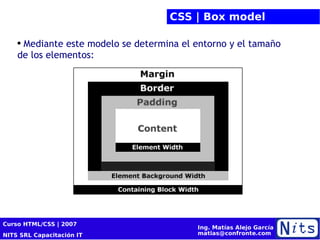
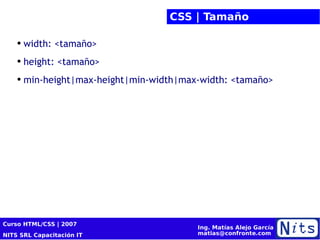
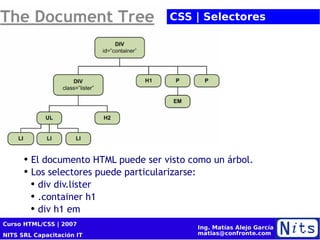
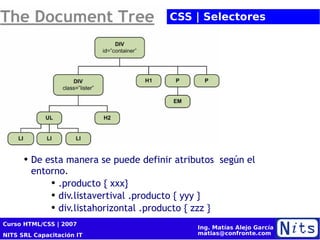
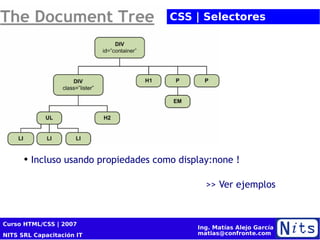
El documento resume la cuarta sesión de un curso de HTML y CSS. Cubre la historia y versiones de HTML, elementos HTML, introducción a CSS incluyendo propiedades de color, texto, fuentes y posicionamiento. También presenta conceptos básicos de diseño de sitios web como cajas de modelo, tablas, listas y selectores CSS. Por último, brinda consejos sobre optimización para motores de búsqueda (SEO).

![Presentación Matías Alejo García mailto: [email_address] msn:matias_alejo@hotmail.com http://linkedin.com/in/matias](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clase4-090803122350-phpapp02/85/Curso-HTML-CSS-4-4-2-320.jpg)




![CSS | Font Atributos del font. font-family : “Arial”, sans-serif font-size: <tamaño> font-stretch: [ultra-|extra-] wider|condensed font-style: italic | oblique font-variant: small-caps font-weight: bold|bolder|lighter|x00 >> Ver ejemplos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clase4-090803122350-phpapp02/85/Curso-HTML-CSS-4-4-7-320.jpg)