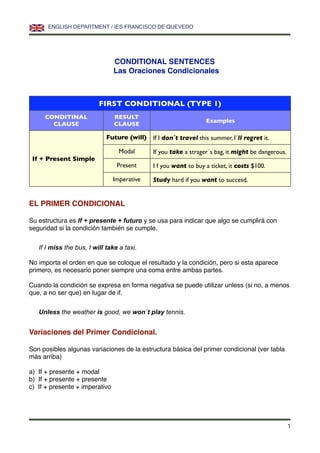
Este documento resume tres tipos de oraciones condicionales en inglés (primera, segunda y tercera condicional) y oraciones temporales. Explica la estructura de cada una y ofrece ejemplos. También menciona posibles variaciones en la estructura de estas oraciones.