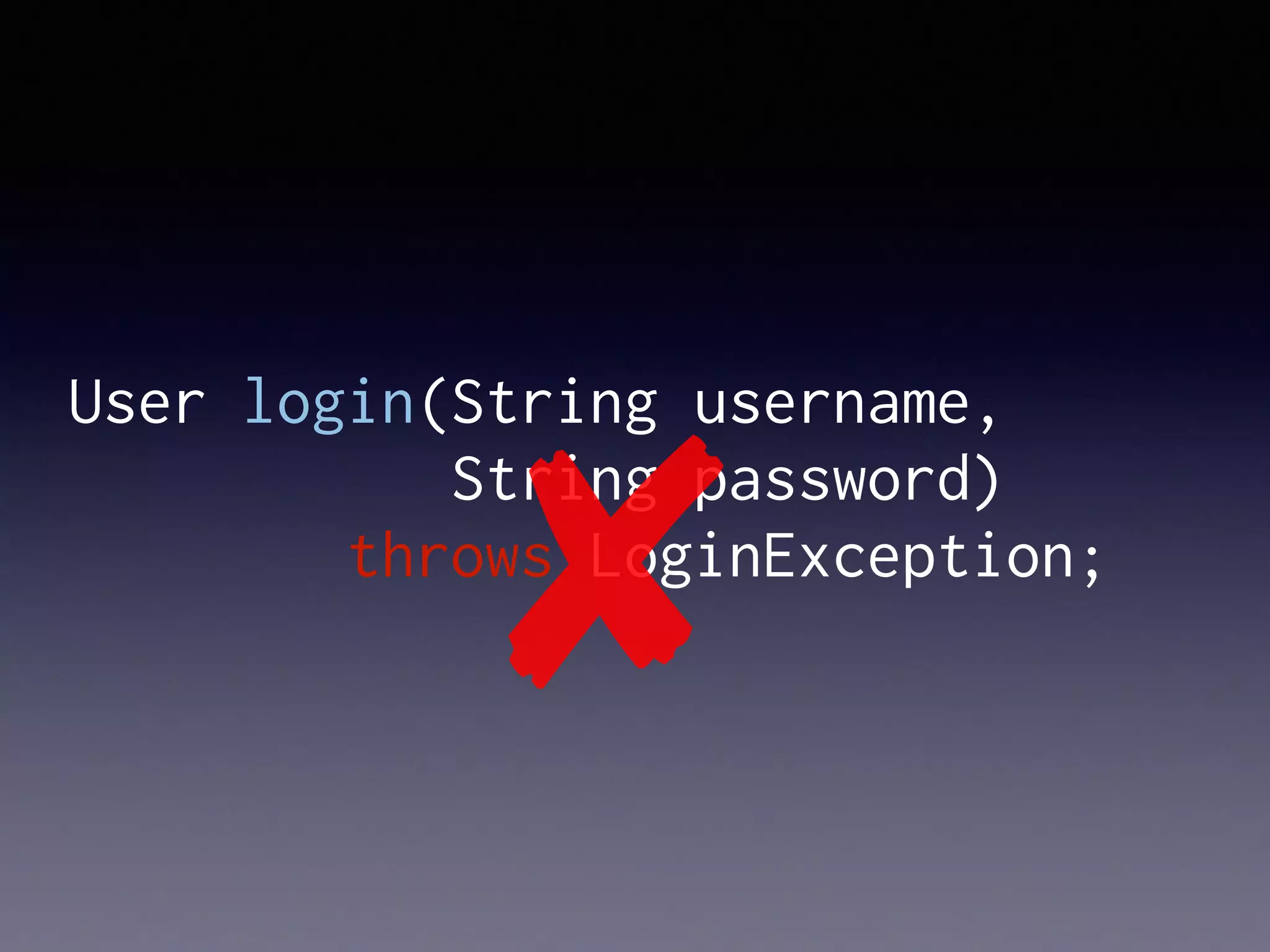
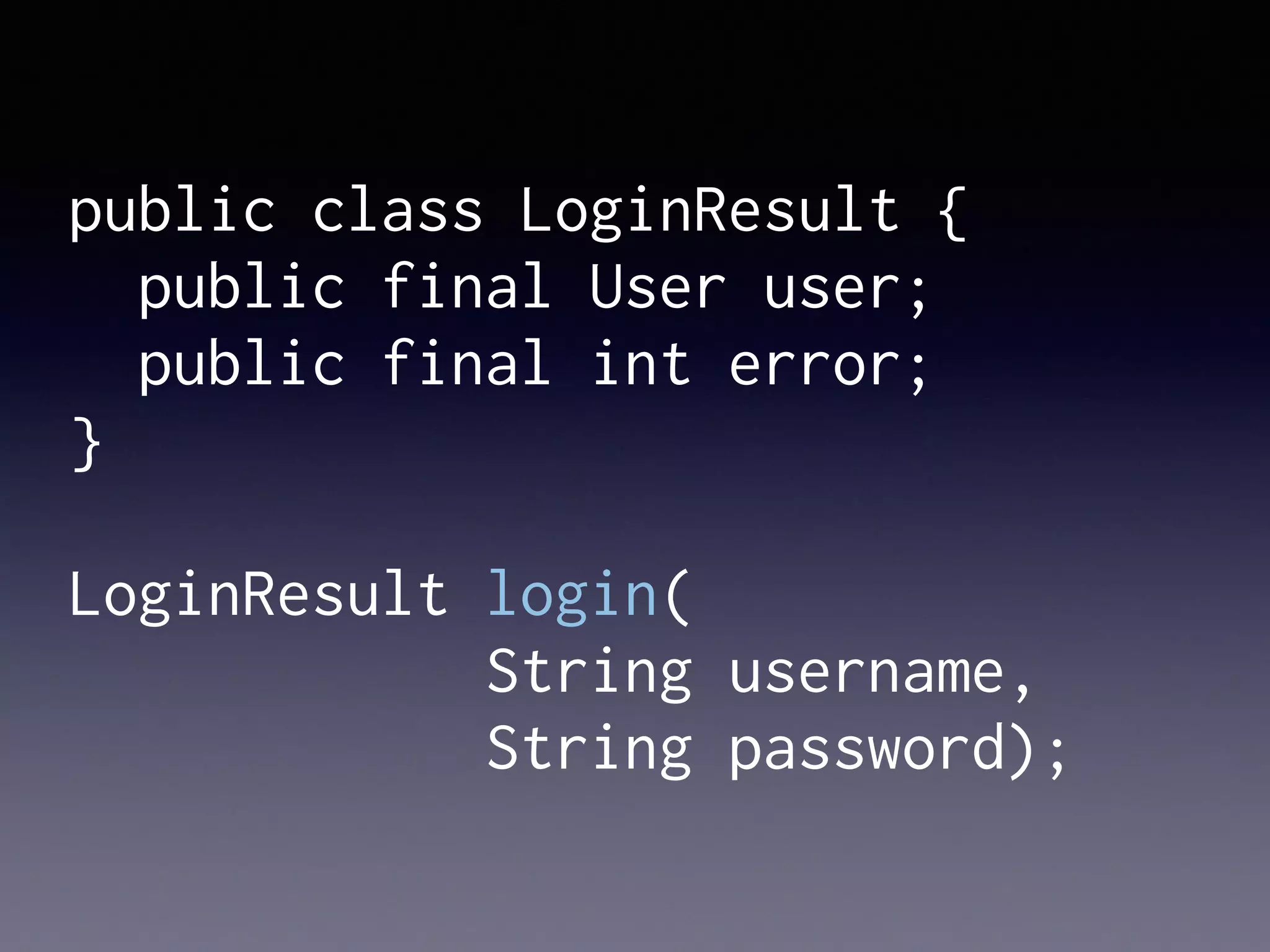
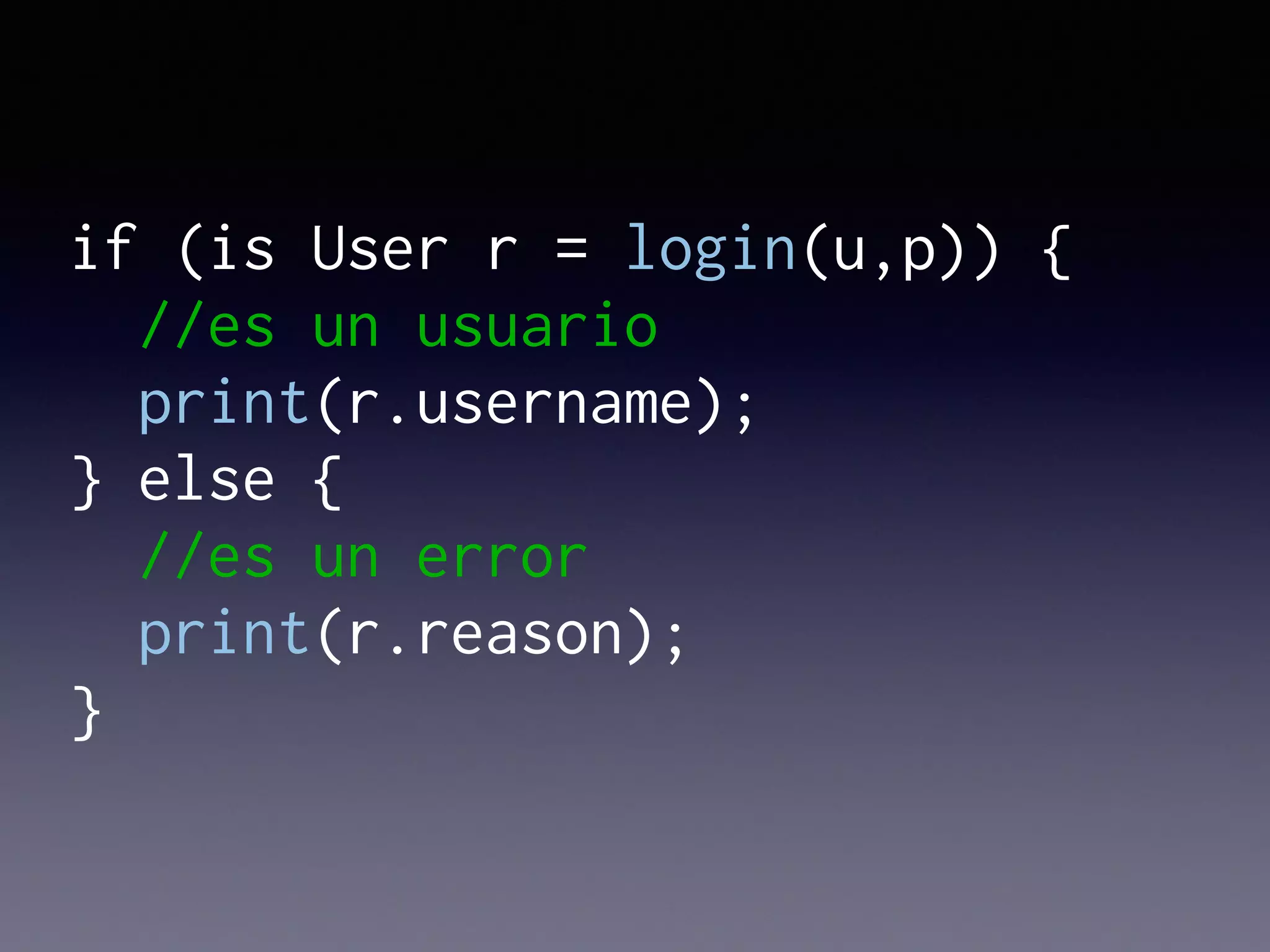
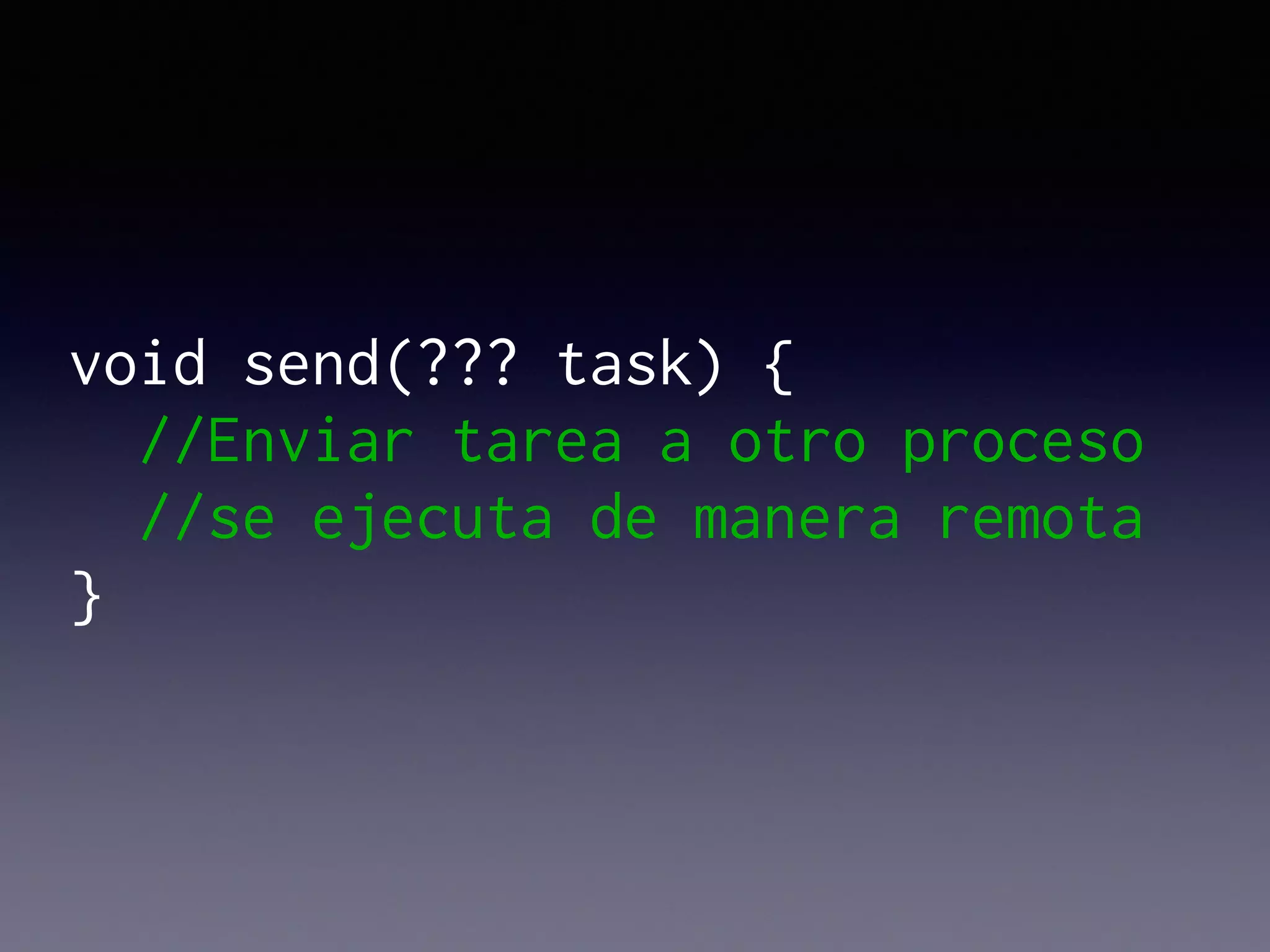
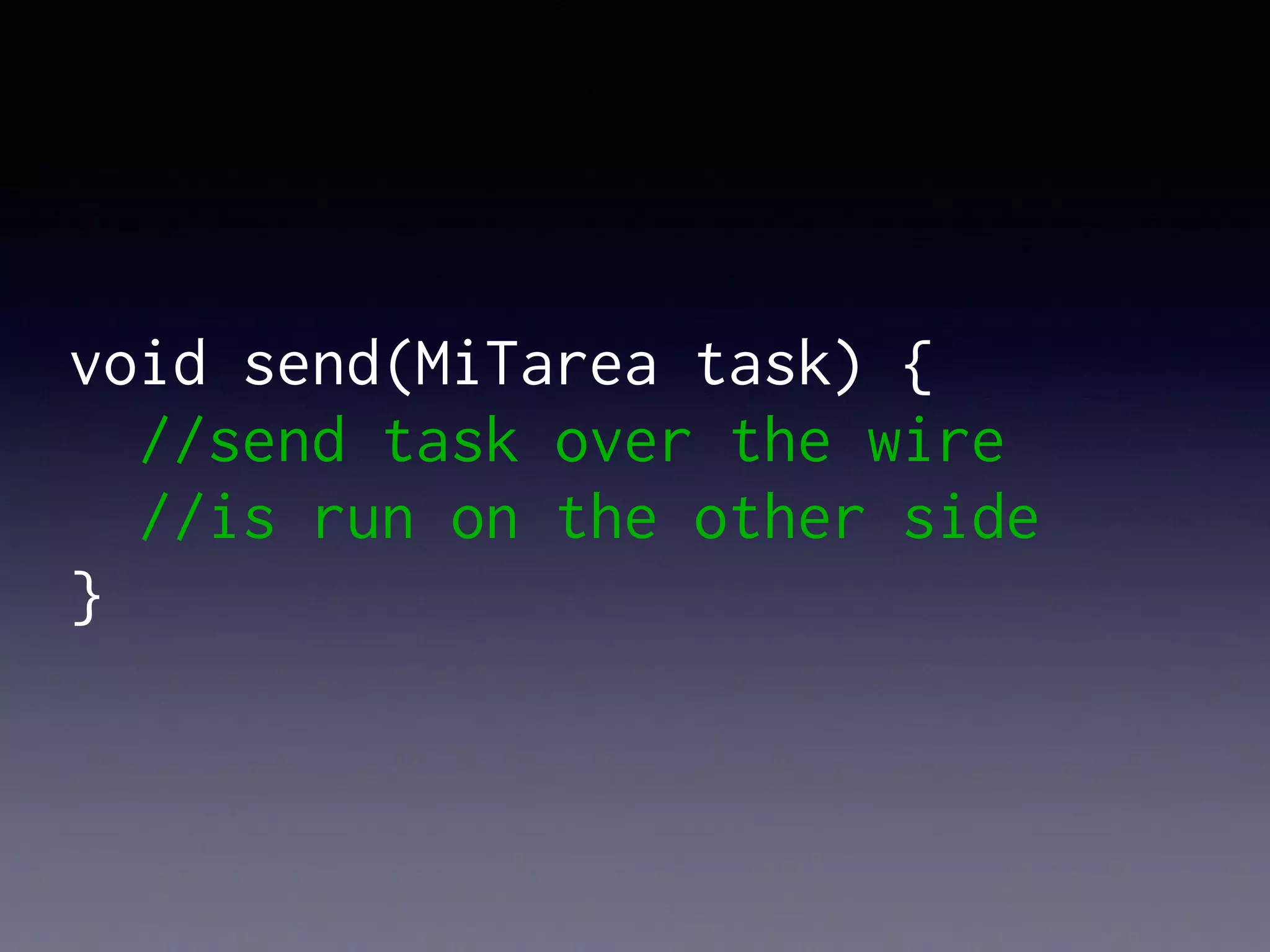
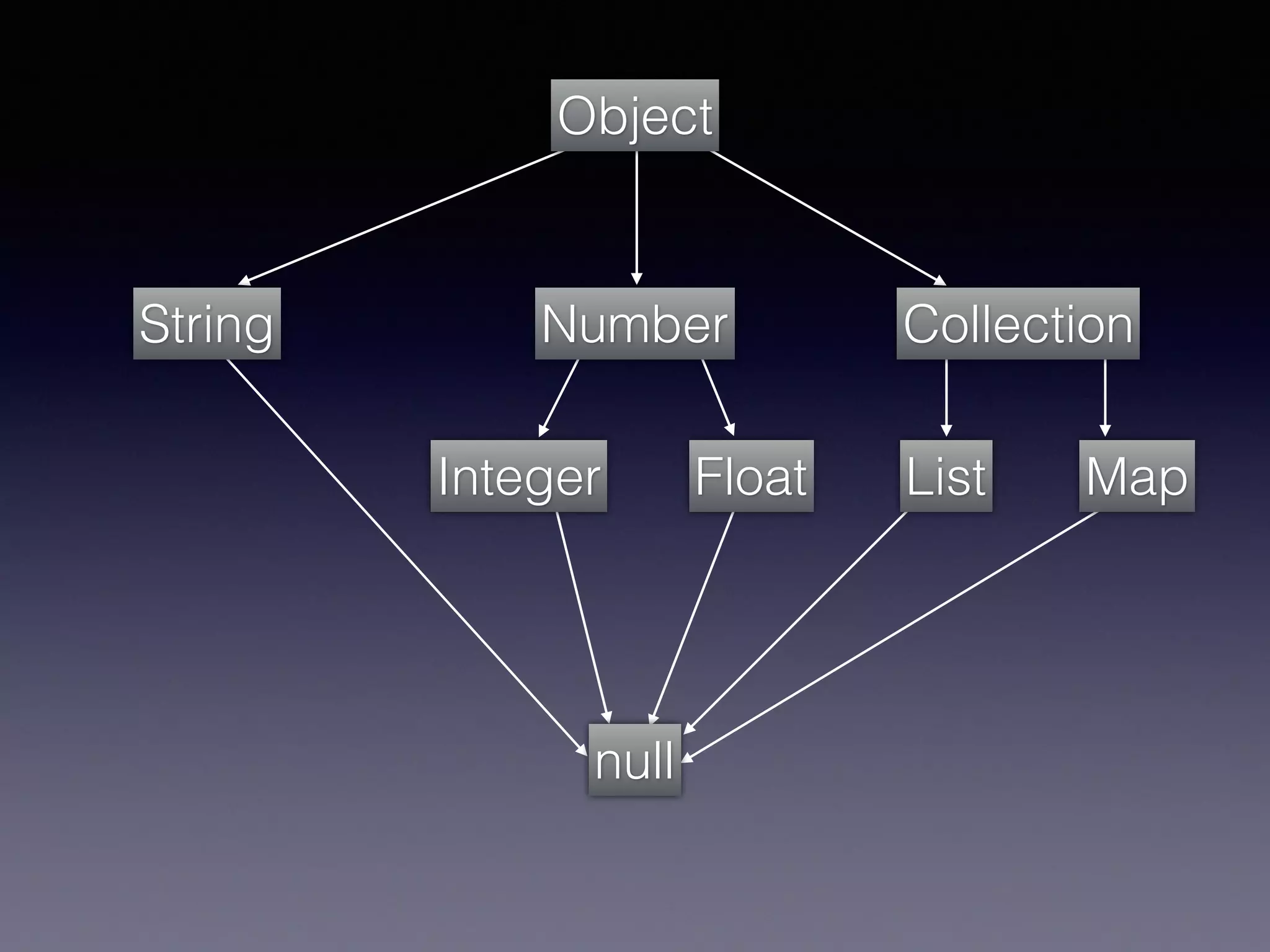
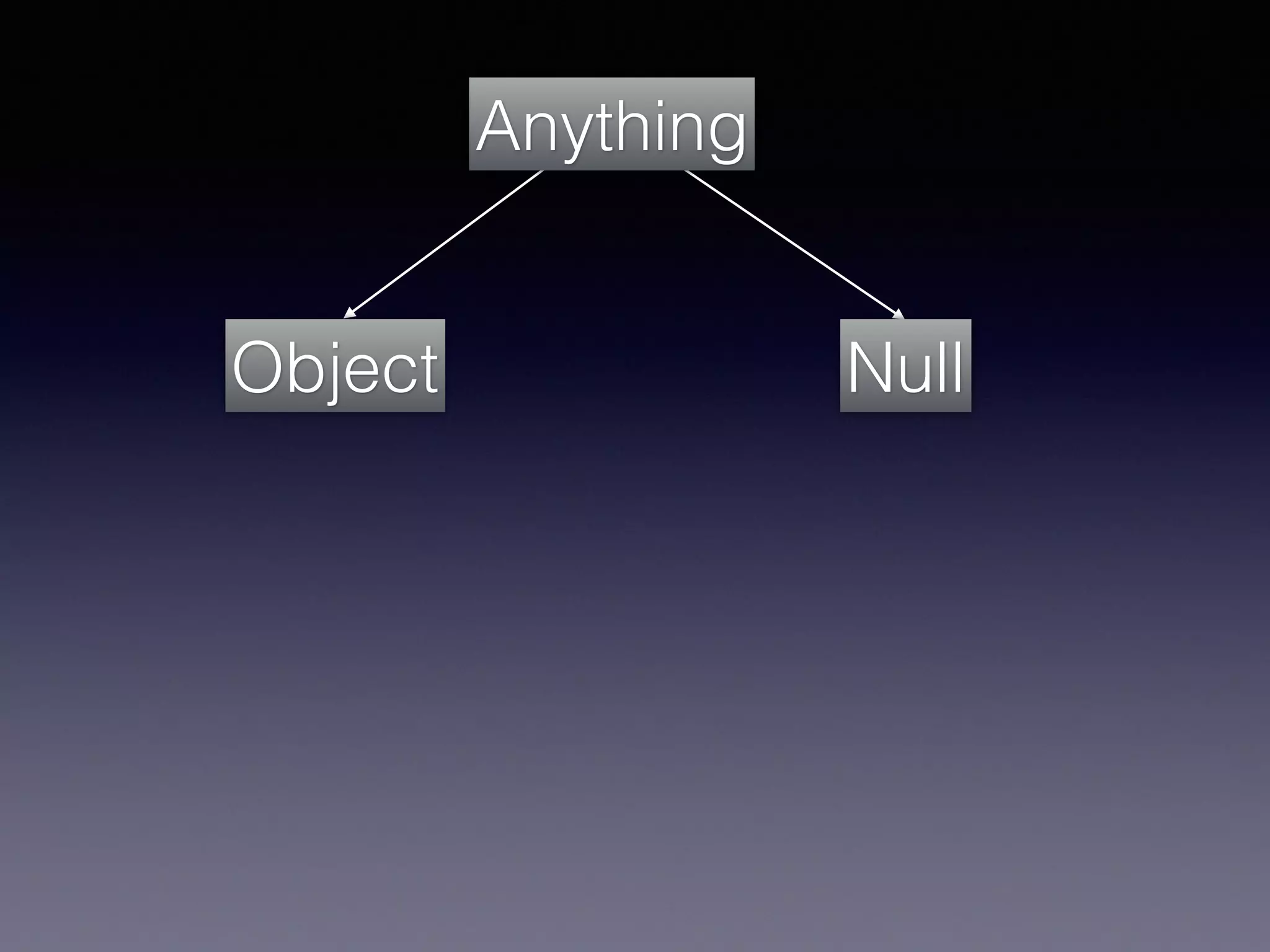
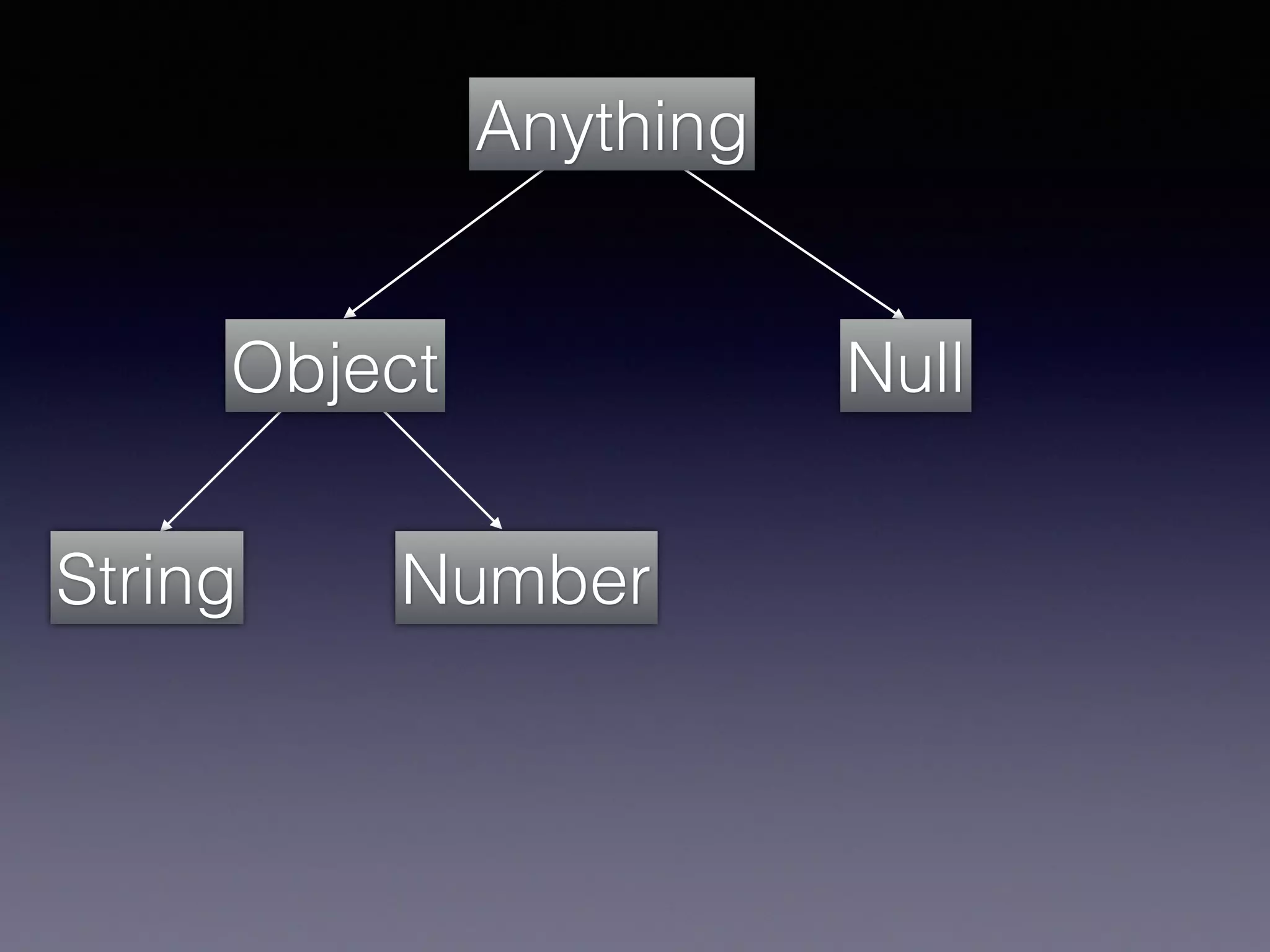
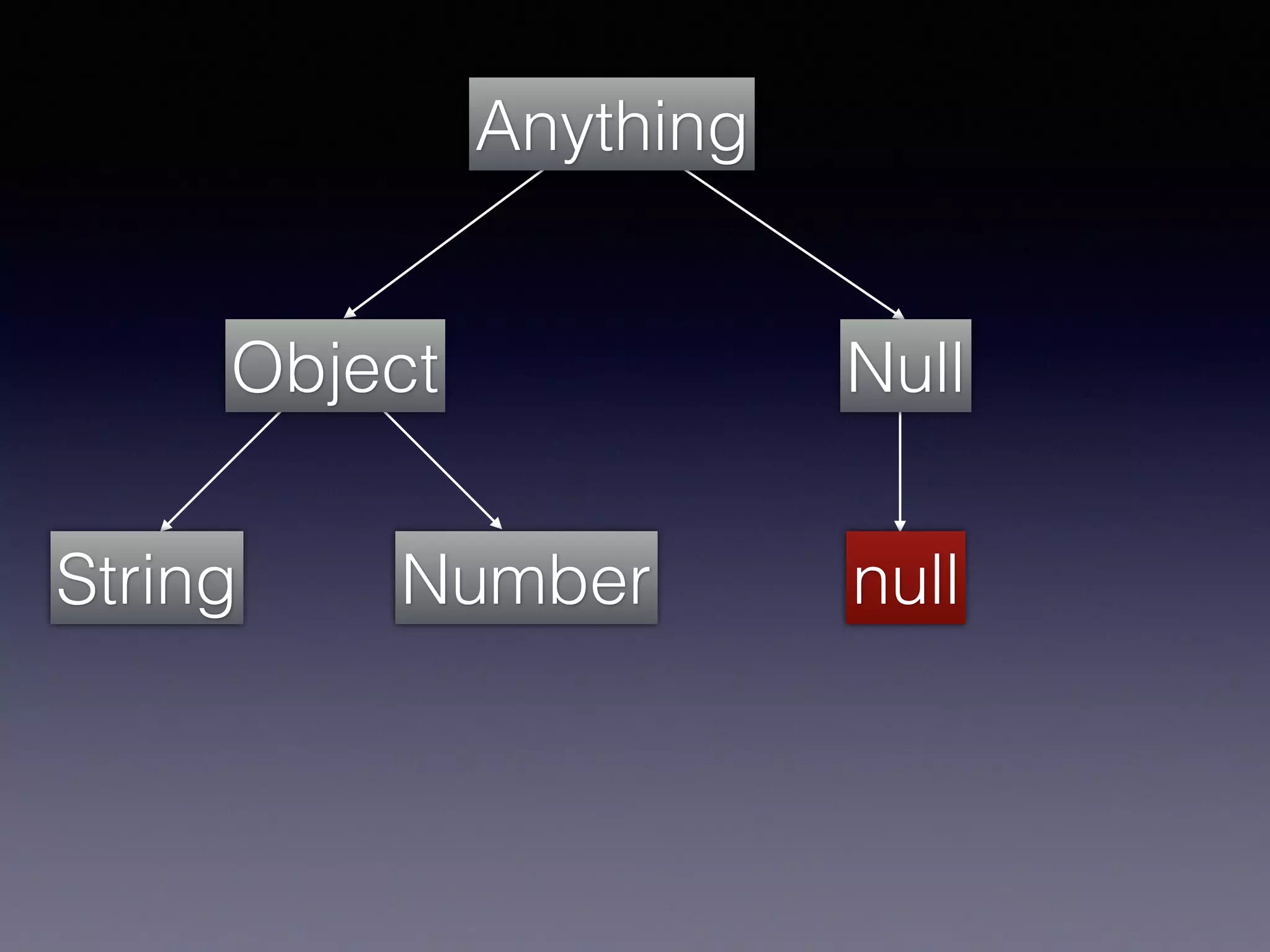
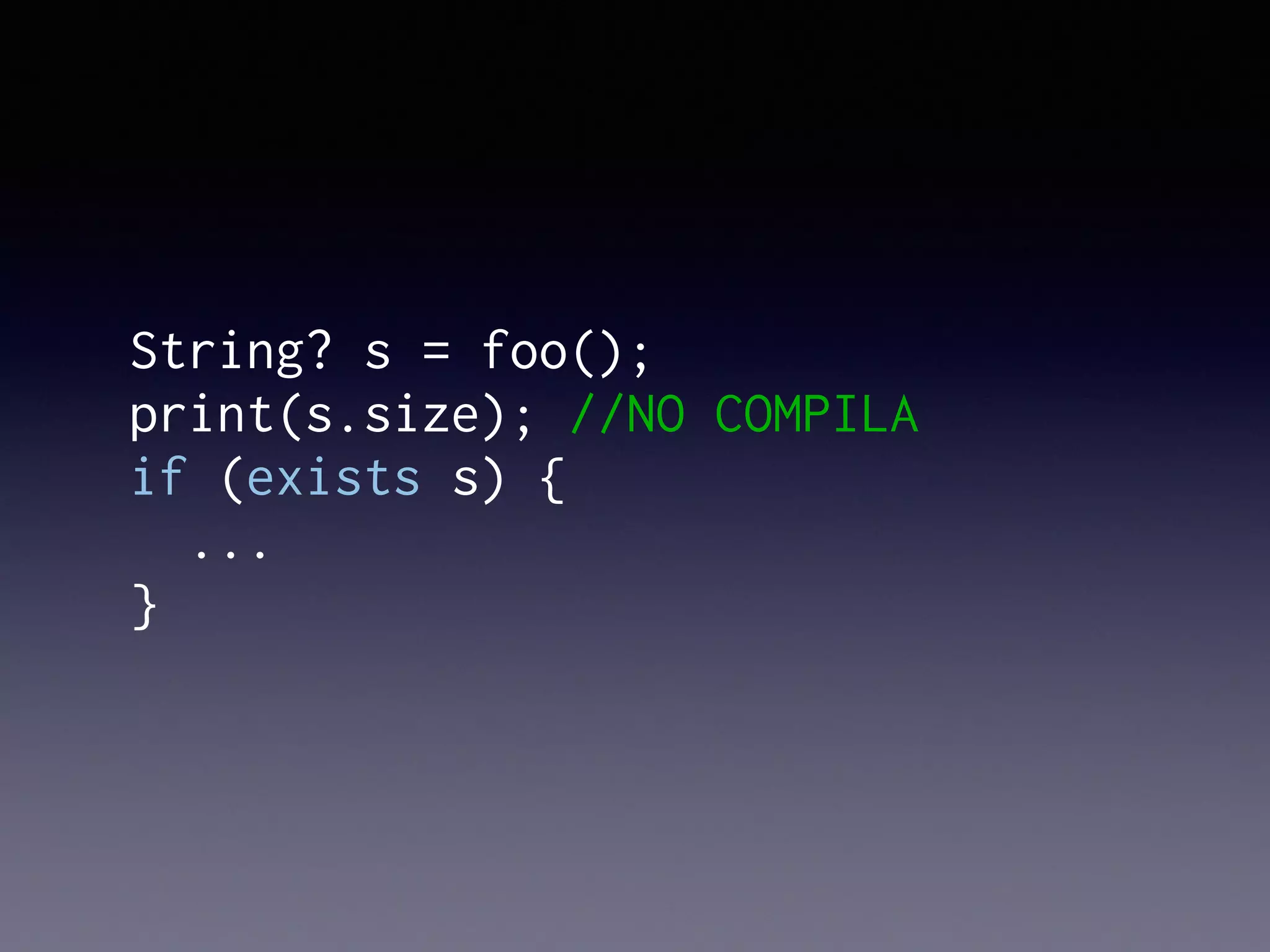
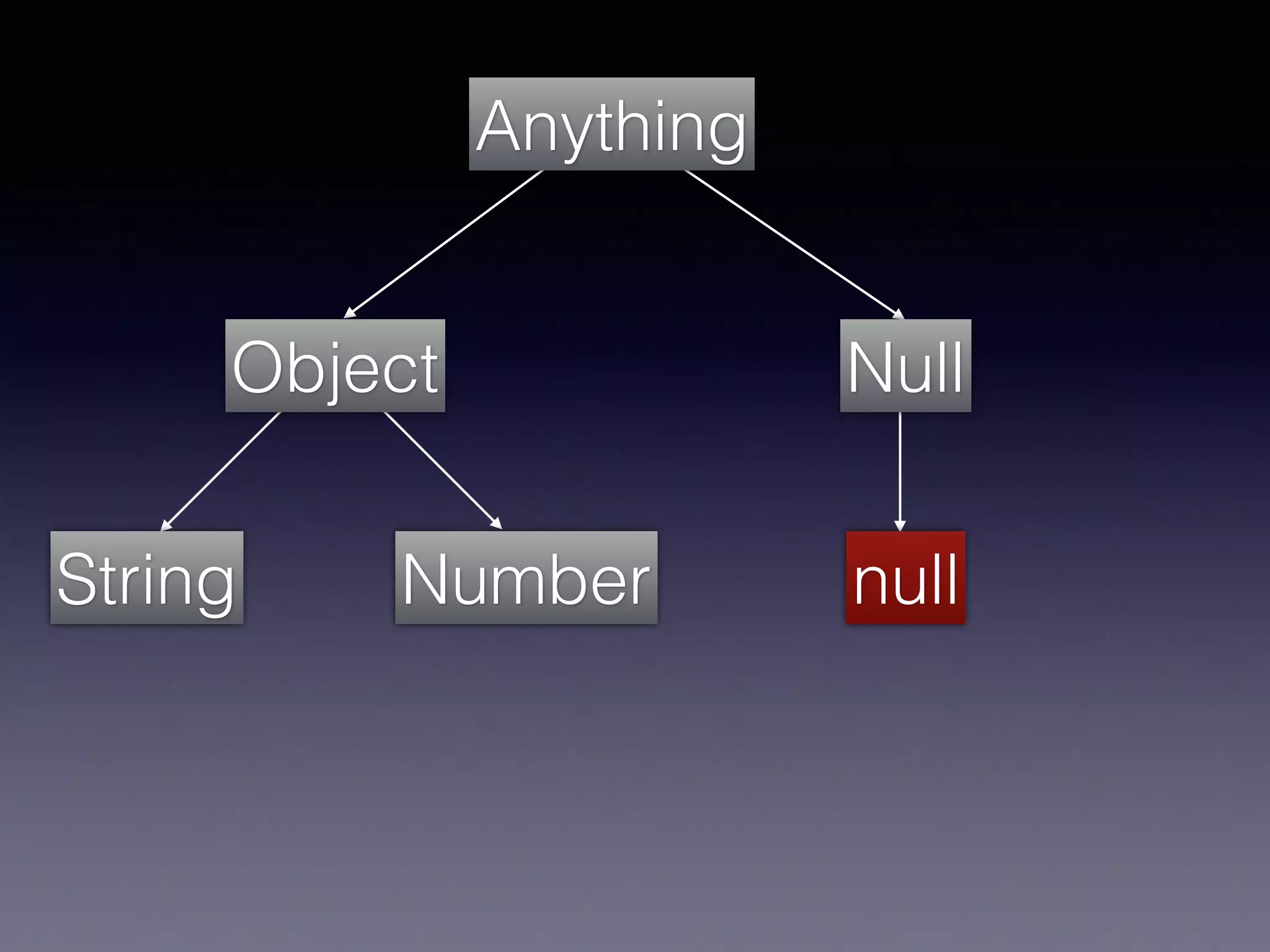
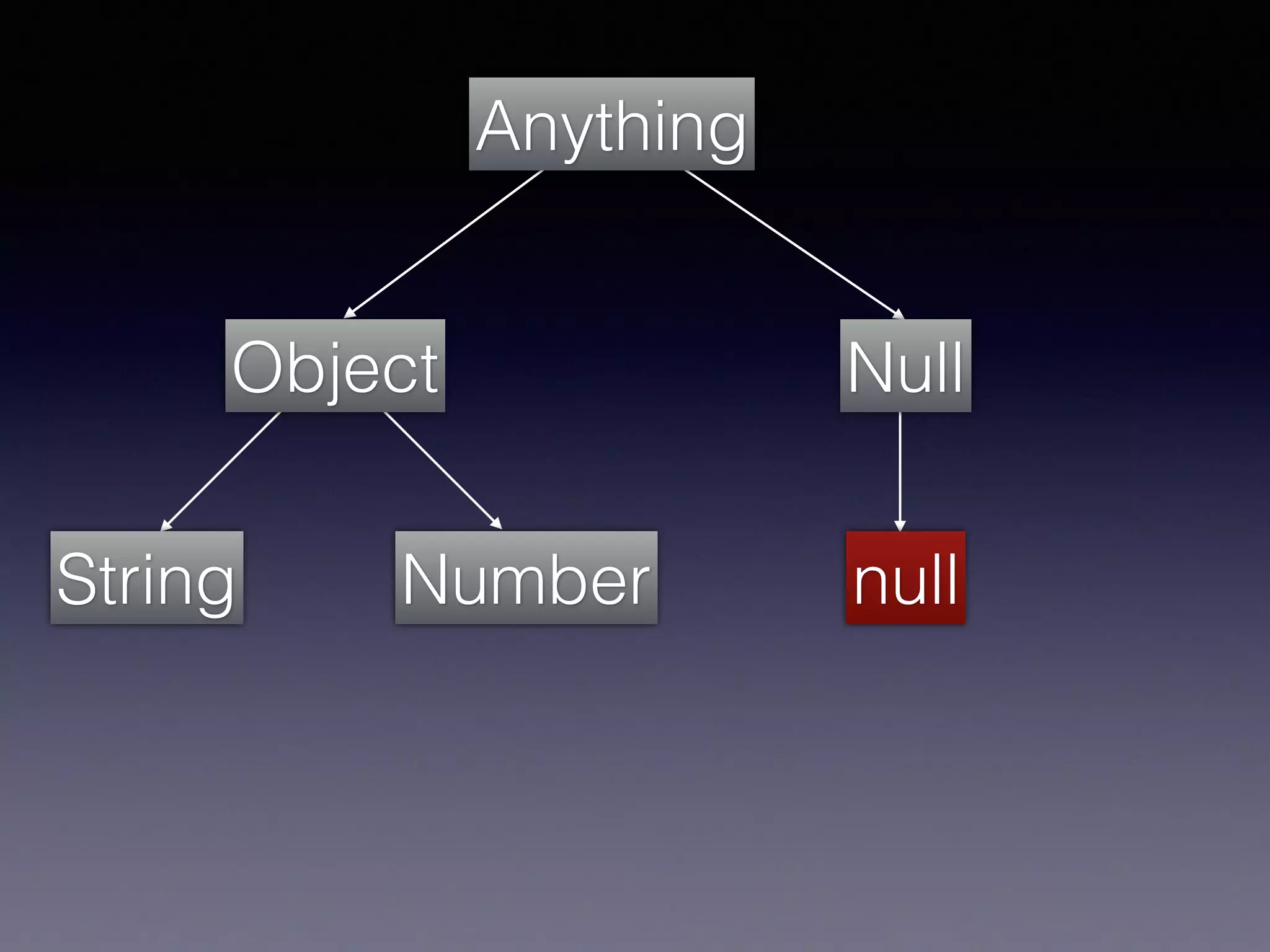
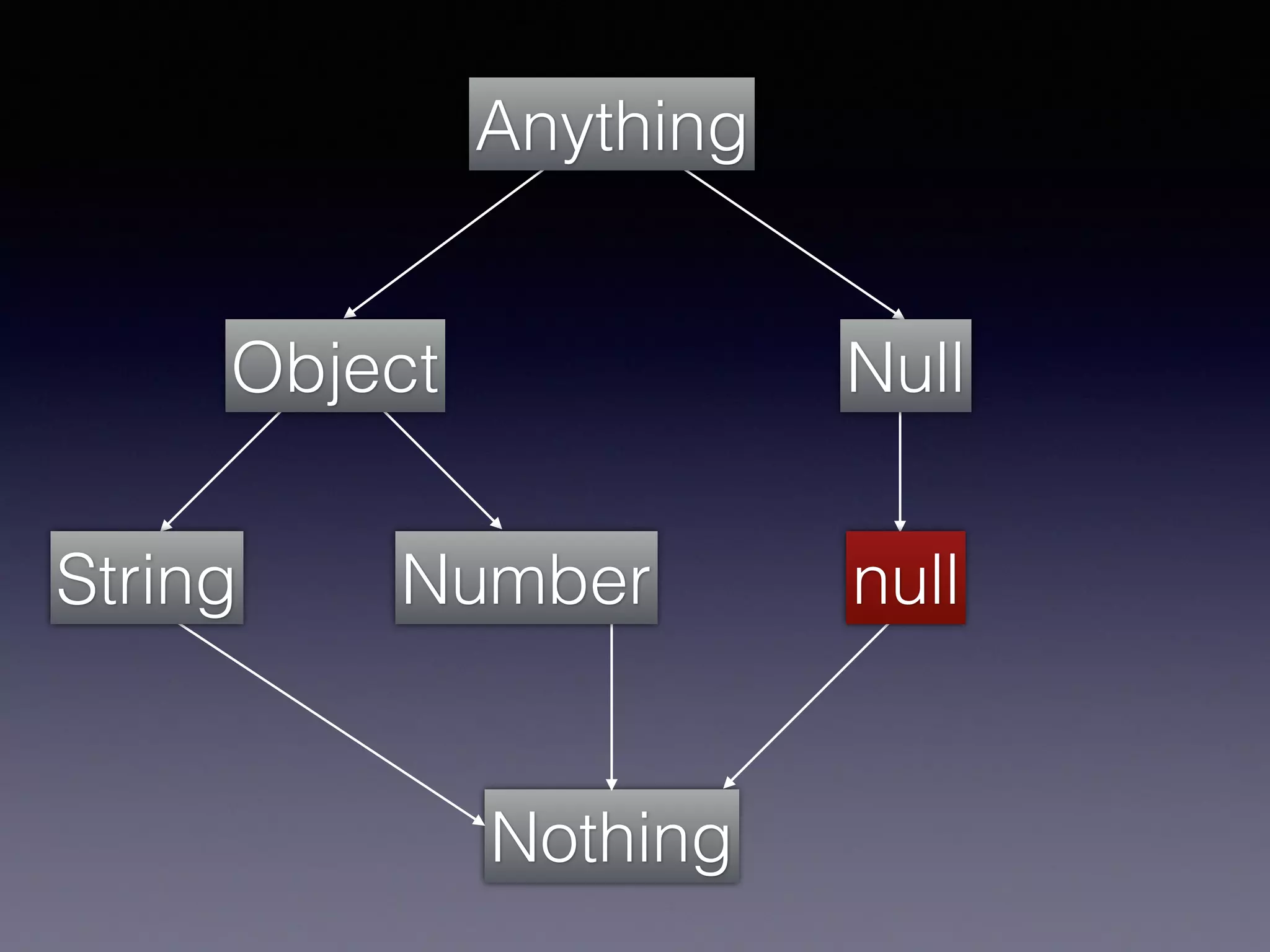
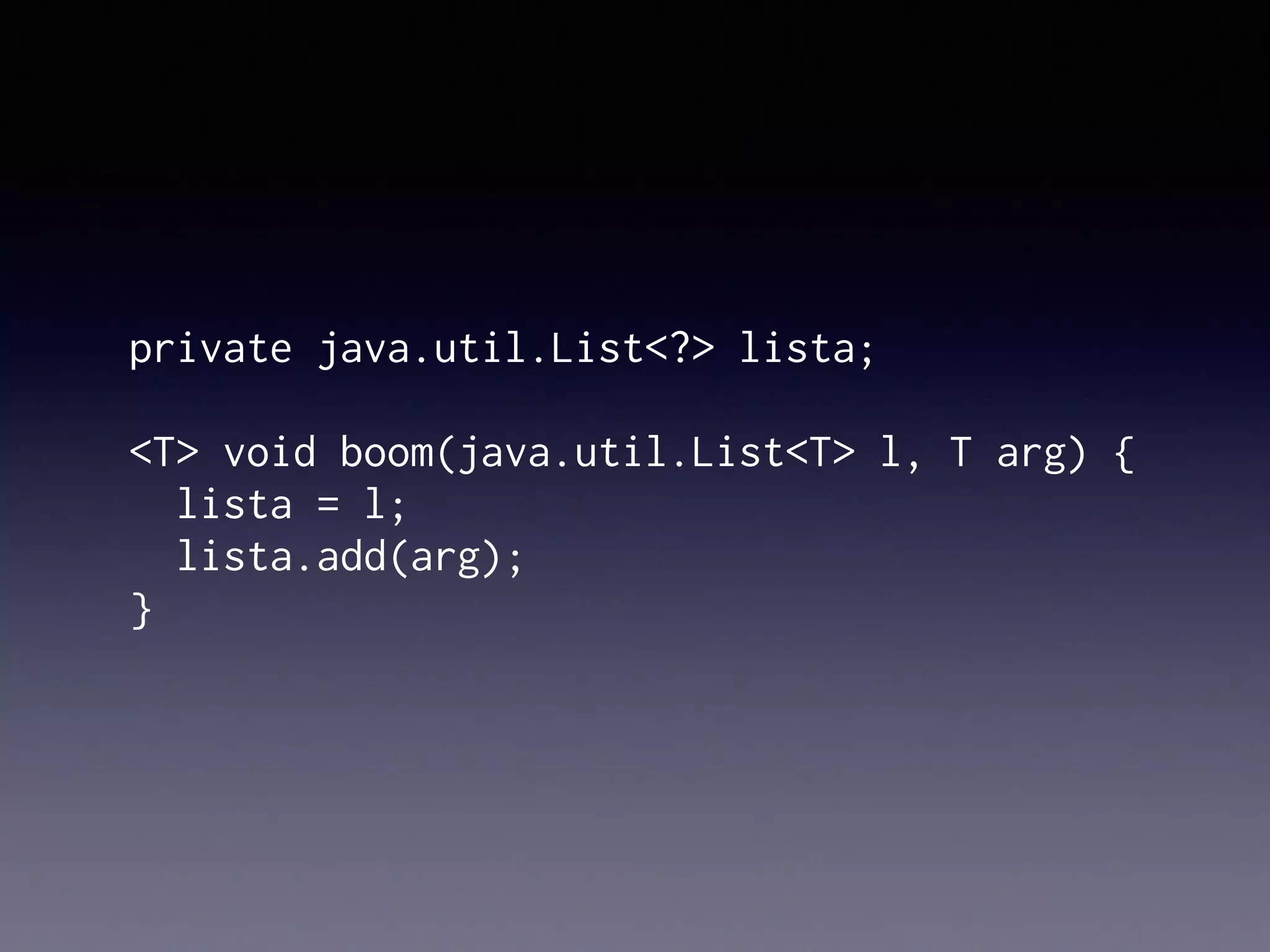
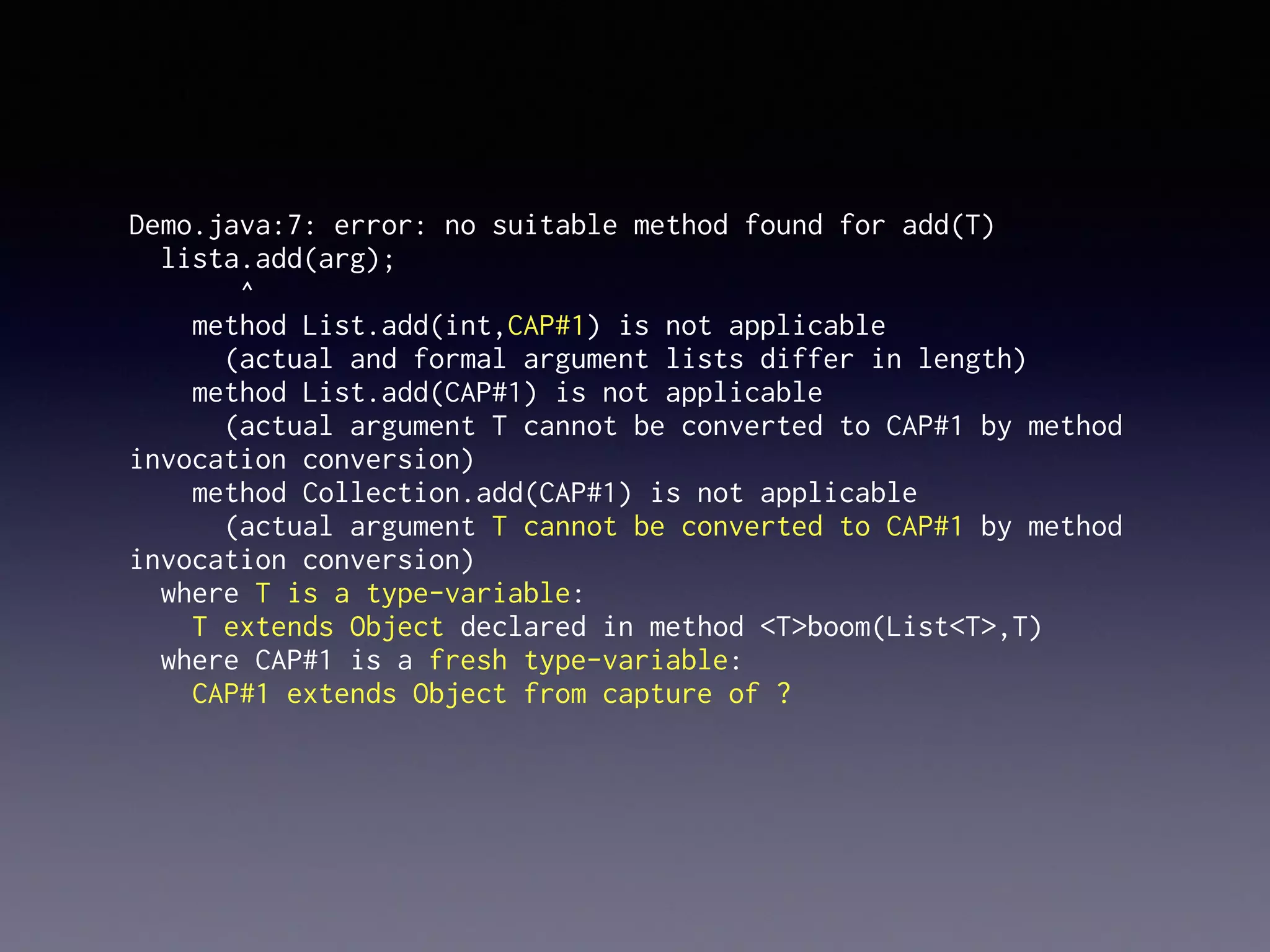
El documento presenta Ceylon, un lenguaje de programación diseñado para superar las limitaciones de Java mediante un sistema de tipos mejorado. Destaca características como tipos de unión, tipos de intersección y soporte para la programación en múltiples plataformas. Además, se abordan problemas comunes en Java y se proponen soluciones efectivas a través de su sistema de tipos avanzado.