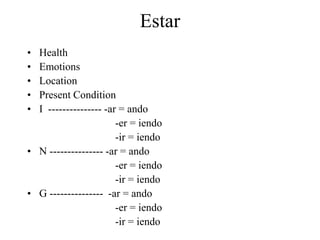
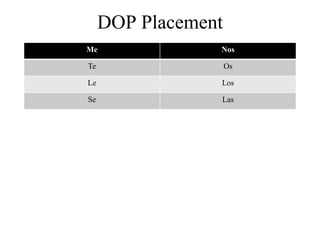
Este documento es un resumen de gramática española. Explica conceptos como el uso de "que" y "cual", los verbos "ser" y "estar", el verbo "gustar" y sus conjugaciones, transiciones, el imperfecto, expresiones de tiempo, verbos reflexivos, mandatos afirmativos y negativos, y los tiempos pretérito y imperfecto.