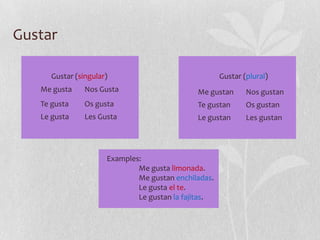
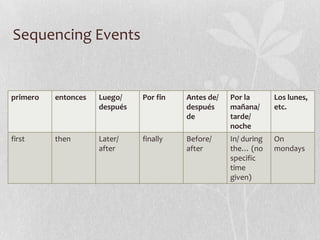
Este documento contiene información sobre varios temas de gramática española, incluyendo nacionalidades, cambios de raíz, "para", pronombres de objeto indirecto y directo, el uso de "gustar", palabras afirmativas y negativas, superlativos, verbos reflexivos, mandatos afirmativos y negativos en español, y secuencias de eventos.