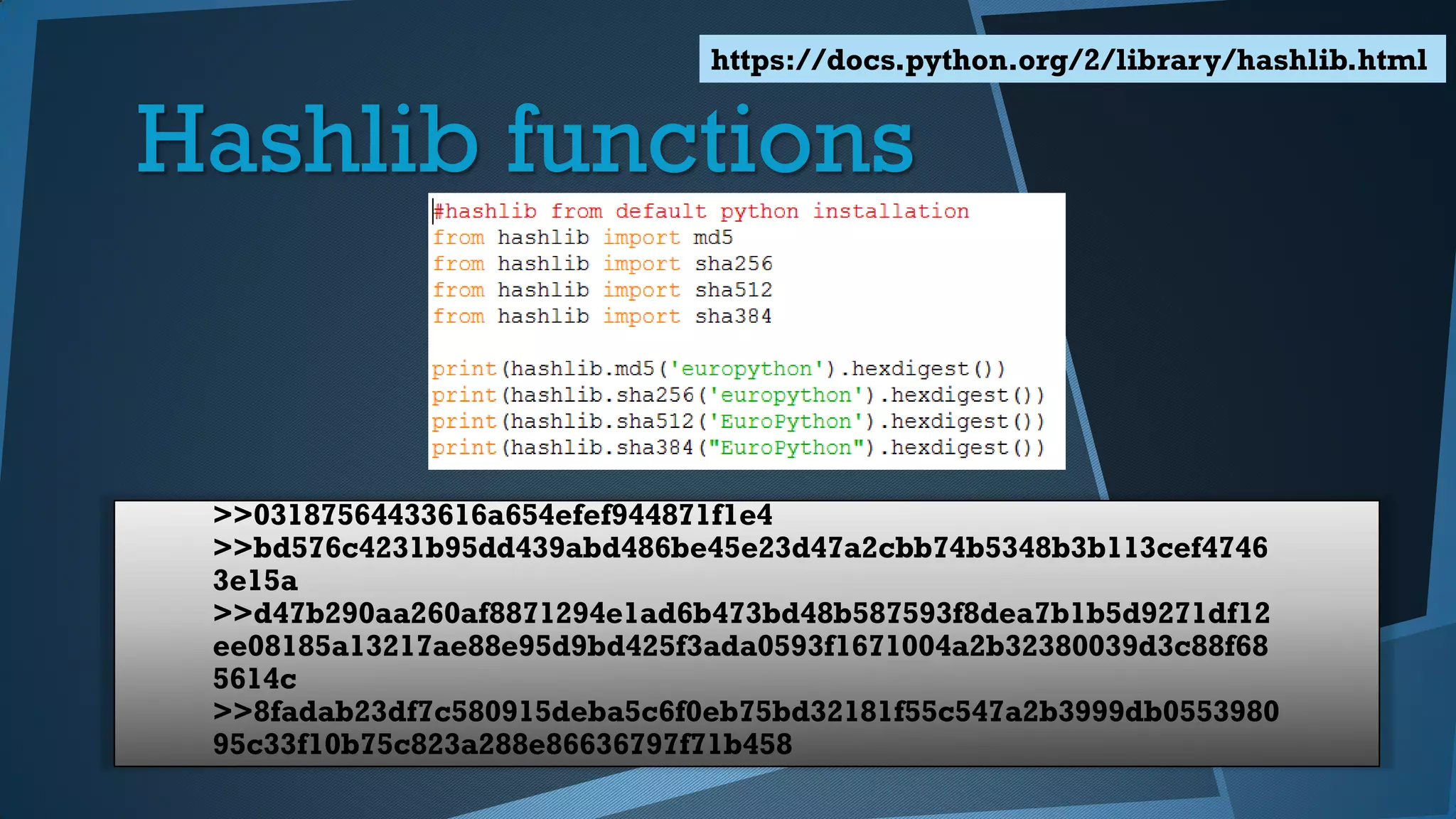
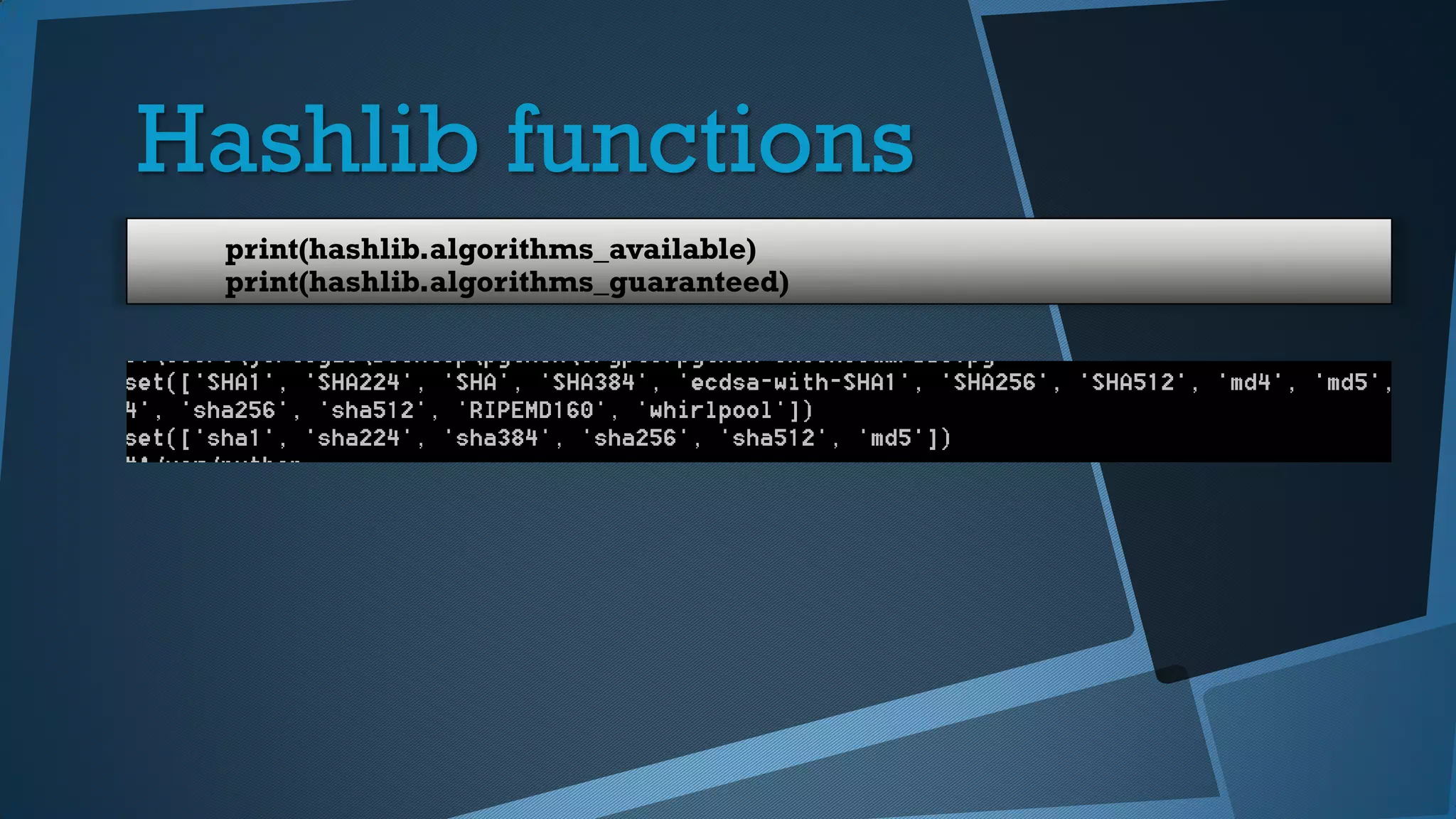
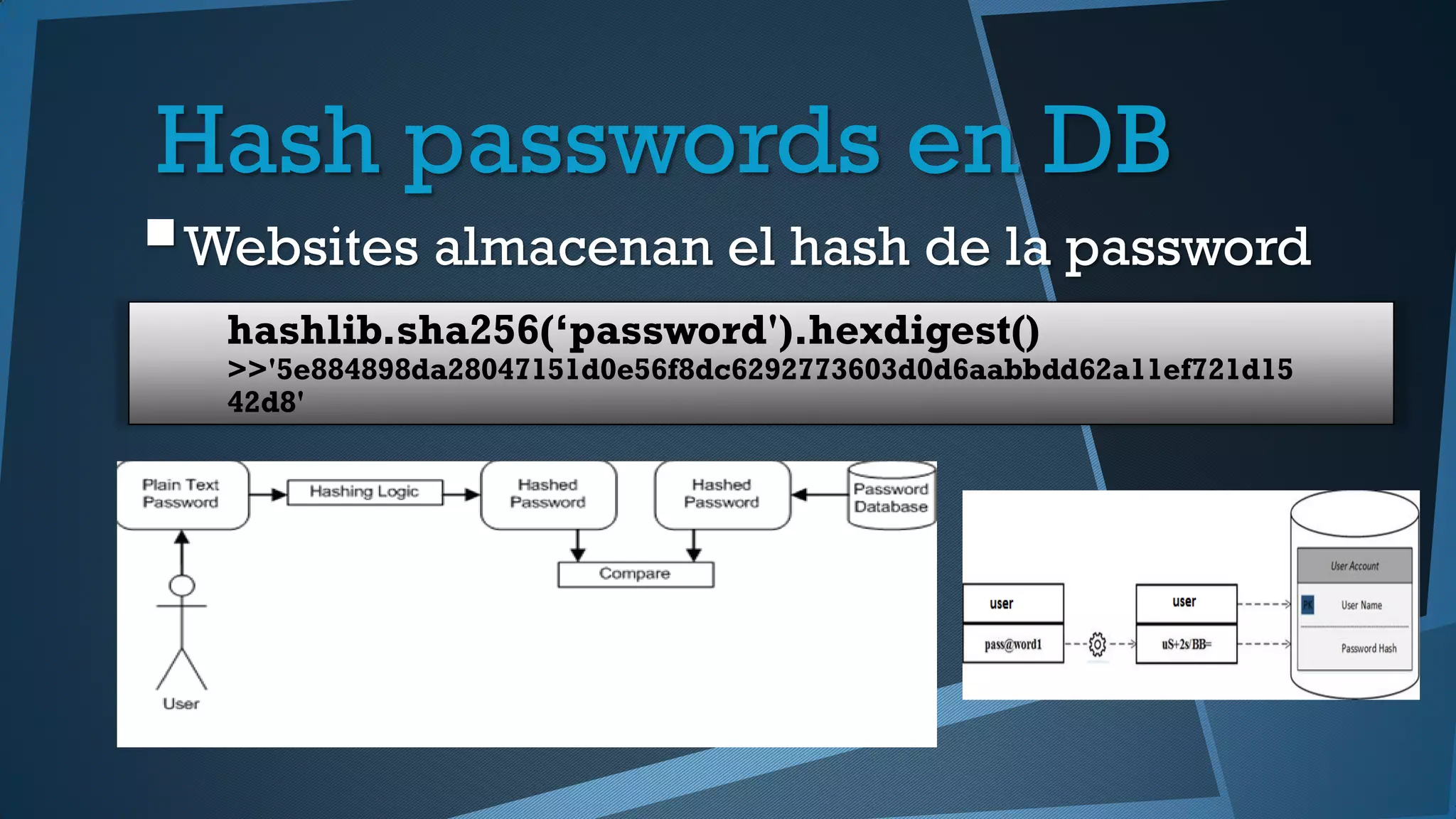
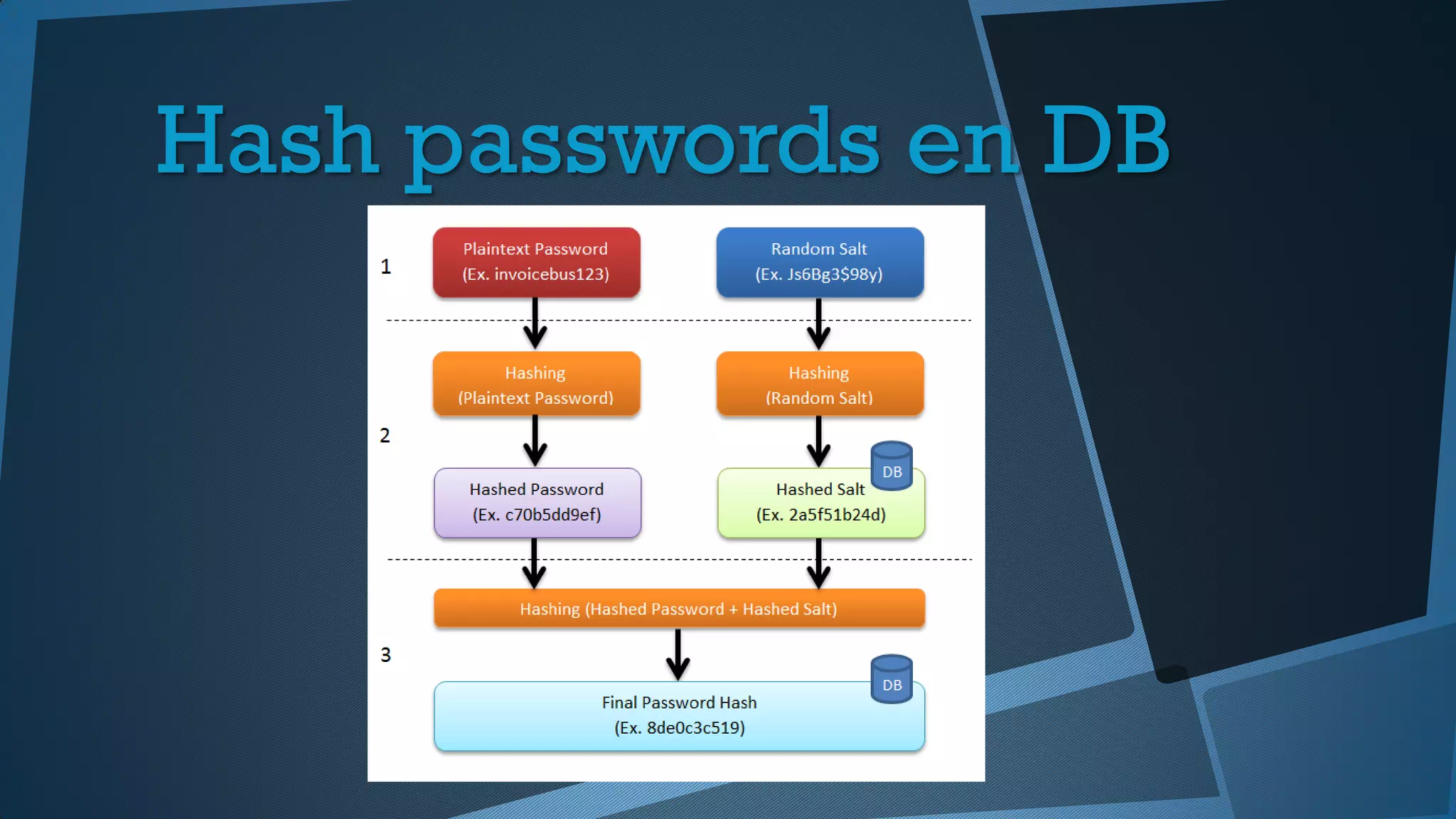
Este documento presenta una introducción a la seguridad y criptografía en Python. Explica conceptos clave como cifrado simétrico y asimétrico, funciones hash, y librerías como PyCrypto y Cryptography. También cubre mejores prácticas de seguridad en Django, incluyendo el almacenamiento seguro de contraseñas, protección contra inyecciones SQL, y el uso de HTTPS.






















![Mejores prácticas
Guardar de forma segura claves secretas y
credenciales
Establecer DEBUG=false en producción en
settings.py
Usar ALLOWED_HOSTS en producción y
asignarle aquellos dominios de los cuales se
tenga control
Limitar accesos admin mediante IP filter
ALLOWED_HOSTS =[*]
ALLOWED_HOSTS =['.yourdomain.com']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonseguridad-151122215411-lva1-app6892/75/Python-Securidad-and-Criptografia-42-2048.jpg)


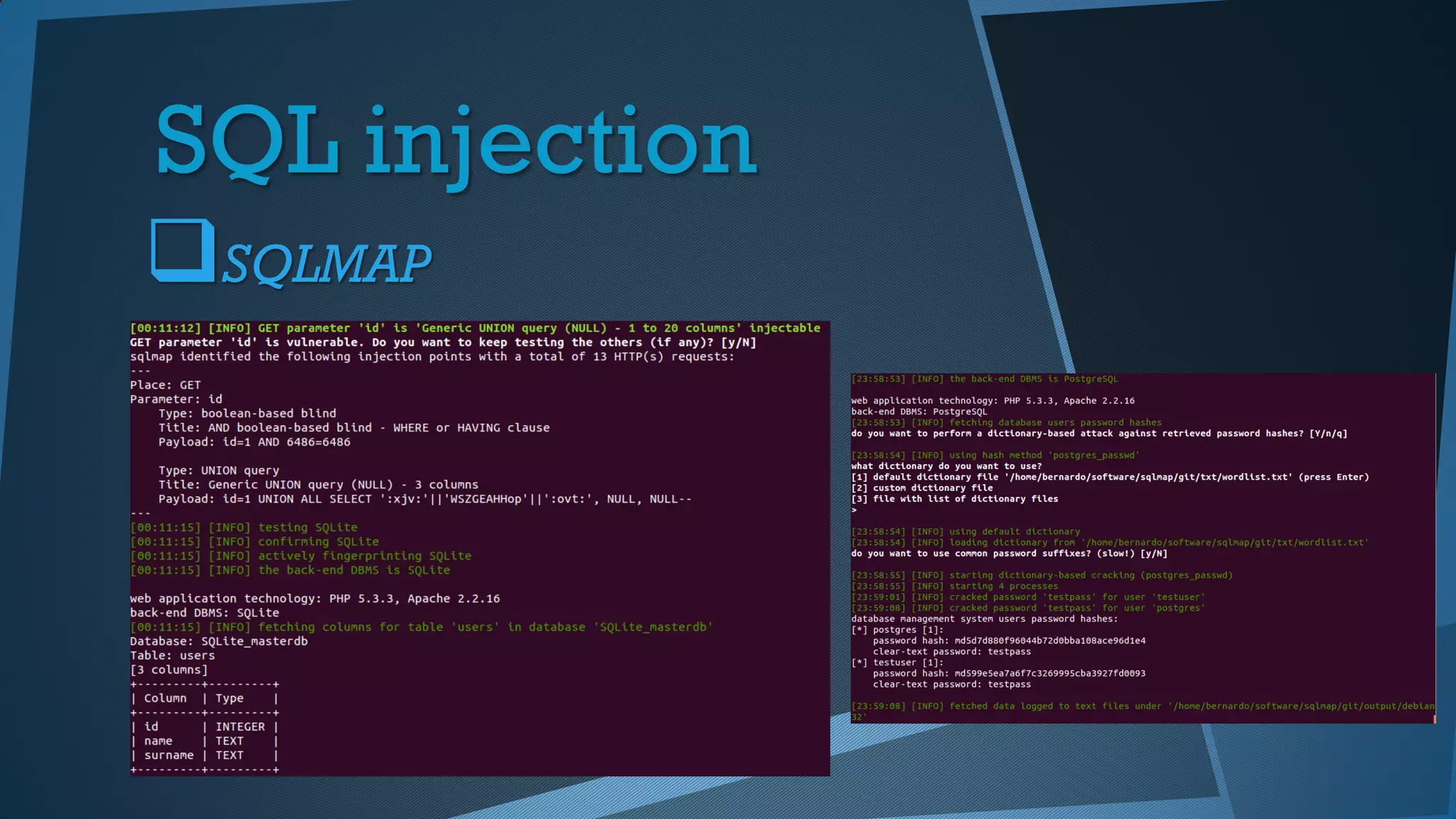
![SQL injection
No confiar en los datos que envía el usuario
Correcto filtrado de los parámetros
Uso de cursores y bind parameter
from django.db import connection
def select_user(request):
user = request.GET['username']
sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = %s"
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, [user])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonseguridad-151122215411-lva1-app6892/75/Python-Securidad-and-Criptografia-45-2048.jpg)

![Cross site Scripting(XSS)
Permite a un atacante obtener información
de la sesión del usuario
Usar el sistema de plantillas de renderizado para escapar los
valores que se pintan en las páginas HTML
from django.shortcuts import render
def render_page(request):
user = request.GET['username']
return render(request, ‘page.html', {‘user’:user})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonseguridad-151122215411-lva1-app6892/75/Python-Securidad-and-Criptografia-48-2048.jpg)