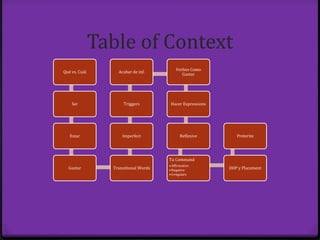
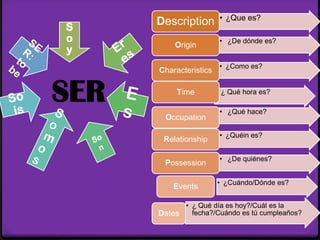
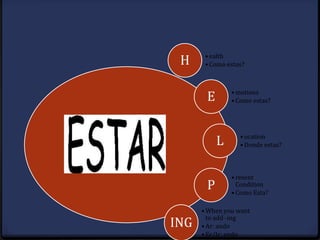
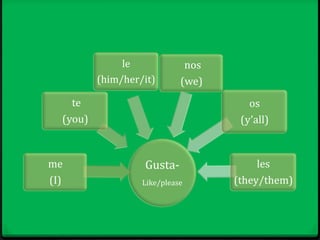
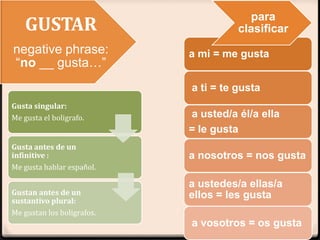
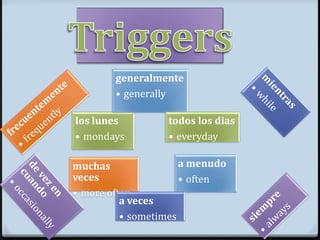
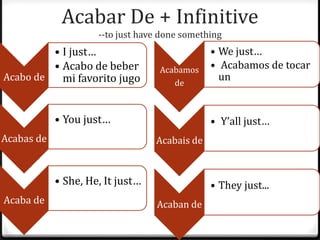
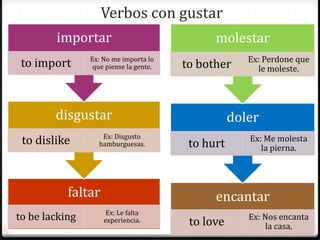
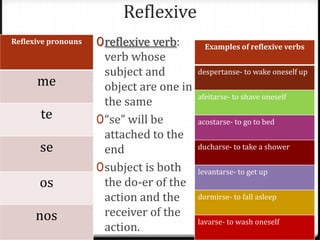
Este documento proporciona instrucciones sobre varios aspectos de la gramática española, incluyendo verbos como gustar, tiempos verbales como el imperfecto y el pretérito, expresiones como hacer + tiempo + que, verbos reflexivos, mandatos afirmativos y negativos, y la colocación de pronombres. El documento ofrece una guía concisa pero completa sobre estos temas fundamentales de la gramática.