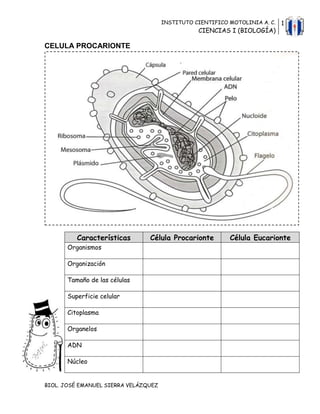
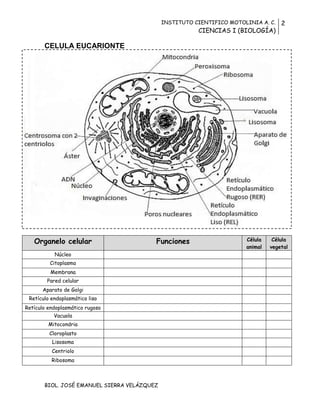
El documento describe las características de las células procariotas y eucariotas. Explica que las células procariotas son más pequeñas, no tienen núcleo ni organelos, y su ADN no está encerrado en un núcleo. Las células eucariotas son más grandes y complejas, contienen un núcleo y varios organelos como la mitocondria, cloroplasto y retículo endoplasmático. También enumera las funciones de los diferentes organelos encontrados en las células animales y vegetales.