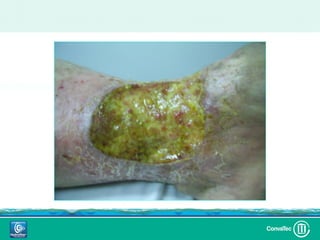
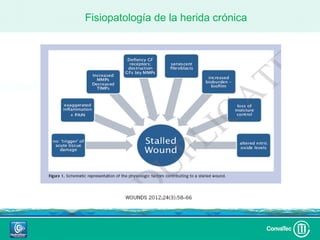
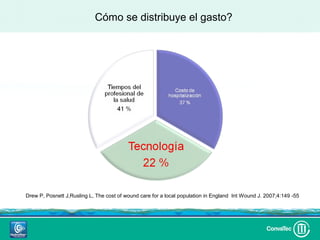
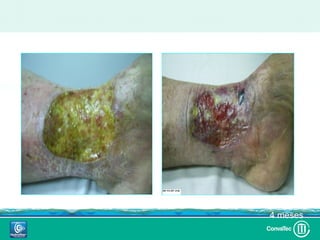
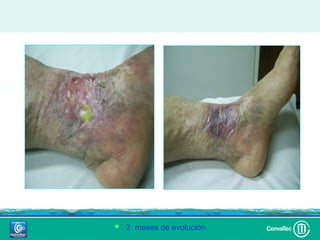
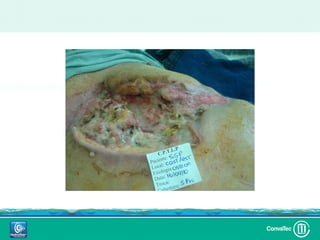
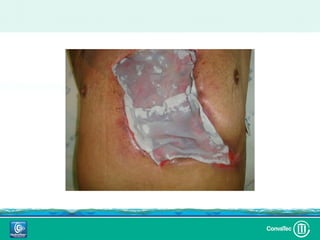
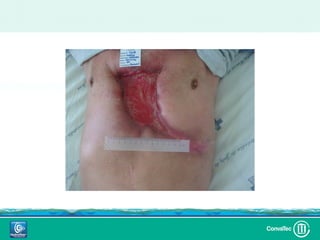
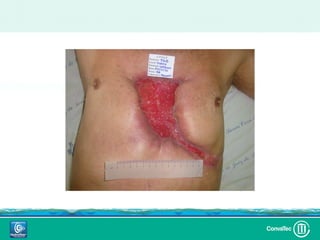
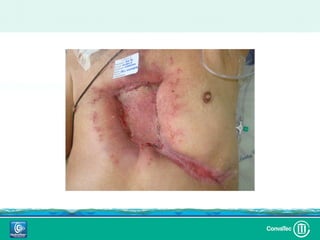
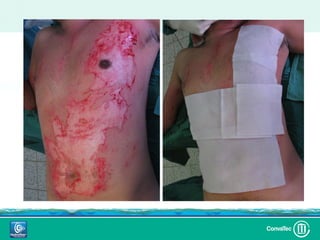
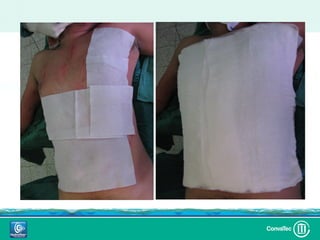
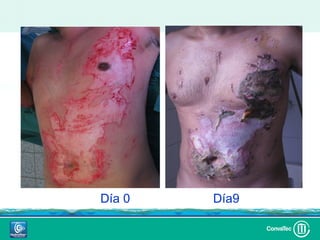
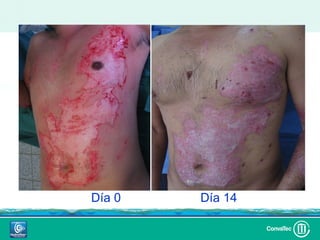
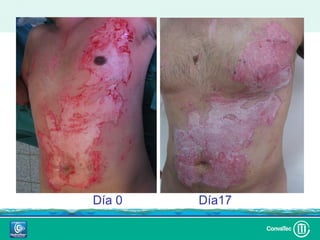
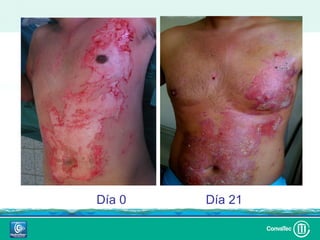
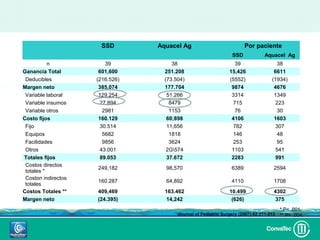
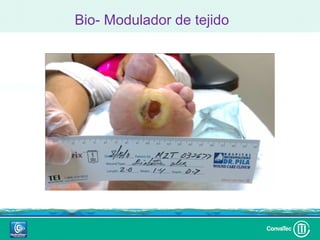
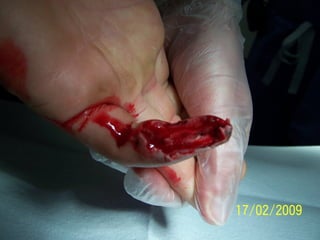
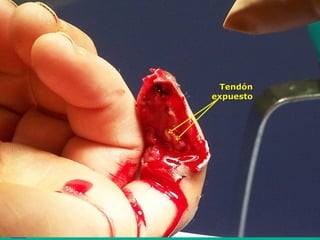
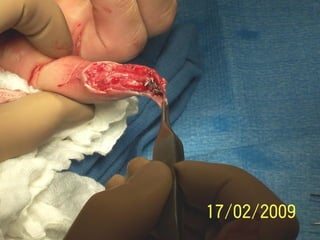
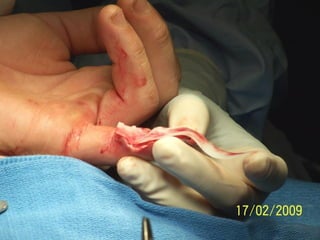
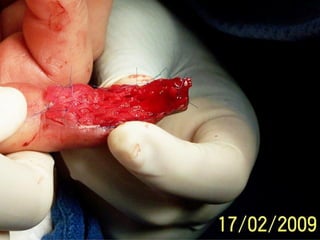
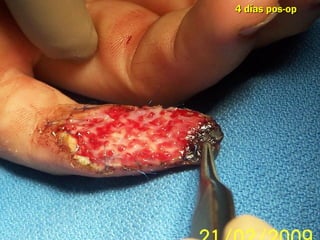
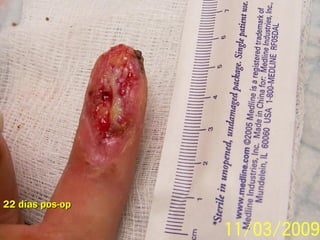
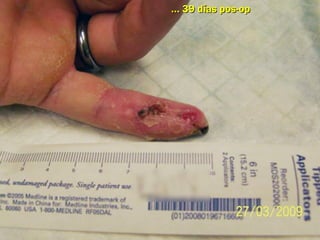
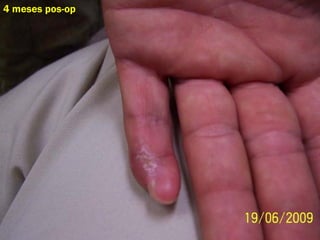
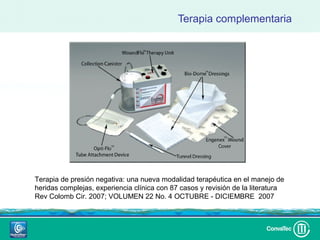
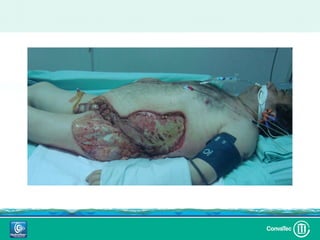
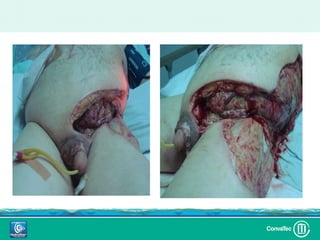
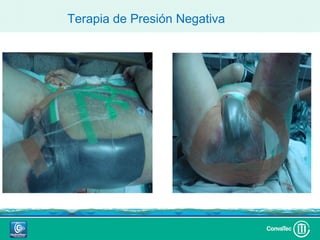
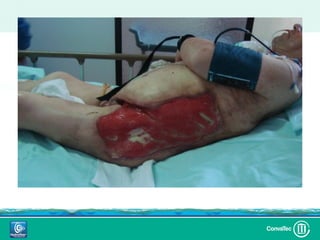
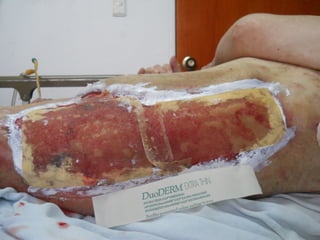
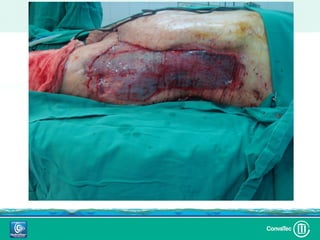
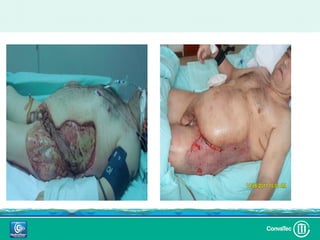
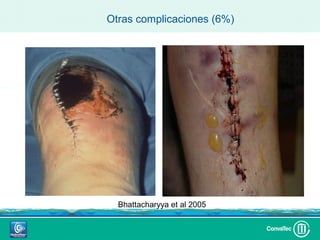
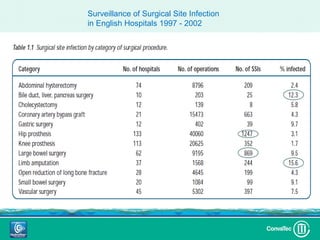
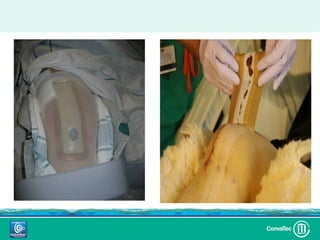
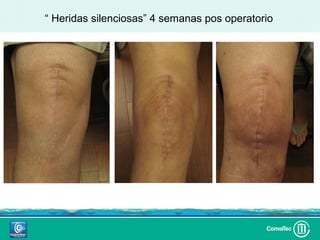
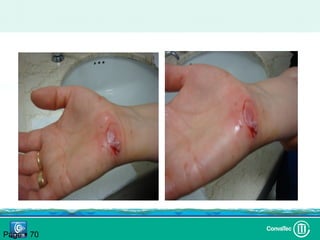
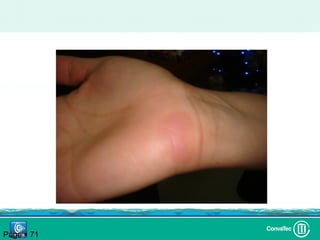
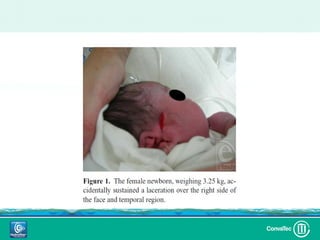
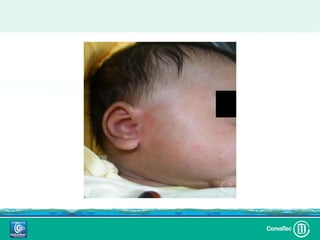
Este documento discute los avances en el tratamiento de heridas difíciles de cicatrizar. Presenta casos clínicos que muestran cómo la tecnología como la terapia de presión negativa y los bio-moduladores de tejido han mejorado los resultados. También analiza la evidencia sobre cómo mantener la humedad y balancear la inflamación para apoyar el proceso de cicatrización. El autor concluye resaltando la necesidad de transferir la evidencia a la práctica para mejorar los resultados y reducir costos en el tratamiento de