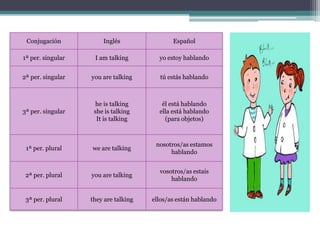
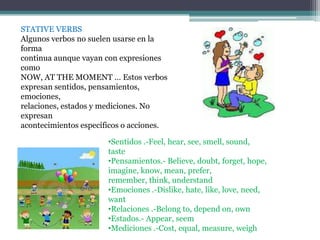
Este documento proporciona instrucciones sobre el uso del presente continuo (presente progresivo) en inglés. Explica las conjugaciones en la 1a, 2a y 3a persona del singular y plural, y cómo se usa en oraciones afirmativas, negativas y preguntas. También cubre expresiones de tiempo comunes y una lista de verbos que no suelen usarse en la forma continua aunque vayan con expresiones de tiempo, ya que expresan estados en lugar de acciones.