Modal verbs
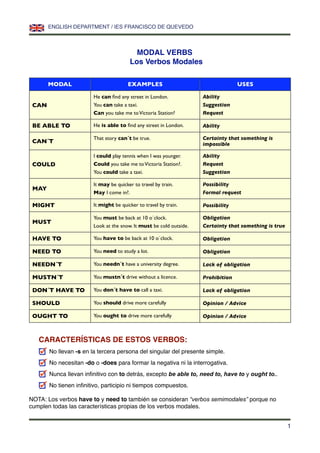
- 1. ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO MODAL VERBS Los Verbos Modales MODAL EXAMPLES USES He can find any street in London. Ability CAN You can take a taxi. Suggestion Can you take me to Victoria Station? Request BE ABLE TO He is able to find any street in London. Ability That story can´t be true. Certainty that something is CAN´T impossible I could play tennis when I was younger. Ability COULD Could you take me to Victoria Station?. Request You could take a taxi. Suggestion It may be quicker to travel by train. Possibility MAY May I come in?. Formal request MIGHT It might be quicker to travel by train. Possibility You must be back at 10 o´clock. Obligation MUST Look at the snow. It must be cold outside. Certainty that something is true HAVE TO You have to be back at 10 o´clock. Obligation NEED TO You need to study a lot. Obligation NEEDN´T You needn´t have a university degree. Lack of obligation MUSTN´T You mustn´t drive without a licence. Prohibition DON´T HAVE TO You don´t have to call a taxi. Lack of obligation SHOULD You should drive more carefully Opinion / Advice OUGHT TO You ought to drive more carefully Opinion / Advice CARACTERÍSTICAS DE ESTOS VERBOS: No llevan -s en la tercera persona del singular del presente simple. No necesitan -do o -does para formar la negativa ni la interrogativa. Nunca llevan infinitivo con to detrás, excepto be able to, need to, have to y ought to.. No tienen infinitivo, participio ni tiempos compuestos. NOTA: Los verbos have to y need to también se consideran “verbos semimodales” porque no cumplen todas las características propias de los verbos modales. 1
- 2. ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO CAN / BE ABLE TO CAN se auxilia de be able to en los tiempos de que carece, y tiene muchos usos: a) Para expresar habilidad o capacidad: “saber”, “poder”. b) Con acciones que empiezan en el pasado pero todavía tienen continuidad en el presente. c) Para hacer peticiones, dar y pedir permiso de manera informal. d) Para indicar posibilidad: We can do that later. (Podemos hacer eso luego). En negativa tiene, además de estos, otros dos usos: e) Para expresar deducción. f ) Para indicar prohibición. You can´t smoke here. (No puedes fumar aquí). BE ABLE TO también indica habilidad y posibilidad como can, pero en los tiempos que le faltan a este verbo modal. Will you be able to do it before six o´clock?. (¿Podrás hacerlo antes de las 6?) COULD a) Se usa para expresar habilidad y capacidad en el pasado. b) Para hacer peticiones o pedir un favor de manera más formal que con can. c) Para hacer sugerencias. d) Para indicar posibilidad, pero dando a entender que es más remota que si usamos can. We could go on friday afternoon.. (Podríamos ir el viernes por la tarde). MAY / MIGHT a) Ambos verbos expresan la posibilidad de que algo ocurra en el presente o en el futuro, sin ser seguro. Como hemos visto antes, can también expresa posibilidad pero denota que las circunstancias reales lo permiten. b) May también se utiliza para pedir y dar permiso de una forma más educada que con can. 2
- 3. ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO MUST / HAVE TO Must sólo tiene presente, así que para el resto de los tiempos se usa have to. a) Los dos verbos expresan necesidad y obligación, pero con must la necesidad es más fuerte. Cuando queremos suavizar la frase utilizamos have to. You must take a decision as soon as possible. (Debes tomar una decisión lo antes posible) She has to work tomorrow. (Tiene que trabajar mañana) b) Must sirve para expresar una conclusión lógica. NEED TO / NEEDN´T a) Need to expresa obligación o necesidad. b) Needn´t indica ausencia de obligación o necesidad. MUSTN´T / DON´T HAVE TO a) Mustn´t indica prohibición. b) Don´t have to tiene un valor totalmente distinto pues significa ausencia de necesidad, igual que needn´t. You don´t have to wash the dishes. (No tienes por qué lavar los platos / no es necesario). SHOULD / OUGHT TO a) Se pueden utilizar indistintamente para dar consejos y hacer recomendaciones, aunque should es mucho más frecuente. Ought to apenas se usa en negativa e interrogativa. 3
- 4. ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO MODAL PERFECTS Los Verbos Modales Perfectos MODAL EXAMPLES USES A certainty or logical MUST HAVE The driver must have lost his way. conclusion about an event in the past. A guess about something which MIGHT / MAY HAVE She might / may have bought a new car. happened in the past. The ability to do something in COULD HAVE You could have avoided that accident. the past, but which in the end was not done. He couldn´t have known about the A certainty that something did COULDN´T HAVE problem. not happen. Advice which was not followed He should have listened to me. in the past. SHOULD HAVE They should have won the competition. Expectations which were not fulfilled in the past. Criticism that was given after SHOULDN´T HAVE You shouldn´t have gone on foot. an event. Must have + participio Se usa para expresar certeza o una conclusión lógica sobre un hecho pasado. Might / May have + participio Se usa para hacer una predicción sobre algo pasado. Could have + participio Indica que hubo la posibilidad de haber hecho algo en el pasado pero que finalmente no se hizo. Couldn´t have + participio En negativa expresa la imposibilidad de que el hecho enunciado se realizara. Should have + participio Se usa para lamentar que algo no ocurriera en el pasado y que no se haya cumplido lo que esperábamos. Shouldn´t have + participio Con este modal expresamos nuestra opinión crítica sobre un hecho pasado indicando que no debería haber ocurrido. 4