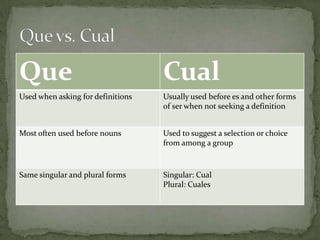
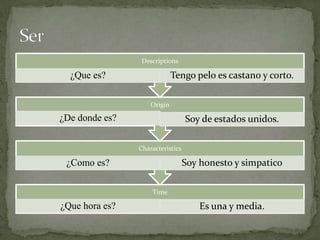
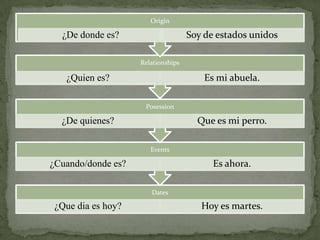
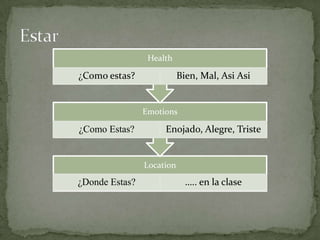
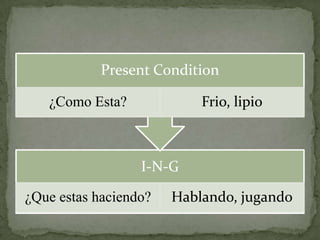
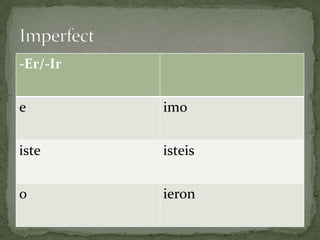
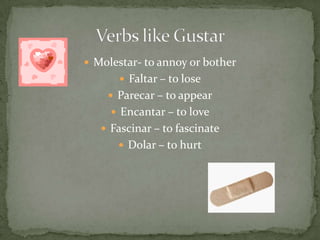
El documento resume las siguientes partes de la gramática española: los usos de "que" y "cual", verbos como "ser", "estar", "gustar", tiempos verbales como el imperfecto y el pretérito, y estructuras como los verbos reflexivos, los mandatos con "tú", la colocación de pronombres, y construcciones con verbos como "gustar", "acabar" y "hacer".