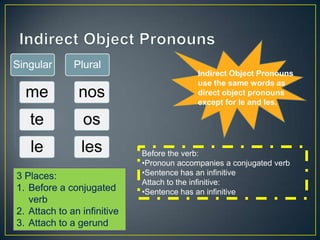
1. El documento presenta una lista de temas gramaticales en español incluyendo nacionalidades, verbos que cambian de raíz, la palabra "para", pronombres de objeto indirecto, la posición de pronombres de objeto, la construcción "gustar", palabras afirmativas y negativas, superlativos, reflexivos, mandatos afirmativos e irregulares con pronombres, y mandatos negativos e irregulares con pronombres.
2. Explica brevemente cada uno de estos temas gramaticales con ejemplos.
3. También inclu