Incrustar presentación
Descargado 25 veces






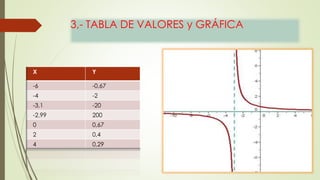
Este documento describe las funciones racionales, definidas como el cociente de dos funciones polinomiales donde el denominador no es cero. Explica que el dominio de una función racional son todos los valores reales excepto aquellos que hacen que el denominador sea cero. También muestra cómo graficar una función racional determinando primero su dominio, luego sus asintotas verticales y finalmente construyendo una tabla de valores para trazar la gráfica.






