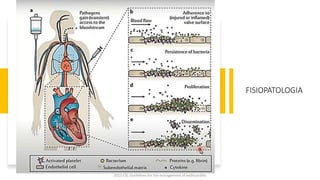
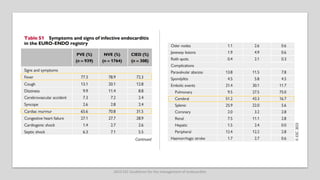
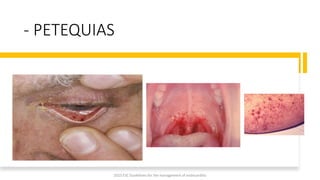
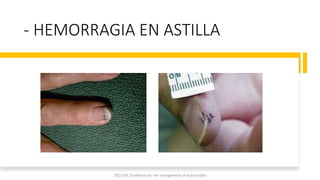
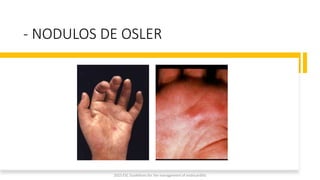
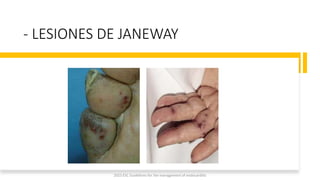
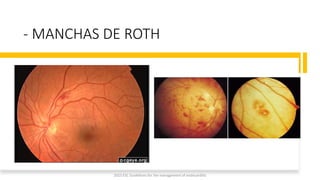
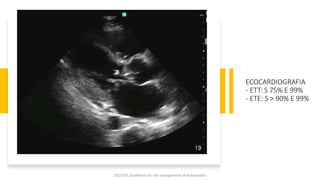
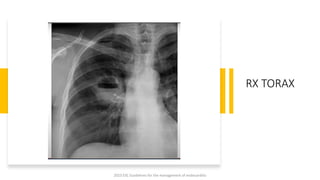
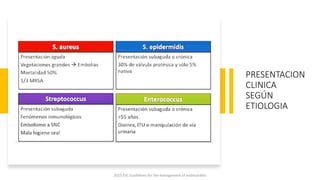
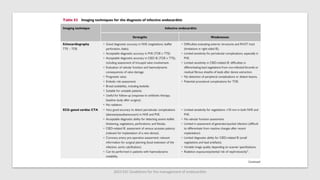
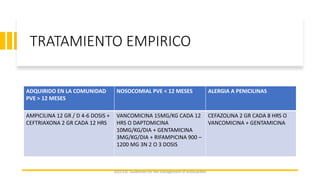
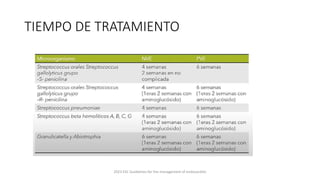
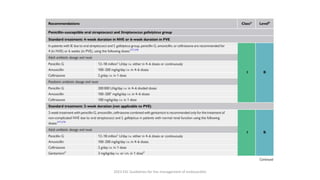
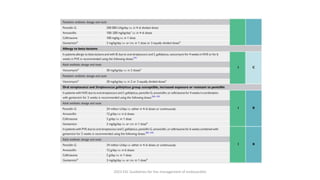
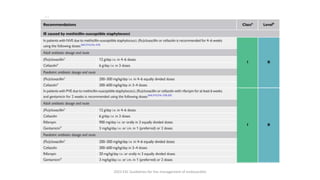
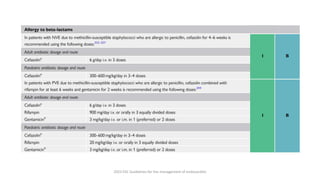
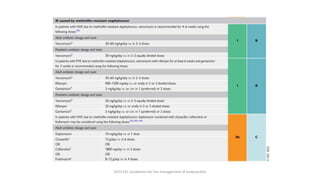
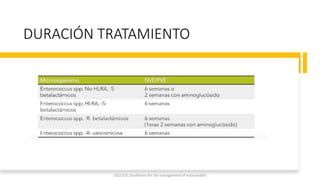
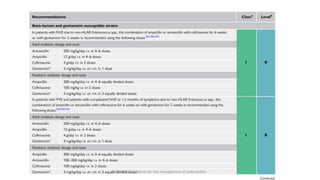
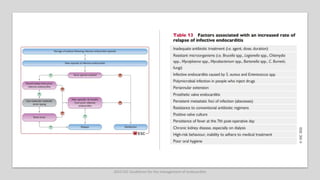
Este documento resume las guías de 2023 de la ESC para el manejo de la endocarditis infecciosa. La endocarditis es una enfermedad infecciosa grave que afecta principalmente las válvulas cardíacas izquierdas. Los principales patógenos son Staphylococcus aureus, estreptococos del grupo viridans y Enterococcus. El diagnóstico se basa en la presentación clínica, exámenes como ecocardiograma y cultivos microbiológicos. El tratamiento consiste en antibióticos según el patógeno