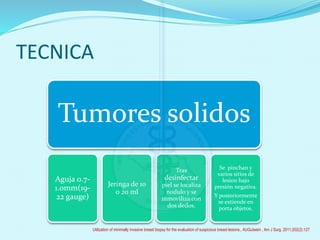
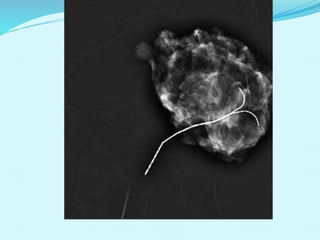
El documento describe diferentes tipos de biopsias para el diagnóstico de lesiones en la mama, incluyendo biopsia con aguja fina, biopsia con aguja de corte, biopsia por vacío y biopsia quirúrgica. Cada método se caracteriza por su especificidad, sensibilidad y complicaciones asociadas. El documento también proporciona detalles sobre la técnica y las indicaciones de cada procedimiento de biopsia.