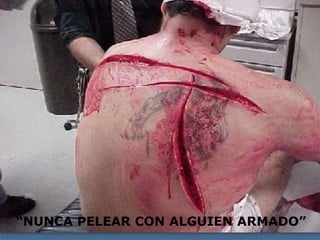
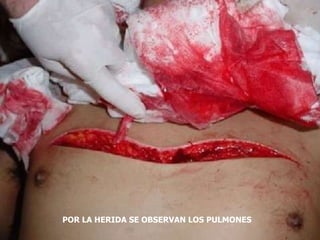
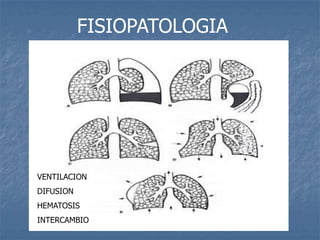
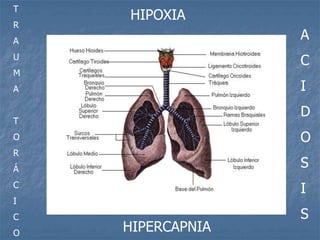
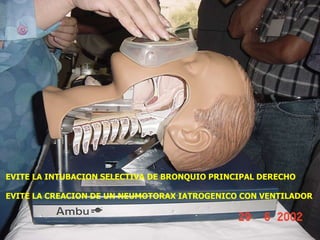
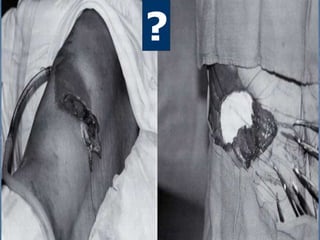
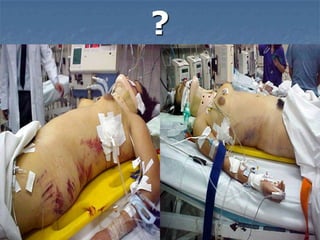
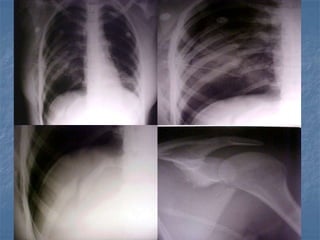
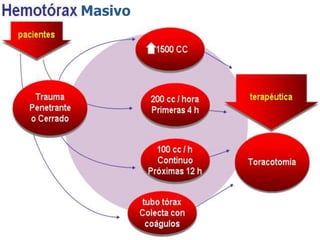
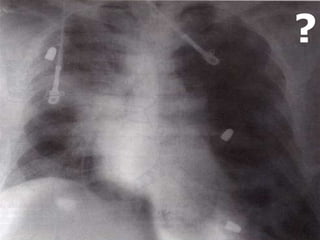
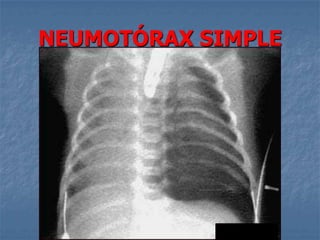
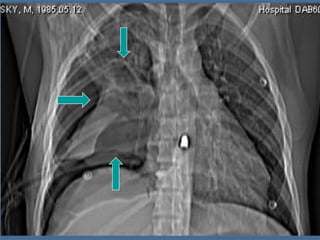
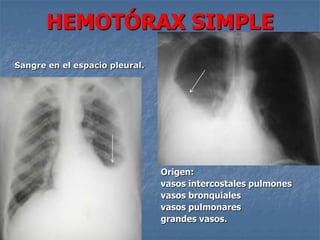
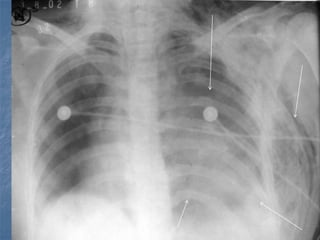
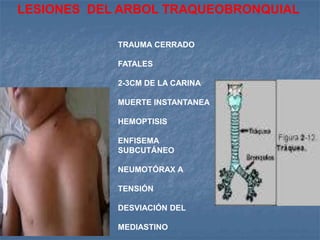
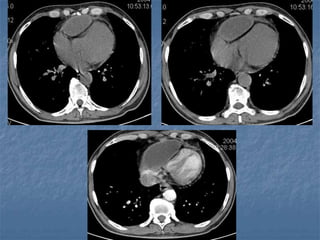
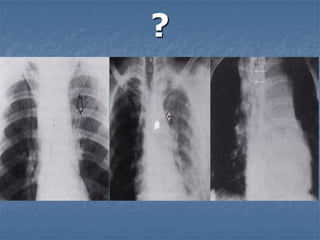
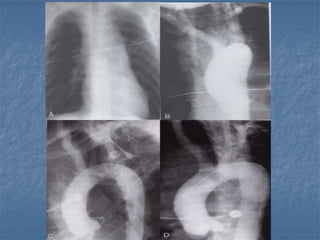
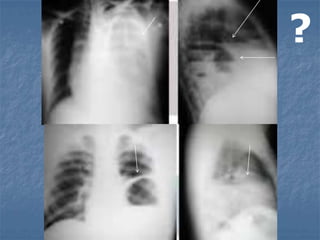
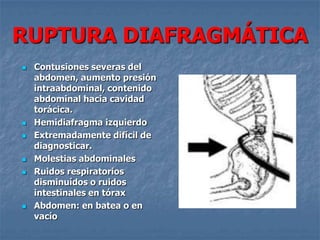
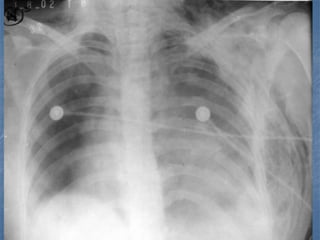
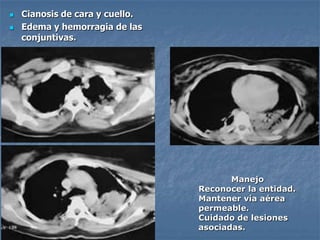
1. El documento describe diferentes tipos de lesiones por trauma de tórax, incluyendo aquellas que ponen en peligro la vida de forma inmediata como obstrucción de la vía aérea, neumotórax a tensión y hemotórax masivo, y aquellas que pueden matar de forma mediata como neumotórax simple y contusión pulmonar.
2. Se explican los síntomas, diagnóstico y tratamiento de cada lesión, haciendo énfasis en la evaluación y estabilización inicial del paciente mediante la re