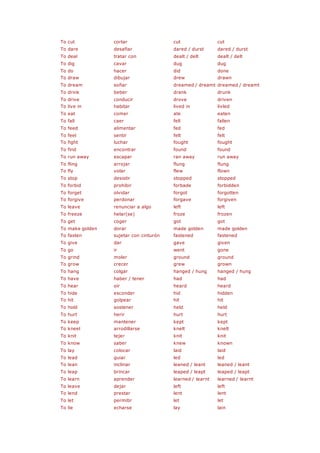
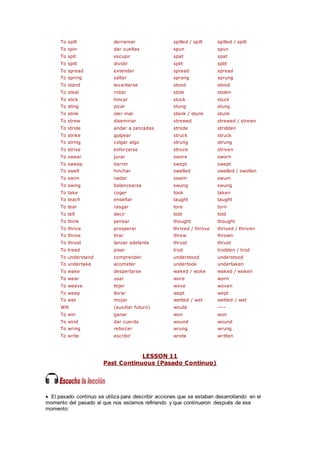
Este documento proporciona una lección sobre pronombres personales sujetos en inglés. Explica los equivalentes en inglés de los pronombres personales en español como "yo", "tú", "él", etc. Además, describe cómo estos pronombres concuerdan con los verbos y su colocación en la oración. Finalmente, incluye una lista de vocabulario relacionado con la familia.

































































































![Annabe lla s hake that thing
M is s Kana Kana
Yo s e xy ladie s want par w ith us
In a tha car w ith us
The m nah w ar with us
In a tha club the m want flex w ith us
To ge t ne xt to us
The m cah ve x w ith us
Fr om tha day m e bor n jah ignite me flame
Gal a call m e name and tis m e fame
It's all good gir l tur n m e on
'Til a e ar ly m orn'
Le t's ge t it on
Le t's ge t it on 'til a e ar ly m orn'
Gir l it's all good jus t turn me on
[x2]
Le t's ge t it on 'til a e ar ly m orn'
Gir l it's all good jus t turn me on
Give it up to me
Ge t out m y he ad and into the bed gir l...
Caus e you done k now, plottin' out the fantasy..
He y baby gir l and it's you a the k ey...yo ...me go s o then
Chor us:
Fr om you look inna m e e ye gal I s e e s he you want m e
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Be caus e you body e nticing you m akin' m e horny
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
We ll if a no today gir l the n a m ust be tomorrow
Whe n you fulfill m y fantasy
Be caus e you k now I give you lovin' s traight lik e an ar row
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Ve r se 1:
So back it up de h..So pack it up ye ah
Caus e I w anna be the man that's r e ally gonna have it up and mack it up and
Slap it up ye ah...So w hat is up ye ah...You k now you got the s inting inna me pants a de velop
and a s w ell up and
Double up ye ah...So gimmie the w ork ye ah caus e if you no gimme the w ork the blue balls a
e r upt ye ah..
So r e v it up de h gal gwaan try you luck de h caus e when you s tir it up you k now me haffi
m e asure up ye ah.
Fr om you look inna m e e ye gal I s e e s he you want m e
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Be caus e you body e nticing you m akin' m e horny
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
We ll if a no today gir l the n a m ust be tomorrow
Whe n you fulfill m y fantasy
Be caus e you k now I give you lovin' s traight lik e an ar row
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Ve r se 2:
He y pr e tty gir l...Say me love fi s e e you walk...
You no habla ingle s but jus t lis ten m e when me a talk
This ya one ye ah fr om me he ar t, woman you got m e caught
You e ve r inna me thoughts and no le ft me inna the dar k, inna the...
Fir s t place gal that's wher e you belong, s o just le t m e flip the switch woman I can tur n it on
and...
Gim m e the passion fr om dusk till dawn...Tel l me if you w ant it fi gw aan...my girl..
Chor us:
Fr om you look inna m e e ye gal I s e e s he you want m e
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Be caus e you body e nticing you m akin' m e horny
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
We ll if a no today gir l the n a m ust be tomorrow
Whe n you fulfill m y fantasy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-100-320.jpg)
![Be caus e you k now I give you lovin' s traight lik e an ar row
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Ve r se 3:
So w hy can't you s ee....we ought to be ....together gir l don't fr ont on me
I jus t w anna be near s o don't have no fe ar and lemme see you br ing your body r ight ove r
he r e
Be caus e you s hould s hare it...girl I'll car e it.....And I'm gonna give you love s o clear
It gonna m ak e you s hine and once you ar e m ine...we be r ockin' it until the e nd of time
Chor us:
Fr om you look inna m e e ye gal I s e e s he you want m e
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Be caus e you body e nticing you m akin' m e horny
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
We ll if a no today gir l the n a m ust be tomorrow
Whe n you fulfill m y fantasy
Be caus e you k now I give you lovin' s traight lik e an ar row
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Ve r se 1:
So back it up de h..So pack it up ye ah
Caus e I w anna be the man that's r e ally gonna have it up and mack it up and
Slap it up ye ah...So w hat is up ye ah...You k now you got the s i nting inna me pants a de velop
and a s w ell up and
Double up ye ah...So gimmie the w ork ye ah caus e if you no gimme the w ork the blue balls a
e r upt ye ah..
So r e v it up de h gal gwaan try you luck de h caus e when you s tir it up you k now me haffi
m e asure up ye ah.
Chor us:
Fr om you look inna m e e ye gal I s e e s he you want m e
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Be caus e you body e nticing you m akin' m e horny
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
We ll if a no today gir l the n a m ust be tomorrow
Whe n you fulfill m y fantasy
Be caus e you k now I give you lovin' s traight lik e an ar row
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Chor us:
Fr om you look inna m e e ye gal I s e e s he you want m e
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Be caus e you body e nticing you m akin' m e horny
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
We ll if a no today gir l the n a m ust be tomorrow
Whe n you fulfill m y fantasy
Be caus e you k now I give you lovin' s traight lik e an ar row
Whe n you gonna give it up to m e
Ye ah Ye ah!! Yoh Yoh!!
I’m still in love with you boy
S] I’m s till in love with you boy…
We ll I’m a hus tle r and a playe r and you I’m not a s tayer
That’s the dutty dutty love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
Say gir l, tr y to unde rstand that a m an is jus t a m an
That’s the dutty dutty love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
Ble s s ings loving from the s tart but you k now w e had to par t
That’s the w ay I give my love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you…
But a m an gotta do what a m an gotta doo…
[Se an Paul]
Gir l, w e ll a ne ve r had to promise you no bling bling fo hold you girl
A jus t the loving weh me fling fling control you gir l
And m ak e you head swirl
And m ak e you body twirl
And m ak e you wanna be my one and only baby girl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-101-320.jpg)
![Night afte r night m e give you love fi k e ep you warm
Gal you ne ve r get this kinda love from you born
And now you want dr aw car d s ay m e just can’t perform
[Chor us 1]
[S] I love you baby
A tr ue a ge t the little loving and me gone
[S] You don’t k now how to love m e
I an I nah no tim e fi no k iss up an char m
[S] Not e ve n how to k iss m e
A tr ue me tak e you little he art by s torm
[S] I don’t k now w hy
Babygir l, Babygir l
[S] I love you baby
A jus t the dutty dutty love
[Chor us 2]
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
We ll I’m a hus tle r and a playe r and you I’m not a s tayer
That’s the dutty dutty love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
Say gir l, tr y to unde rstand that a m an is jus t a m an
That’s the dutty dutty love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
Ble s s ing loving fr om the start but you k now w e had to part
That’s the w ay I give my lo ve
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you…
But a m an gotta do what a m an gotta doo…gir l
[Se an Paul]
A tr ue me give her tug love and s ay bye bye bye
M e tur n ar ound s he as k the question why why why
Whe n m e le aving m e see the gal cr y cr y cr y
And it hur ts my he art to te ll lie lie lie
So don’t cr y no m ore
Baby gir l for s ure
Jus t r emember the good times w e had before
[Chor us 1]
[S] I love you baby
A tr ue a ge t the little loving and me gone
[S] You don’t k now how to love m e
I an I nah no tim e fi no k iss up an char m
[S] Not e ve n how to k iss m e
A tr ue me tak e you little he art by s torm
[S] I don’t k now w hy
Babygir l, Babygir l
[S] I love you baby
A jus t the dutty dutty love
[Chor us 2]
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
We ll I’m a hus tle r and a playe r and you I’m not a s tayer
That’s the dutty dutty love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
Say gir l, tr y to unde rstand that a m an is jus t a m an
That’s the dutty dutty love
[S] I’m s till in love w ith you boy…
Ble s s ings loving from the s tart bu t you k now w e had to par t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-102-320.jpg)
![That’s the w ay I give my love
[Sacha]
I don’t k now w hy [x3]
I don’t k now [x3]
I don’t k now w hy
I’m s till in love …
Break it off
[Se an Paul]
Br e ak It Off
Br e ak in it off
And s e ttin it off in da r e al way
M ak in da gir ls dem chill de y mind
M ak in dem have a good time
Ya m an
SPZ long s ide RiRi
Com e down now Rihanna
Te k it to de m Tek it to de m girl
[Re fr ain]
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty (most de finitely)
Se t if off boy
And m ak e me hot all ova m y body
(Br e ak it off, tak e it off, miss take it off) (Br eak it off tonight) (Yo)
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty (yo, yo)
Se t it Off boy (ye ah, ye ah)
M ak e me hot all ova m y body
Br e ak it off tonight (yo)
[Ve r se 1]
Str uggle and pain wha s he fe ll all de while
And s he want a good m an to give her de style
Wild child
So s he der e pon me file
It´s a long tim e now me wha plow de s ile
Plow de s ile meh car r u n r un lik e de nile
And de m ost e nergy meh whan gi he r tonight
Give he r tonight
Gan m ak e s he fe el r ight
M ak e s he fly lik e a k ite that r each a ne w he ight
Ah w e give it to de gyal dem
M ak e dem r eel up and bawl
And m ak e dem s tart call
Anytim e s he w ant it back she ha fi call Dutty Paul
Adm ittin it on de s pot I k now de r eal Se an Paul
Whe n de tr aits so gr eat
Cuz s he feelin top up and tall w at de ting s ay
[Re fr ain]
Br e ak it off boy (immediate if not before)
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty (pumba)
Se t if off boy
And m ak e me hot all ova m y body
(Br e ak it off, tak e it off, yo m iss tak e it off) (Br e ak it off tonight) (Yo)
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty ( yo, yo)
Se t it Off boy (ye ah, ye ah, yo yo, yo a yo, RiRi, SPZ)
M ak e me hot all ova m y body
Br e ak it off tonight (yo, yo)
[Ve r se 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-103-320.jpg)
![No doubt
Gyal u s houlda know SP and a s cout(?)
Naughty s w eat s o s hout(?)
M ak e ya bawl out (shout)
M ak e ya holla m e gah give affection in your dir ection
We go all out
Gyal, jus t follow we if ya love e nergy
If ya w han pe digree
Cr uis e lik e Pe nelope
M ak e a s ee yuh jus t bounce wit de Dutty Le e
We k e e p givin you de Q to de U to de A (ye a) to de L to de I to de T to de Y
Gir l I got to tr y (tr y)
Tak e yuh booty m ake you r e ach to de S.K.Y.
Wom an I got to s ay (s ay)
Da w ay u m ove is makin me hype
Gir l cuh yuh k now say yuh S to de E to de X to de Y (Pum ba Pumba)
[Re fr ain]
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty (s exiness)
Se t it off boy
M ak e me hot all ova m y body (yo, yah go yo, no doubt)
Br e ak it off tonight (yo RiRi)
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty (Blaze u p on no r ain no s tress)
Se t it off boy
M ak e me hot all ova m y body
Br e ak it off tonight (yea, yo, ya yo)
[Rihanna]
Boy (Uh huh)
The w ay you push up on me I
Whan ge t da r oughest wine I dun k now ya lik e (ay, yo, ay)
Fuh s ho w e gonna break it off ton ight (yoga macchugga uh)
Ooooo boy
We r e ally s houldn´t w aste no time (sing it)
Com e le t me back up on ya dancehall´s tight (br ing it)
And I´m hopin baby u don´t mind
Cuz I r e ally w anna break it off tonight (instantaneous)
[Re fr ain]
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty (ay)
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty
Se t it off boy
M ak e me hot all ova m y body (baby gir l, yo, baby gir l)
Br e ak it off tonight (yo give it up give it up s en on)
Br e ak it off boy
Cuz ya got m e fe elin naughty ( yo)
I w anna k now boy
If I could be ya s haw ty
Se t it off boy
M ak e me hot all ova m y body
Br e ak it off tonight
Angel
I s it and w ait
doe s an angel contemplate my fate
And do the y k now
The place s where we go
Whe n w e're grey and old
'caus e I have been told
That s alvation le ts their wings unfold
So w hen I'm lying in m y bed
Thoughts r unning through my head
And I fe e l that love is dead
I'm loving angels ins tead](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-104-320.jpg)





![Cleanin Out My Closet
Have you e ve r be en hated or dis criminated against? I have , I've been
pr ote sted and demonstrated against. / Pick e t s igns for my wicked r hymes. Look at
the tim es. Sick is the mind of the m otha fuckin' k id that's be hind / all this
com motion. Em otions r un de ep as ocean's e xplodin.' Tempers flar ing from par ents,
jus t blow 'em off and k eep goin.' / Not tak in' nothin' fr om no one, give 'em
he ll long as I'm breathin.' Ke e p k ickin' as s in the m ornin,' an' takin' names in
the e ve ning. / Le avem with a tas te as s our as vinegar in they m outh. Se e, they
can tr igge r m e but they never figure me out. / Look at m e now, I be t ya pr obably
s ick of m e now. Ain't you mama, I'ma m ake you look s o r idiculous now.
Chor us 2X
I'm s or ry, Mama. I ne ver m eant to hurt you. I ne ver meant to m ake you cr y, but
tonight I'm cle anin' out my clos et.
I got s ome s keletons in my clos et and I don't k now if no one k nows it. So be fore
the y thr own m e inside my coffin and close it, / I'm a e xpose it. I'll tak e you
back to 73 be for e I e ver had a m ulti-platinum s ellin' CD. / I w as a baby, m aybe
I w as just a couple of m onths. M y faggot father must have had his panties up in
a bunch, / cuz he s plit. I w onder if he e ven k issed me goodbye. No, I don't on
s e cond thought, I jus t fu ckin' wished he w ould die . / I look at Hailie and I
couldn't picture leavin' he r s ide. Eve n if I hate d Kim , I gr it m y te eth and I'd
tr y / to m ak e it w ork w ith her at le ast for Hailie 's s ake. I m aybe m ade s ome
m is takes but I'm only human. But I'm man e no ugh to face them today. / What I did
w as s tupid, no doubt it was dumb, but the smartest s hit I did w as tak e them
bulle ts out of that gun. / Cuz id'a k illed 'em, shit I w ould have s hot Kim an'
him both. It's my life , I'd like to w elcome y'all to The Em in em Show.
Chor us 2X
Now I w ould ne ver dis m y own mama just to get r ecognition. Take a s e cond to
lis te n for you think this r ecord is dis sin,' / But put your self in m y position.
Jus t tr y to e nvision witnessin' your M ama poppin' pr escription pills in the
k itche n, / bitchin' that s omeone's always goin' throuh he r purse and s hits
m is sin.' Going through public housing s ystems, victim of M unchausen's s yndrome.
M y w hole life I w as m ade to be lieve I w as s ick w hen I w asn't 'til I gr ew up, now
I ble w up. It m akes you s ick to ya s tomach, / doesn't it? Was n't it the r eason
you m ade that CD for m e, M a? So you could try to jus tify the way you treated m e,
M a? / But gue s s what, ye r gettin' older now and it's cold when your lonely. An'
Nathan's gr owin' up s o quick, he 's gonna k now that your phoney. / And Hailie 's
ge tting' s o big now, you s hould see he r, s he's beautiful. But you'll ne ver s ee
he r , s he won't e ven be at your funeral. / Se e what hurts me the m ost is you
w on't admit you was wrong. Bitch, do ya s ong. Ke ep tellin' yourself that you was
a m om. / But how dar e you try to tak e what you didn't help m e to get. You
s e lfish bitch, I hope you fuckin' bur n in he ll for this s hit. / Re m ember when
Ronnie die d and you s aid you wished it w as me? We ll, guess what, I a m de ad. De ad
to you as can be .
Chor us 4X
Donde e s tá mi tr ampa, no te ngo ninguna tr ampa en mis aur iculares, allí ya ' voy, s í, yo ', yo
'...
Le han odiado s iempre o dis criminado contra, tengo, yo he s ido pr otestado y de mostrado
contr a, e l piquete firma par a mis r imas traviesas, mir ada e n los tiempos, enfermo es m ente
de l
cabr ito que está detrás, todo e ste commotion, emociones de l motherfuckin ' funcionadas
pr ofundamente como e xplodin del océ ano ',
ge nios que s eñalan por m edio de luces de padres, em d el s oplo justo de l ' apagado y de l
goin de la s ubs istencia ', no tak in ' nothin ' de nadie,
dé ' infie r no del e m de lar go como s oy br eathin ', as no del k ickin de la s ubsistencia e l ' e n e l
m or nin ', ' nom bres de l takin ' e n
igualando, de je e l ' em con un gusto tan am argo como vinagre ade ntro que ar ticulan, los ve n
pue de accionarme pero
nunca m e calcularán hacia fuera, mirada e n m í ahora, yo apostar on e l ya ' pr obablemente
e nfe rmo de mí ahora, no e stá us ted mama,
e l i'm a hace le mir ada tan r idícula ahora...
[ ESTRIBILLO ]
Es toy ape s adumbrado que e l m ama, yo nunca s ignificó las timar le, yo nunca s ignificó hacer le
gr ito, pe ro e stoy esta noche
cle anin ' fue ra de mi ar mario, {una m ás ve z}, dije que s oy mama ape sadumbrado, nunca
s ignifiqué par a las timarle, I
nunca s ignificó hace rle grito, pe ro s oy e sta noche cle anin ' fue ra de m i armario...
Cons e guí algunos esqueletos e n mi ar mario y no s é s i nadie lo s abe, tan antes de que ellos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-110-320.jpg)
![lanzados me
de ntr o de mi ataúd y cié r relo, e xposición del i'ma é l, yo le t omar á de nuevo a '73, ante s de
que tuvie ra s iempre a
Cd de l s e llin del m ulti-platino ', e r a un bebé, yo e ra quizá jus to un par de meses, mi padre
de l faggot
de bo haber tenido sus pantie par a ar riba e n un manojo, causa que é l partió, m e pregunto s i
é l inclus o be sado me adiós,
ningún no e n e l s egundo pe nsamiento, I que e l fuckin jus to ' deseaba que é l moriría, yo m ira
Hailie e I
no podr ía r e presentar le avin ' s u late ral, incluso s i odié Kim , yo cie rr a fuer temente mis
die ntes y Inte ntaría, hace rlo
tr abaje con e lla por lo m enos para e l m otivo de Hailie , yo incur rió e n quizá algunas
e quivocaciones per o s oy solamente humano, pero yo s on
s ir va bas tantes para hace rles frente hoy, qué lo hice e ra e stúpido, ninguna duda que e ra
m udo, per o e l más e legante
la m ie rda I e r a toma e llos las balas fuera de e se arma, e m matado id'a de la caus a ', m ierda
Habr ía tir ado
Kim y é l am bos, e s m i vida, yo quisiera dar la bie nvenida al y'all al Em ine m demostración...
[ ESTRIBILLO ]
Ahor a nunca los diss mi pr opio mama ape nas conseguiría e l r econocimiento, lle vo un
s e gundo e spérele a e scuchar
pie ns e que e ste e xpediente e s dissin ', pe ro puesto e n m i posición, intento jus to a pr evea e l
w itnessin '
s u poppin ' píldoras del m ama de la pr escripción e n la cocina, bitchin ' e s e al guien s iempre
goin '
con s u m onedero y m issin de las mierdas ', pas ando a tr avés de s istemas de la cubie rta
pública, víctim a de
El s índr ome de Munchausen, mi vida e ntera m e hicieron par a cr eer que e ra e nfermo cuando I
no e r a ' has ta que cr ecí
e ncim a de, ahora s oplé par a ar riba, é l le hago e nfermo e stómago del ya ', no é l, no e r a é l la
r azón que us ted hizo
que e l Cd par a m í, mA, as í que usted podría intentar justificar la m anera us ted me tr ató, mA,
pe r o conjetura qué, s u
e l ge ttin ' m ás vie jo ahora y é l e s fríos cuando s u s olo, y Nathan que cr ece para ar r iba tan
apr is a, é l va a
s e pa que s u farsante, y Hailie que consigue tan gr ande ahora, usted de ben ver la, e lla e s
he r mosa, pe ro
us te d nunca la ve r á, e lla incluso no e stará e n su e ntierro, ve qué m e las tima el la m ayoría e s
us te d no
adm ita que us ted e ra incorrecto, perr a, que hace s u canción, te llin de la s ubsistencia ' us ted
m is mo que us ted e ra una mama, pe ro cómo atr evimiento
us te d intenta tomar lo que us ted no me ayudó a conseguir , us ted perr a egoíst a, yo le e sper a
que madur a del fuckin ' ade ntro
e l infie r no par a esta mierda, r ecuerda cuando Ronnie murió y us ted dijo usted de seaba que
e r a yo, conje tura bie n
cuál, s oy m ue rto, absolutamente a us ted como puede s er...
Lose Your Self
Look , if you had one s hot, or one opportunity
To s e ize e verything you e ver wanted -One moment
Would you captur e it or jus t le t it s lip?
Yo, His palm s ar e sweaty, knees weak, arms ar e he avy
The r e's vomit on his s weater alr eady, m om's s paghetti
He 's ne r vous, but on the s u rface he looks calm and r eady
To dr op bombs, but he keeps on forgetting
What he w r ote down, the whole cr owd goes s o loud
He ope ns his m outh, but the w ords won't come out
He 's chok in, how e verybody's chokin now
The clock 's r un out, time's up over, bloah!
Snap back to r e ality, Oh the re goes gravity
Oh, the r e goes Rabbit, he choked
He 's s o m ad, but he w on't give up that e asy
No, he w on't have it , he k nows his whole back city's r opes
It don't m atter, he's dope
He k nows that, but he's broke
He 's s o s tacked that he k nows
Whe n he goes back to his m obile home, that's when it's
Back to the lab again yo
This w hole r ap city
He be tter go capture this moment and hope it don't pass him](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-111-320.jpg)
![[Chor us:]
You be tte r lose yourself in the music, the moment
You ow n it, you be tter ne ver le t it go
You only ge t one s hot, do not miss your chance to blow
This opportunity comes once in a life time yo,
You be tte r lose yourself in the music, the moment
You ow n it, you be tter ne ver le t it go
You only ge t one s hot, do n ot miss your chance to blow
This opportunity comes once in a life time you be tter,
His s oul's e scaping, through this hole that it's gaping
This w orld is m ine for the tak ing
M ak e me k ing, as we move toward a, new w orld order
A nor mal life is borin, but s uperstardom's clos e to post m ortom
It only gr ow s harder, only gr ows hotter
He blow s us all ove r these hoes is all on him
Coas t to coas t shows, he's know as the globetrotter
Lone ly r oads, God only k nows
He 's gr own far ther fr om home, he's no father
He goe s home and barely k nows his own daughter
But hold your nose cause he re goes the cold water
The s e ho's don't want him no m o, he 's cold pr oduct
The y m oved on to the ne xt s chmoe who flows
He nos e dove and s old nada
So the s oap oper a is told and unfo lds
I s uppose it’s old par tner, but the be at goes on
Da da dum da dum da da
[Chor us:]
You be tte r lose yourself in the music, the moment
You ow n it, you be tter ne ver le t it go
You only ge t one s hot, do not miss your chance to blow
This opportunity comes once in a life time yo
You be tte r lose yourself in the music, the moment
You ow n it, you be tter ne ver le t it go
You only ge t one s hot, do not miss your chance to blow
This opportunity comes once in a life time yo, you better
No m or e games, I'ma change w hat you call r age
Te ar this m othafuckin r oof off lik e 2 dogs cage d
I w as playin in the be ginnin, the mood all changed
I be e n chewed up and s pit out and booed off s tage
But I k e pt r hymin and s tepwritin the ne xt cypher
Be s t be lieve s omebody's payin the pied piper
All the pain ins ide am plified by the fact
That I can't ge t by w ith my 9 to 5
And I can't pr ovide the r ight type of life for my family
Caus e man, these goddam food s tamps don't buy diapers
And it's no m ovie, ther e's no M akai Pfeiffer, this is m y life
And the s e times ar e s o hard and it's getting e ven harder
Tr yin to fe e d and water my s eed, plus
Te e ter-totter caught up between tr ying to be a father and a pr ima donna
Baby m am a dr ama's s creamin on and
Too m uch for m e to wanna
Stay in one s pot, another day of m onotony
Has gotte n m e to the point, I'm like a s nail
I've got to for mulate a plot or I e nd up in jail or s hot
Succe s s is m y only m othafuckin option, failure's not
M om , I love you, but this trailer's got to go
I cannot gr ow old in Sale m's lot
So he r e I go is m y s hot.
Fe e t fail m e not or not this m ay be the only opportunity that I got
[Chor us:]
You be tte r lose yourself in the music, the moment
You ow n it, you be tter ne ver le t it go
You only ge t one s hot, do not miss your chance to blow
This opportunity comes once in a life time yo
You be tte r lose yourself in the music, the moment
You ow n it, you be tter ne ver le t it go
You only ge t one s hot, do not miss your chance to blow
This opportunity comes once in a life time you be tter,You can do anything you s et your m ind
to, m an](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ingles-210601231459/85/Ingles-112-320.jpg)




