Digestive system
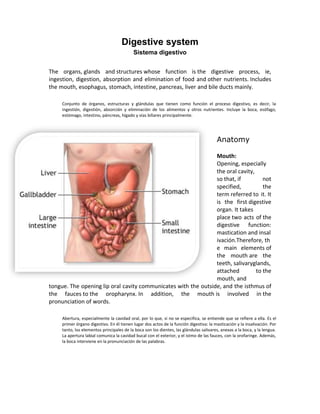
- 1. Digestive system Sistema digestivo The organs, glands and structures whose function is the digestive process, ie, ingestion, digestion, absorption and elimination of food and other nutrients. Includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestine, pancreas, liver and bile ducts mainly. Conjunto de órganos, estructuras y glándulas que tienen como función el proceso digestivo, es decir, la ingestión, digestión, absorción y eliminación de los alimentos y otros nutrientes. Incluye la boca, esófago, estómago, intestino, páncreas, hígado y vías biliares principalmente. Anatomy Mouth: Opening, especially the oral cavity, so that, if not specified, the term referred to it. It is the first digestive organ. It takes place two acts of the digestive function: mastication and insal ivación.Therefore, th e main elements of the mouth are the teeth, salivaryglands, attached to the mouth, and tongue. The opening lip oral cavity communicates with the outside, and the isthmus of the fauces to the oropharynx. In addition, the mouth is involved in the pronunciation of words. Abertura, especialmente la cavidad oral, por lo que, si no se especifica, se entiende que se refiere a ella. Es el primer órgano digestivo. En él tienen lugar dos actos de la función digestiva: la masticación y la insalivación. Por tanto, los elementos principales de la boca son los dientes, las glándulas salivares, anexas a la boca, y la lengua. La apertura labial comunica la cavidad bucal con el exterior, y el istmo de las fauces, con la orofaringe. Además, la boca interviene en la pronunciación de las palabras.
- 2. Esophagus: Portion of digestive tract between the pharynx and stomach. It has three layers of the intestinal tract characteristics: mucosa, submucosa and muscle. The muscle fibers of the proximal portion of the pharynx are ribbed, while the neighboring portion of the stomach are smooth. Esófago: Porción del tubo digestivo comprendida entre la faringe y el estómago. Posee las tres capas características del tubo intestinal: mucosa, submucosa y muscular. Las fibras musculares de la porción próxima a la faringe son estriadas, mientras que en la porción vecina al estómago son lisas. Stomach: Dilated portion of the digestive tract between the esophagus and duodenum. Presents a greater curvature and a smaller and is distinguished in the three parts: the background, at the top, the body and antrum. The mucosal lining
- 3. of the cavity hasa large number of folds, especially if it is empty and secretesgastric juice. The layers forming the wall are the mucosa and submucosa, muscular and serosa. The opening of the esophagus into the stomach called the cardia and connecting the stomach to the duodenum, pylorus, and this remains normally closed by the action of the pyloric sphincter. Estómago: Porción dilatada del tubo digestivo, situado entre el esófago y el duodeno. Presenta una curvadura mayor y otra menor y se distinguen en él tres porciones: el fondo, en la parte superior; el cuerpo y el antro pilórico. La mucosa que reviste su cavidad presenta gran cantidad de pliegues, sobre todo si está vacío y segrega el jugo gástrico. Las capas que forman su pared son: la mucosa y la submucosa, muscular y serosa. La apertura del esófago en el estómago se llama cardias y la que comunica el estómago con el duodeno, píloro; esta permanece normalmente cerrada por la acción del esfínter pilórico. Small intestine: The portion of the intestinal tract between the pylorus and the cecum. It is divided into duodenum, jejunum andileum. Intestino delgado: La porción del tubo intestinal comprendida entre el píloro y el ciego. Se divide en duodeno, yeyuno e íleon. Duodenum: First of the small intestine, about twelve fingers in length (hence the name), which communicates with the stomach bythe pylorus and continues with the jejunum. He was distinguished in four parts: the first presents the duodenal bulb and is the only one that has a certain mobility, while the others are attached to theposterior abdominal wall, so they are fixed. On the whole, has a C-shaped path rather closed, which houses the head of the pancreas. In the second portion of duodenum, common bile flowtogether and pancreatic duct. Duodeno: Primera porción del intestino delgado, de unos doce dedos de longitud (de ahí el nombre), que se comunica con el estómago por el píloro y continúa con el yeyuno. Se distinguen en él cuatro porciones: en la primera presenta la ampolla duodenal y es la única que tiene un
- 4. cierta movilidad, mientras que las otras están adosadas a la pared posterior del abdomen, por lo que son fijas. En conjunto, tiene una trayectoria en forma de C bastante cerrada, en la que se aloja la cabeza del páncreas. En la segunda porción del duodeno desembocan juntos el colédoco y el conducto pancreático. Jejunum: Portion of small intestine between the duodenum and ileum. The passage of the duodenum to the jejunum forms an acute angle (duodeno- jejunal), which is fixed to the diaphragm bythe ligament of Treitz. Yeyuno: Porción de intestino delgado comprendido entre el duodeno y el íleon. El paso del duodeno al yeyuno forma un ángulo agudo (ángulo duodeno-yeyunal), que queda fijado al diafragma mediante el ligamento de Treitz. Ileum: Intestinal portion extending between the jejunum and cecum.His bowel loops are located, usually in the hypogastrium and right iliac fossa. Ileon: Porción intestinal que se extiende entre el yeyuno y el ciego. Sus asas intestinales se localizan, por lo general, en el hipogastrio y fosa ilíaca derecha.
- 5. Large intestine: The portion of the intestinal tract comprising the cecum, colon and rectum. intestino grueso: Porción del tubo intestinal que comprende el ciego, el colon y el recto. Blindgut: First portion of the intestine, in a fornix, which partly as an extension of the appendix. In the blind leads the ileum (ileocecalvalve), continues with the ascending colon and is located in theright iliac fossa. Ciego: Primera porción del intestino grueso, en forma de fondo de saco, del que parte como una prolongación el apéndice vermiforme. En el ciego desemboca el íleon (válvula ileocecal), continúa con el colon ascendente y se localiza en la fosa ilíaca derecha. Colon: Portion of the large intestine that extends the cecum to the rectum. There are four parts: ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid. The transverse colon has a relatively large meso, so it is more mobile than other parts. Colon: Porción del intestino grueso que se extiende del ciego al recto. Se distinguen cuatro partes: ascendente, transverso, descendente y sigmoideo. El colon transverso posee un meso relativamente amplio, por lo que es más movible que las otras partes. Rectum: Portion of the large intestine, about 12 cm in length. It follows the sigmoid colon and ends at the anal canal. It presents adilatation, the rectal ampulla, which often are stored feces. Recto: Porción terminal del intestino grueso, de unos 12 cm de longitud. Es una continuación del colon sigmoideo y termina en el canal anal. Presenta una dilatación, la ampolla rectal, en la que, con frecuencia, se almacenan heces.
- 6. Páncreas: Midgut gland caused. It has a triangular prismatic shape, with head, body and tail. It is attached to the posterior abdominal wall (s retropitoneal) and her head is framed by theduodenum. There are two types of secretion: digestive and endocrine. The pancreatic juice acts by the corresponding enzymes on carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It is excretedthrough the pancreatic duct in the second portion of duodenum.The internal secretion of the pancreas occurs in pancreatic islets (or Langerhans) and corresponds to the insulin and glucagon. Páncreas: Glándula originada del intestino medio. Tiene una forma prismática triangular, con cabeza, cuerpo y cola. Se encuentra adosado a la pared posterior del abdomen (es retropitoneal) y su cabeza se halla enmarcada por el duodeno. Tiene dos tipos de secreción: digestiva y endocrina. El jugo pancreático actúa, mediante las correspondientes enzimas, sobre los glúcidos, las proteínas y las grasas. Se excreta, mediante el conducto pancreático, en la segunda porción del duodeno. La secreción interna del páncreas tiene lugar en los islotes pancreáticos (o de Langerhans) y corresponde a la insulina y al glucagón.
- 7. Liver: Digestive organs, the longest in the body (weighing about 1.5kg), located in the abdominal cavity below the diaphragm, rightupper quadrant. Plays multiple roles. As an organ of the digestive system secretes bile that poured into the duodenum through thebile duct. In the interdigestive periods, bile is stored andconcentrated in the gallbladder. Metabolism, performs important functions in the regulation of blood glucose, catabolites in neutralizing toxic substances, etc. Hígado: Órgano del aparato digestivo, el más voluminoso del organismo (pesa alrededor de 1,5 kg), situado en la cavidad abdominal, debajo del diafragma, en el hipocondrio derecho. Desempeña múltiples funciones. Como órgano del aparato digestivo, segrega la bilis que vierte en el duodeno por medio del colédoco. En los periodos interdigestivos, la bilis se almacena y se concentra en la vesícula biliar. En el metabolismo, realiza importantes funciones en la regulación de la glucemia, en la neutralización de catabolitos y sustancias tóxicas, etc. Gallbladder: S mall bag, about 40 ml capacity an d 10 cm long, which stores and concentrates bile secreted during theinterdigestive periods. Bile comes to it through the cystic duct. The gallbladder is located on the visceral side of the liver, using a slightrelief on its front edge that corresponds, in its cutaneous projection, the right costal margin at about 4 cm from the midline.
- 8. Vesícula biliar: Pequeño saquito, de unos 40 ml de capacidad y 10 cm de largo, donde se almacena y concentra la bilis segregada durante los periodos interdigestivos. La bilis llega a ella por medio del conducto cístico. La vesícula se encuentra en la cara visceral del hígado, haciendo un ligero relieve en su borde anterior que corresponde, en su proyección cutánea, al borde costal derecho a unos 4 cm de la línea media. Spleen: This organ, in spite of having no digestive function, hasclose anatomical relationships with the digestive system. Itabdominal viscera in nature hemopoiética (lymphocytes), located in the left hypochondrium. It has a large number of lymphoidfollicles and, in addition to producing lymphocytes, is the graveyard of red blood cells, ie, is responsible for destroying oldred blood cells. Bazo: Este órgano, a pesar de no tener ninguna función digestiva, tiene relaciones anatómicas estrechas con el sistema digestivo. Es una víscera abdominal, de naturaleza hemopoiética (linfocitos), situada en el hipocondrio izquierdo. Tiene un gran número de folículos linfoideos y, además de producir linfocitos, es el cementerio de los glóbulos rojos, es decir, es el encargado de destruir los eritrocitos viejos. Major diseasesof the digestive system
- 9. Esophagitis: Inflammation of the internal wall of the esophagus. Acidic medicines and irritating food are the causes of the imflammation. Therefore, it is advisable to have a healthy diet and to use antiacid. La esofagitis: Ocurre cuando la pared interior del esófago se inflama. La causa de esta inflamación se debe al ingerir medicamentos ácidos. o alimentos irritadores. Por lo tanto, se recomienda una dieta saludable y el uso de antiácidos. Esophagus Ulcer: An irritation of the esphagus similar to a gastroduodenal ulcer. Stomachaches, lost of weight, burping and salivation are the main symptoms. The elimination of hot spicy food helps to reduce the pain. Others say that drinking milk every two hours soothes the pain. La úlcera del esófago: Es una irritación del esófago que tiene común parecido con una úlcera gastroduodenal. El dolor de estómago, enflaquecimiento, eruptos y salivación son los principales síntomas. Para aliviar el dolor se recomienda eliminar el consumo de alimentos picantes. También se dice que el tomar leche cada dos horas alivia el malestar.
- 10. Gastritis: Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach. Gastritis is one consequence of excessive alcohol, aspirine and tar consumption. Strong gastric pain, lost of appetite and bloody vomit are the main symptoms. Rest is recommended. A stomach "wash" is necessary if the gastritis is caused by a toxic. La gastritis: Ocurre cuando la membrana mucosa del estómago se inflama. La gastritis es producida por el consumo excesivo de alcohol y medicinas con aspirina y alquitrán. La persona que tiene gastritis aguda sufre de dolores gástricos; pierde el apetito y vomita sangre. Para recuperarse de aconseja el reposo. Un lavado de estómago es necesario si la gatritis es causada por el consumo de venenos. Gastroenteritis: Inflammation of the stomach and intestinal mucous membrane. Gastroenteritis is caused by alcohol, food poisoning or an intestinal influenza. Bacteria such as Salmonella also cause gastroenteritis. Therefore, it is not healthy to eat old food. To eliminate gastroenteritis, a complete suspension of food is necessary while vomiting and nausea persists. La gastroenteritis aguda: Es la inflamación de la membrana mucosa del estómago y de los intestinos. El abuso del alcohol, una intoxicación alimenticia o una gripe intestinal causan la gastroenteritis. Otra forma de contraer esta enfermedad es por medio de los alimentos contaminados por bacterias del grupo salmonela. Por eso no de debe de comer alimentos que no estén frescos. Para eliminar la gastroenteritis se aconseja el reposo y la total eliminación de alimentos mientras duren las náuseas y los vómitos. Gastroduodenal Ulcer: Gastroduodenal ulcer produces a wound in the stomach destroying the internal wall of the small intestine. Ulcers were once thought to be caused by stress, but now we know the bacterium Helicobactus is the primary cause. People with blood type O are more susceptible to ulcers. It is advisable to eliminate the consumption of coffee, spicies, alcohol and tea.
- 11. La úlcera gastroduodenal: Esta úlcera es una reacción al medio ambiente. La úlcera gastroduodenal produce una llaga en el estómago que destruye la pared del intestino delgado. Las personas con sangre del tipo O son las más susceptibles a este tipo de úlcera. Se recomienda toda eliminación de café, especias, alcohol y té. Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix. Appendicitis is extremely dangerous because it can cauise peritonitis, a life-threatening disease. Pain in the right side of the womb, location of the appendix, nausea and fever are the principal symptoms. La apendicitis: La apendicitis es una inflamación del apéndice. El riesgo de la apendicitis radica en el potencial de causar una peritonitis, una enfermedad mortal. El dolor en el lado derecho del vientre, lugar dónde se ubica el apéndice, las náuseas y la fiebre son los síntomas principales de la apendicitis. Para eliminar esta enfermedad es necesario una intervención quirúrgica.
- 12. Constipation: Constipation is a condition in which bowel movements are infrequent or incomplete. Stress and lack of exercise can cause constipation. To prevent constipation, it is necessary to eat food rich in fibre and to get enough exercise. El extreñimiento: La tensión por mínima que sea puede causar el extreñimiento. La falta de ejercicios es también otra de sus causas. Para evitar el extreñimiento se recomienda comer alimentos ricos en fibra y hacer ejercicio. Peritonitis: Inflammation of the peritoneum. When the peritoneum breaks, urine, toxins, and bacteria infect the viscera producing peritonitis. This disease is dangerous because it maybe difficult to detect the cause of the infection. La peritonitis: El peritoneo es la membrana que cubre las vísceras abdominales. Cuando la bolsa estaca que forma el peritoneo se rompe, la orina, las toxinas y las bacterias infectan a las víceras produciendo una peritonitis. Esta enfermedad es grave porque en es difícil detectar la causa de infección.
- 13. Intestinal Occlusion: An intestinal occlusion occurs when fecal matter is trapped in the intestine. Vomiting, constipation, abdominal cramps, and strain are the symptoms. La oclusión intestinal: Ocurre cuando materias fecales se detienen un alguna parte del intestino. Los síntomas son los vómitos, el extreñimiento, los calambres abdominales y la distensión. Colitis: Inflammation of the colon. Colitis maybe caused by intense emotional stress. The person with colitis feels pain in the abdomen because gases accumulate in the intestine. Other symptoms are diarrhea and constipation. La colitis: La colitis es una enfermedad muy común. Es provocada por intensos momentos emocionales. La persona con colitis siente un molestoso dolor en el abdomen debido a que los gases se acumulan en el intestino. Otros síntomas son la diarrea y el extreñimiento combinados. Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas due to alcoholism and gall stones. In some cases, pancreatitis can be confused with
- 14. other diseases because similar symptoms appear with mumps, infectious mononucleosis, appendicitis, and cardiac crisis. Surgical treatment is necessary, for it could end in peritonitis. On the other hand, chronic pancreatitis causes severe damage to the pancreas, causing death in some cases. Diabetics and alcoholics tend to have chronic pancreatitis. La pancreatitis aguda y crónica: La pancreatitis aguda es una inflamación del páncreas causada por el alcoholismo y por el sufrimiento de cálculos biliales. En muchas ocaciones se confunde con otras enfermedades porque suele aparecer con las paperas, la mononucleosis infecciosa, la apendicitis, la crisis cardíaca y la apendicitis. Se debe tratar quijurgicamente porque suele terminar en una peritonitis. Por otro lado, la pancreatitis crónica daña más al páncreas causando la muerte en muchos casos. Los diabéticos y alcohólicos tienden a sufir este tipo de pancreatitis. Infectious Hepatitis (Type A) and Seum Hepatitis (Type B): Hepatitis A is an epidemic virus. Its has a 15 to 20 day incubation period. The disease may be inapparent, mild, severe, or occasionally fatal. Hepatitis A is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. Bilirubin is indicative of hepatitis A. Drinking water polluted by excrement, for example, could cause hepatitis B. This kind of hepatitis can also be transmitted from person to person through semen or saliva, especially during its incubation period, which is 50 to 160 days. Urticaria is indicative of hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is more dangerous than hepatitis type A because it tends to cause liver complications. La hepatitis infecciosa (hepatitis A) y la hepatitis serosa (hepatitis B): La hepatitis B se produce por medio del consumo de aguas contaminadas por excrementos humanos. Este tipo de hepatitis es transmitida de persona a persona, especialmente durante el período de incubación. La bilirrubina es un indicador de la hepatitis A. La hepatitis B es transmitida por jeringas contaminadas y por transfuciones de sangre. También se puede obtener por medio del semen y la saliva. Una urticaria es el indicador de la hepatitis B. Este tipo de hepatitis es más grave que la del tipo A porque tiende a causar complicaciones con el hígado.
- 15. Liver Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a fibroid or granular induration in the liver. It is associated with failure in the function of hepatic cells and interference with blood flow in the liver. Cirrhosis can be caused by alcoholism. Therefore, it is necessary to stop consuming alcohol in order to stabilize cirrhosis. La cirrosis del hígado: Es una enfermedad mortal causada por el alcoholismo. Al hígado le salen unas granulaciones rosadas ya que puede ejercer sus funciones. Es necesario dejar de tomar alcohol para estabilizar la cirrosis.