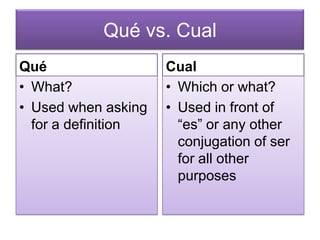
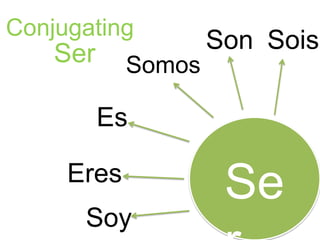
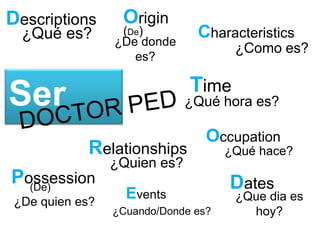
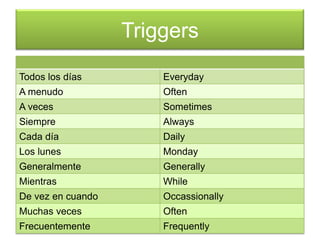
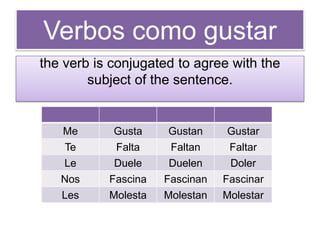
Este documento proporciona una lista de términos y conceptos gramaticales en español. Incluye verbos como ser, estar, gustar y reflexivos, así como tiempos verbales como el imperfecto y el pretérito. También cubre temas como conjugaciones, comandos en la forma tú, y expresiones como ¿Cómo estás? y Hay que + infinitivo.