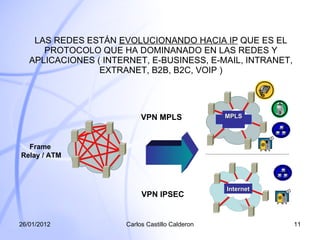
El documento proporciona una introducción a las Redes Privadas Virtuales (VPN). Explica que una VPN permite la conectividad entre múltiples sitios a través de una red compartida con los mismos atributos de una red privada. Describe dos tecnologías VPN principales: MPLS y IPsec, y cómo cada una funciona para crear túneles seguros a través de una red pública. También resume los diferentes tipos de implementaciones de VPN como sitio a sitio, acceso remoto y extranet.