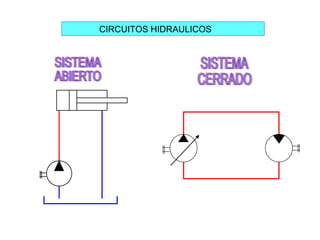
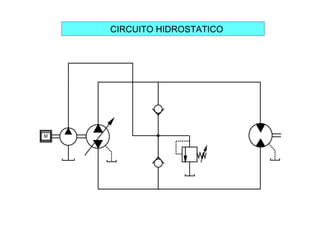
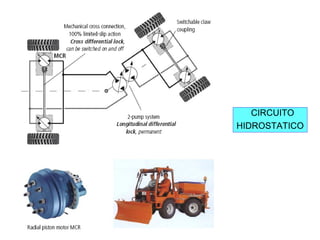
Este documento describe los sistemas hidrostáticos y circuitos hidráulicos cerrados. Explica que un circuito hidrostático típico consiste en una bomba hidráulica conectada a un motor hidráulico, y describe aplicaciones comunes como equipos de perforación, sistemas de cabrestantes y equipos descargadores.