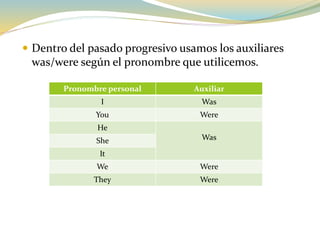
El documento explica la diferencia entre el pasado simple y el pasado progresivo en inglés. El pasado simple se usa para acciones completadas en el pasado, mientras que el pasado progresivo describe acciones que estaban ocurriendo durante un período de tiempo en el pasado. El documento proporciona ejemplos y estructuras gramaticales para ambos tiempos verbales en inglés.