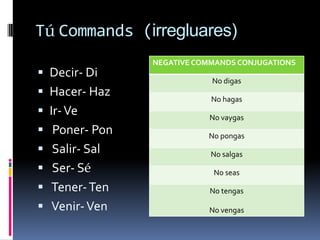
Este documento es un resumen de un libro de gramática española. Contiene 15 secciones que explican diferentes aspectos de la gramática como los verbos ser y estar, los verbos como gustar, los tiempos verbales como el imperfecto y el pretérito, y más. Explica conceptos gramaticales de manera concisa con ejemplos para cada regla.