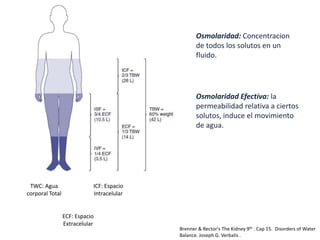
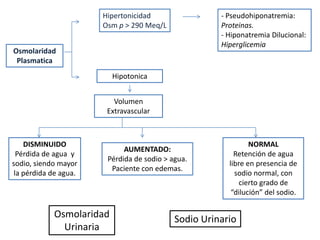
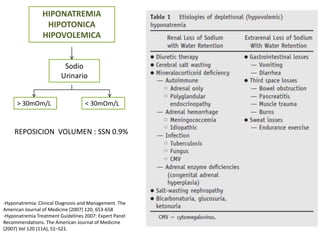
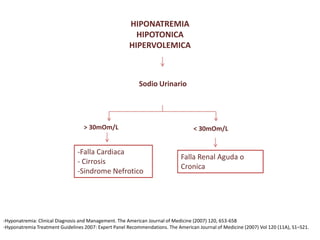
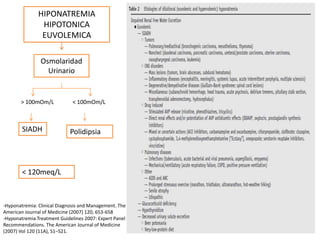
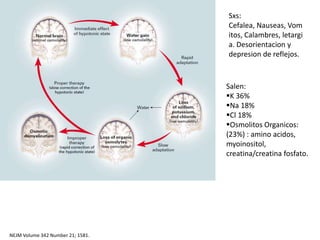
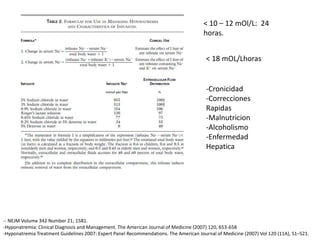
El documento aborda la hiponatremia, un trastorno hidroelectrolítico caracterizado por niveles de sodio inferiores a 130 meq/l, que puede aumentar significativamente la mortalidad si se presenta de forma aguda. Se describen diferentes tipos de hiponatremia (isotónica, hipertonica, dilucional) y su relación con diversas condiciones clínicas. Además, se incluyen directrices de tratamiento y manejo de la hiponatremia basadas en recomendaciones de expertos.