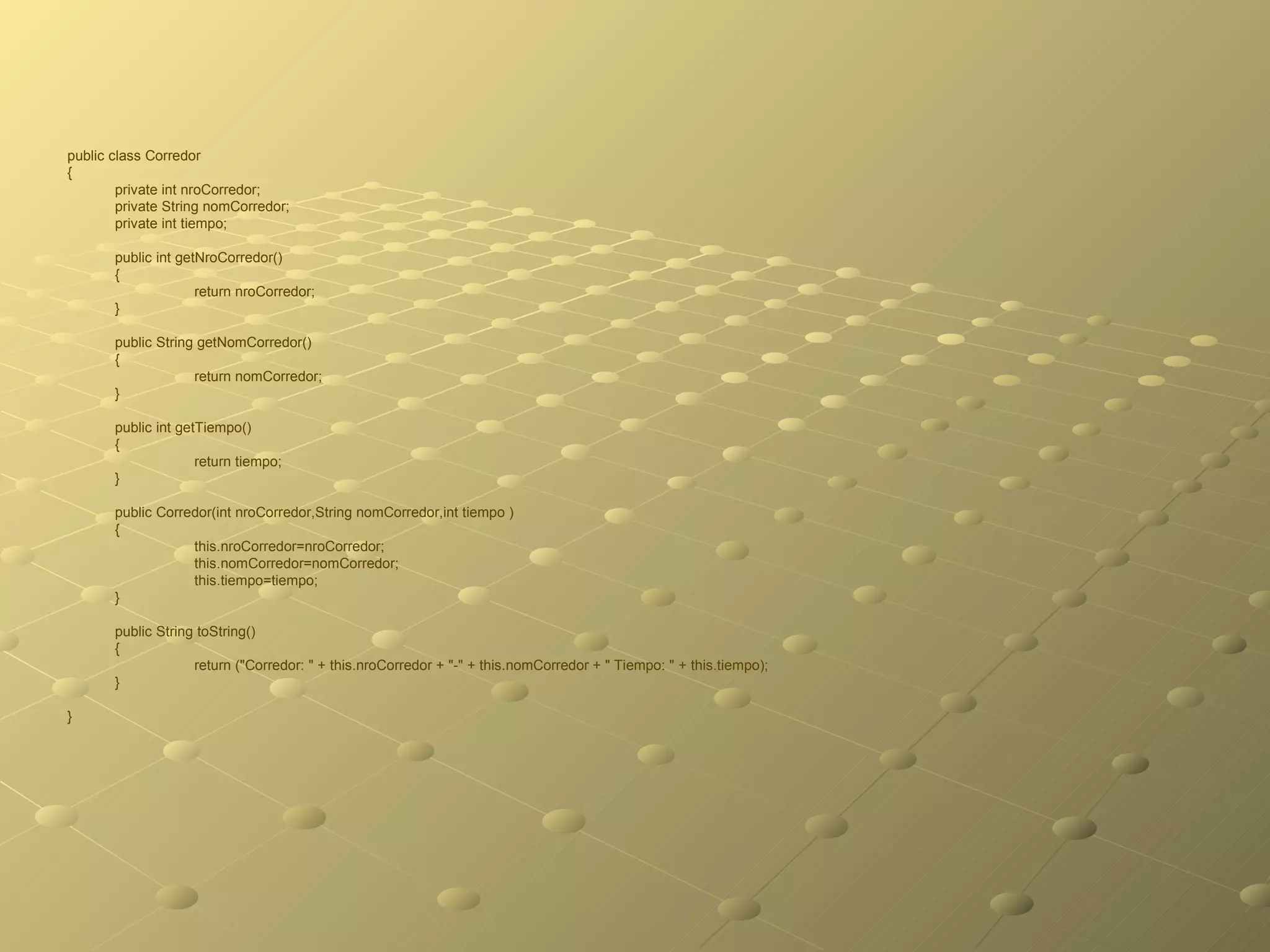
Este documento describe una clase Corredor que almacena información de un corredor individual, una clase Carrera que almacena un arreglo de objetos Corredor, y una clase AdministraCarrera que administra el ingreso y visualización de datos de corredores para una carrera. La clase Carrera contiene métodos para agregar corredores, mostrar el vector de corredores, y calcular el promedio de tiempos. La clase AdministraCarrera solicita los datos de entrada y los agrega a un objeto Carrera, luego muestra los datos de cada corredor y


![public class Carrera { private Corredor [] vecCorredores; private int cantCorredores; //Constructor de la clase Carrera public Carrera() { //Setea en 0 el contador de corredores this.cantCorredores=0; //Crea el vector vecCorredores this.vecCorredores=new Corredor[100]; } public int getCantCorredores() { return this.cantCorredores; } public void agregarCorredor(int nroCorredor,String nomCorredor,int tiempo) { Corredor c= new Corredor(nroCorredor, nomCorredor, tiempo); this.vecCorredores[cantCorredores]=c; cantCorredores++; } public Corredor [] mostrarVectorCorredores() { return (this.vecCorredores); } public double promedioTiempos() { double suma; int i; suma=0; for (i=0;i<this.cantCorredores;i++) { suma=suma+vecCorredores[i].getTiempo(); } return(suma/this.cantCorredores); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentacinarraysobjetos-110531184742-phpapp02/75/Presentacion-arraysobjetos-4-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.*; public class AdministraCarrera { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner entrada=new Scanner(System.in); entrada.useDelimiter(System.getProperty("line.separator")); //Declaraciones int nroCorredor, tiempo, i; String nomCorredor, resp; //Creacción del objeto car del tipo clase Carrera Carrera car=new Carrera(); //Ingreso de datos de todos los corredores System.out.print("Hay datos para cargar? (S/N)"); resp=entrada.next(); while(resp.equalsIgnoreCase("S")) { System.out.print("Ingrese nro de corredor: "); nroCorredor=entrada.nextInt(); System.out.print("Ingrese nombre de corredor: "); nomCorredor=entrada.next(); System.out.print("Ingrese tiempo de la carrera: "); tiempo=entrada.nextInt(); //Pedir agregar este corredor car.agregarCorredor(nroCorredor, nomCorredor, tiempo); System.out.print("Hay datos para cargar? (S/N)"); resp=entrada.next(); } //Mostrar los datos de todos los corredores utilizando el toString System.out.println("Datos de todos los corredores utilizando el toString"); for(i=0;i<car.getCantCorredores();i++) { System.out.println(car.mostrarVectorCorredores()[i].toString()); } //Mostrar el tiempo promedio de la carrera System.out.println("El tiempo promedio de la carrera fue: " + car.promedioTiempos()); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentacinarraysobjetos-110531184742-phpapp02/75/Presentacion-arraysobjetos-5-2048.jpg)